Spurring more biofilm growth for efficient wastewater treatment
Foaming plastic carriers creates uneven surfaces, more area for necessary microorganisms
2024-09-04
(Press-News.org)
For the sake of the environment and our quality of life, effective treatment of wastewater plays a vital role. A biological method to treat sewage using moving, biofilm-covered plastic items known as carriers has been gaining prominence, and an Osaka Metropolitan University-led team has found ways to make the process more efficient.
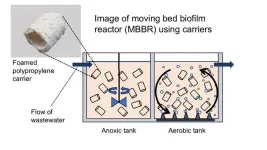
The moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) process purifies wastewater by putting these carriers in motion to get the biofilm’s microorganisms into greater contact with organic matter and other impurities. The more biofilm that can be attached to the plastic carriers, the more microorganisms that are available to clean the wastewater.
OMU Professor Masayuki Azuma and Associate Professor Yoshihiro Ojima of the Graduate School of Engineering worked with a team from Kansaikako Co., an Osaka-based company specializing in water treatment-related products, and found that polypropylene carriers foamed to create uneven surfaces and more surface area allowed 44 times more biofilm formation than smooth plastic carriers.
Moreover, adding waste biomass such as composted seaweed when foaming further enhanced the performance of the foamed plastic carriers, especially in terms of nitrate removal during the MBBR process.
“Since there is a wide variety of wastewater, it will be necessary to prove that these foamed carriers also have superior suitability to various wastewater,” stated Professor Azuma. “It is clear that the addition of waste biomass improves the performance of the carriers, so we expect that further performance enhancement can be achieved depending on the additive.”
The findings were published in Environmental Technology & Innovation.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-04
A common image of cats today comes in the form of cute cat memes online, but these furry felines commonly experience kidney disease. Amid advances in medicine to improve people’s quality of life, an Osaka Metropolitan University-led team has, for the first time in the world, generated high-quality feline induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which have the potential to help companion animals and humans alike.
Human iPSCs have been generated using just four genes known as transcription factors, but feline iPSCs have been difficult to generate. Graduate School of Veterinary Science Professor Shingo Hatoya led the team in introducing six transcription factors via the Sendai virus ...
2024-09-04
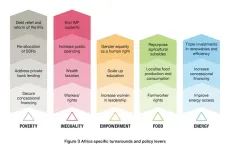
In the best-case scenario, called the "Giant Leap," Sub-Saharan Africa could see poverty drop from 500 million to 25 million people, hunger nearly eradicated, and universal access to education, clean water, and sustainable electricity. On the other hand, the "Too Little Too Late" scenario paints a grim picture where poverty rises to 900 million, hunger still affects 180 million, and over a billion people lack clean water. The Too Little Too Late scenario is based on existing policies in the region. These two scenarios highlight the critical importance of action this decade to drive five extraordinary turnarounds in the areas of poverty, inequality, ...
2024-09-04
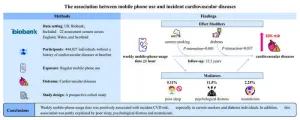
Philadelphia, September 4, 2024 – A new study has found that regular mobile phone use was positively associated with incident cardiovascular diseases risk, especially in current smokers and individuals with diabetes. In addition, this association was partly attributed to poor sleep, psychological distress, and neuroticism. The article in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier, details the results of this large-scale prospective cohort study.
Yanjun Zhang, MD, Division of Nephrology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, explains, "Mobile phone use is a ubiquitous exposure in modern society, so exploring its impact on health has ...
2024-09-04
COLUMBUS, Ohio – About half of adults can identify cigarettes and e-cigarettes, but just one in four would recognize oral nicotine pouches, and these easily available products are growing increasingly popular among teens and young adults, according to a recent study commissioned by The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James).
Oral nicotine pouches are small packets filled with a flavored powder containing nicotine and other chemicals that are tucked between the lip and gums. ...
2024-09-04
Introduction
As a new degree of freedom, the orbital angular momentum of electromagnetic waves exceeds the traditional frequency, phase, and amplitude, and is expected to promote the infinite expansion of channel capacity. Recently, a team of research professor Chao-Hai Du from Peking University and Professor Xiaofei Zang's research group from the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology have carried out in-depth cooperation. Based on the research foundation of both sides in the field of terahertz and metasurface, a new method of generating polarization-multiplexed terahertz vortex combs using all-silicon metasurface has been ...
2024-09-04
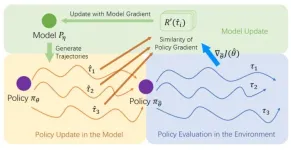
Recently, model-based reinforcement learning has been considered a crucial approach to applying reinforcement learning in the physical world, primarily due to its efficient utilization of samples. However, the supervised learned model, which generates rollouts for policy optimization, leads to compounding errors and hinders policy performance. To address this problem, the research team led by Yang YU published their new research on 15 August 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education ...
2024-09-04
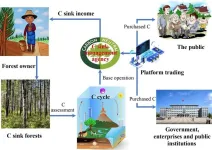
Since the first industrial revolution, the rapid development of the human economy and society has directly exacerbated the process of CO2 emission from human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, industrial processes, agriculture, and land use activities. With the continuous increase of global greenhouse gas concentration dominated by CO2, the greenhouse effect is becoming more and more obvious, and the trend of global warming is becoming more and more serious. To cope with the continuous warming of the global climate and mitigate ...
2024-09-04
Combine cyberbullying, smartphone use, lack of sleep and poor mental health, and you have the perfect storm for a teenage meltdown.
Australian researchers have polled more than 50,000 primary and secondary school students aged 7-19 years about the link between their sleep and nighttime phone habits, experience of cyberbullying and stress levels.
Researchers from the Behaviour-Brain-Body Research Centre at the University of South Australia found that across all genders and age groups, phone use overnight not only robbed children of sleep, but it also had a negative impact on their mental health, ...
2024-09-04
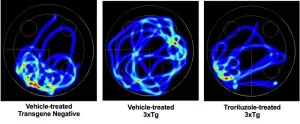
AUBURN, AL — In a recent development in Alzheimer's disease research, Auburn University scientists have studied a new drug, troriluzole, that can prevent brain changes leading to memory loss and cognitive decline in a mouse model of the disease. This study, recently published in the Journal of Neurochemistry, is the first to show how troriluzole can target early-stage alterations associated with Alzheimer’s, providing new hope for potential treatments.
Dr. Miranda Reed, a Professor in the department ...
2024-09-04
Pennington Biomedical Research Center’s Dr. Jeff Keller is evaluating the potential for delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC, and cannabidiol, or CBD, to reduce the behaviors indicating agitation, distress or anxiety in patients with Alzheimer’s disease or other forms of dementia. The study is designed for hospice-eligible patients who are either receiving hospice care or who are eligible for hospice, and who are exhibiting agitation concurrently with a diagnosis of dementia. There are currently no FDA-approved medications to treat agitation at the end-of-life stages in dementia patients.
The “Life’s End Benefits of Cannabidiol and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Spurring more biofilm growth for efficient wastewater treatment
Foaming plastic carriers creates uneven surfaces, more area for necessary microorganisms