How do new words arise in social media?
The position of users of X (formerly Twitter) in the network predicts the fate of the new words they use, study finds
2024-09-03
(Press-News.org) The more centrally connected someone is within their social media network, the more likely that new words they use will become adopted into mainstream language, according to a new study published this week in PLOS Complex Systems by Louise Tarrade of École Normale Supérieure, France, and colleagues.
Language evolves within a social context and variations in a language are always in competition with each other. In everyday language, words are constantly being created, but not all these words persist.
In the new study, researchers analyzed more than 650 million tweets written in French between 2012 and 2014 to identify 400 words that were new to appear in the social media network X (then called Twitter) during that time. Then, they tracked the diffusion of these words over the following five years, and looked at the position and connectivity of users who adopted the words.
The team found that initial adopters of new words, or “lexical innovations” are similar to each other, regardless of whether the innovations later succeed (as language changes) or fade away (as temporary buzzes). However, in the later propagation phase for lexical innovation, there were statistically significant differences between changes and buzzes. On average, the words that eventually persisted were used by people who were more central to their community, and remained in circulation at low levels for a longer period before entering a growth phase (18.5 months in circulation compared to 6.5 months for buzzes). Words that became only temporary buzzes were used by people with less central positions within a social network and had a more rapid rise in use – followed by a rapid decline.
“Our research examines lexical innovations at scale across millions of social media users,” the authors say. “We show that words adopted by users who are more central in their community and easily in contact with other communities become established in the language, and vice versa. Thus, the position in the network of speakers who adopt these words is enough to predict their fate.”
The authors add: “Doing sociolinguistics with digital data and computational methods offers the opportunity to scale up and reveal social dynamics at the population level.”
############
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Complex Systems: https://journals.plos.org/complexsystems/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcsy.0000005
Citation: Tarrade L, Chevrot J-P, Magué J-P (2024) How position in the network determines the fate of lexical innovations on Twitter. PLOS Complex Syst 1(1): e0000005. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcsy.0000005
Author Countries: France
Funding: J.-P. M., J.-P. C. and L.T. are grateful to the ASLAN project (ANR-10-LABX-0081, https://aslan.universite-lyon.fr/) of the Université de Lyon for its financial support within the French program "Investments for the Future" operated by the National Research Agency (ANR). The data collection has been supported by the SoSweet ANR project (ANR-15-CE38-0011-03, https://anr.fr/) attributed to J.-P. M. and J.-P. C. The authors are also grateful to University of Grenoble Alpes and Ecole Normale Supérieure de Lyon for the support for publication. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-03
In US community efforts to prevent childhood obesity, women leaders with more experience and connections have the greatest impact.
####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Complex Systems: https://journals.plos.org/complexsystems/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcsy.0000004
Article Title: Determinants and facilitators of community coalition diffusion of prevention efforts
Author Countries: United States
Funding: TM, MP, and CE received funding from the ...
2024-09-03
After four years, a guidebook for the future of autonomous trucking has driven across the finish line.
In 2020, the Virginia Tech Transportation Institute (VTTI) and 17 partners were awarded a $7.5 million grant from the U.S. Department of Transportation to develop a concept of operations. The final report, published in July, includes best practices for the implementation of automated driving systems (ADS) in large trucks and policy issues for fleets to consider across eight topic areas.
“We’re excited that the Federal Motor Carrier ...
2024-09-03
A patient dozes off in a dental chair despite the anxiety of an impending procedure. A seemingly unremarkable act but — for dentists versed in the latest sleep research — this red flag hints at a life-threatening condition.
In a research review published in the Journal of the American Dental Association, Rutgers Health researchers identified dentists as an unexpected player in the battle against life-threatening sleep disorders.
The review suggests dental professionals have unique opportunities to screen for conditions such as obstructive sleep apnea, a disorder that affects millions of Americans and is linked to serious health risks, including cardiovascular ...
2024-09-03
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced $125 million in funding for two Energy Innovation Hub teams to provide the scientific foundation needed to seed and accelerate next generation technologies beyond today’s generation of lithium (Li)-ion batteries. These multi-institution research teams, led by Argonne National Laboratory and Stanford University, will develop scientific concepts and understanding to impact decarbonization of transportation and incorporation of clean energy into the electricity grid.
Rechargeable batteries, such as Li-ion and lead-acid batteries, have had a ...
2024-09-03
The University of Ottawa has been awarded a $1 million grant from the Ontario Research Fund – Research Excellence (ORF-RE) to support the “Secure, Intelligent and Trustworthy Ecosystems for Connected and Autonomous Vehicles” (SITE-CAV) project.
Led by Burak Kantarci,Full Professor, School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, uOttawa’s Faculty of Engineering, the project aims to accelerate the development and integration of connected and autonomous vehicles (CAVs – or vehicles equipped with sensors and decision-making software that drives and controls it without direct ...
2024-09-03
Today the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced the creation of two new Energy Innovation Hubs. One of the national hubs, the Energy Storage Research Alliance (ESRA), is led by DOE’s Argonne National Laboratory and co-led by DOE’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL).
ESRA (pronounced ez-ruh) brings together nearly 50 world-class researchers from three national laboratories and 12 universities to provide the scientific ...
2024-09-03
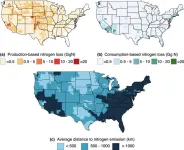
Anyone who’s researched ways to lower their environmental impact has likely heard they should eat less meat, particularly beef. Even at scale, cows are an inefficient way to feed people — it takes nearly four tons of water to recoup one ton of beef, and many farming practices emit greenhouse gasses and pollutants.
University of Pittsburgh researchers are the first to trace one of those pollutants, nitrogen, along the U.S. beef supply chain at the county level. They found high spatial disconnect between where ...
2024-09-03
Virtual reality (VR) video games that combine screen time with exercise are a great way to get fit, but game designers face a major challenge – like with regular exercise, adherence to ‘exergames’ is low, with most users dropping out once they start to feel uncomfortable or bored.
Computer scientists at the University of Bath believe they’ve found a solution: create exergames that use sensors to continuously measure a person’s emotional state while they exercise, then tweak the game – for instance, making ...
2024-09-03
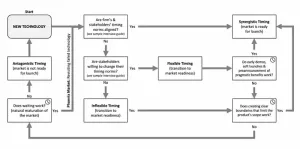
New research from Bayes Business School (formerly Cass) finds that being on the cutting edge of technology is not enough to ensure success in the market, and managers must strategically time launches to create a source of opportunity and credibility for the firm.
The study, led by Dr Thomas Robinson, Senior Lecturer in Marketing at Bayes, with Dr Ela Veresiu, Associate Professor of Marketing at Schulich School of Business, York University, Toronto, develops a framework for guiding organisations on the best situations for a product launch.
The research identifies four timing situations that can confront marketing managers. Knowing ...
2024-09-03
ROCHESTER, Minn. — A team of Mayo Clinic researchers has developed an innovative computational tool that analyzes the gut microbiome, a complex ecosystem of trillions of bacteria, fungi, viruses and other microorganisms within the digestive system, to provide insights into overall well-being.
In a new study published in Nature Communications, the tool demonstrated at least 80% accuracy in differentiating healthy individuals from those with any disease. The tool was developed by analyzing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How do new words arise in social media?
The position of users of X (formerly Twitter) in the network predicts the fate of the new words they use, study finds