(Press-News.org) New research shows that parasitic nematodes, responsible for infecting more than a billion people globally, carry viruses that may solve the puzzle of why some cause serious diseases.
A study led by Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine (LSTM) used cutting-edge bioinformatic data mining techniques to identify 91 RNA viruses in 28 species of parasitic nematodes, representing 70% of those that infect people and animals. Often these are symptomless or not serious, but some can lead to severe, life-changing disease.
Nematode worms are the most abundant animals on the planet, prevalent in all continents worldwide, with several species infecting humans as well as agriculturally and economically important animals and crops. And yet in several cases, scientists do not know how some nematodes cause certain diseases.
The new research, published in Nature Microbiology, opens the door to further study of whether these newly discovered viruses – only five of which were previously known to science – could contribute to many chronic, debilitating conditions. If a connection can be proven, it could pave the way for more effective treatments in the future.
Mark Taylor, Professor of Parasitology at LSTM, said: “This is a truly exciting discovery and could change our understanding of the millions of infections caused by parasitic nematodes. Finding an RNA virus in any organism is significant, because these types of viruses are well-known agents of disease. When these worms that live inside of us release these viruses, they spread throughout the blood and tissues and provoke an immune response.
“This raises the question of whether any of the diseases that these parasites are responsible for could be driven by the virus rather than directly by the parasitic nematode.”
Parasitic nematodes including hookworms and whipworms can cause severe abdominal problems and bloody diarrhoea, stunted development and anaemia. Infection with filarial worms can lead to disfiguring conditions such as lymphoedema or ‘elephantiasis’, and onchocerciasis, or ‘river blindness’, that leads to blindness and skin disease.
The study authors propose that these newly identified viruses may play a role in some of these conditions. For example, Onchocerciasis-Associated Epilepsy (OAE) that occurs in children and adolescents in Sub-Saharan Africa has recently been associated with onchocerciasis, but it is not known why this causes neurological symptoms such as uncontrollable repeated head nodding, as well as severe stunting, delayed puberty and impaired mental health.
One of the viruses in the parasites that cause onchocerciasis identified in the new study is a rhabdovirus – the type that causes rabies. The authors of the study suggest that if this virus is infecting or damaging human nerve or brain tissue, that could explain the symptoms of OAE.
The full extent and diversity of the viruses living in parasitic nematodes, how they impact nematode biology and whether they act as drivers of disease in people and animals now requires further study.
The illuminating discovery of these widespread yet previously hidden viruses was first made by Dr Shannon Quek, a Postdoctoral Research Associate at LSTM and lead author of the new study, who had initially been using the same data mining method to screen for viruses within mosquitoes that spread disease, before deciding to investigate nematodes.
Dr Quek, who is from Indonesia, a country burdened by many parasitic nematodes, said: “As a child, I saw a lot of people infected with these diseases and I suffered from the dengue virus on three occasions. That got me interested in tropical diseases. Diseases caused by parasitic nematodes are very long-term, life-long illnesses that persistently affect people. It has a significant impact on people's quality of life, their economic outputs and mental health.
“There are a lot of studies about the microbiomes of mosquitoes, and how the bacteria that lives inside can block the spread of viruses, which might stop vector-borne diseases like dengue. This interplay between organisms in the same host led me to think - what else might be inside parasitic nematodes as well? Which after my discovery will now be the focus of our research.”
The study also involved researchers from University of Antwerp and KU Leuven, Belgium, Brock University, Canada, University of Queensland, Australia, University of Buea, Cameroon and the University of Energy and Natural Resources, Ghana.
ENDS
Notes for Editors
For more information, or to request a copy of the paper ahead of publication, please contact dominic.smith@lstmed.ac.uk.
From 10:00 BST on 4 September 2024, the paper will be available via: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-024-01796-6.
END
Newly discovered viruses in parasitic nematodes could change our understanding of how they cause disease
2024-09-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Qunkasaura: New sauropod dinosaur from the Cretaceous discovered in the Iberian Peninsula
2024-09-04
A new study led by Portuguese paleontologist Pedro Mocho, from the Instituto Dom Luiz of the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Lisbon (CIÊNCIAS), has just been published in the Communications Biology journal, which announces a new species of sauropod dinosaur that lived in Cuenca, Spain, 75 million years ago: Qunkasaura pintiquiniestra.
The more than 12,000 fossils collected from 2007 onwards during works to install the Madrid-Levante high-speed train (AVE) tracks revealed this deposit, giving rise to one of the most relevant collections ...
Sports concussions in non-athletes not linked to long-term cognitive effects: study
2024-09-04
Sports-related concussions (SRC) may not be associated with long-term cognitive risks for non-professional athletes, a study led by a UNSW medical researcher suggests. In fact, study participants who had experienced an SRC had better cognitive performance in some areas than those who had never suffered a concussion, pointing to potential protective effects of sports participation.
Published in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry (JNNP), the research reveals that individuals who reported experiencing any SRC during their lifetime had a marginally better cognitive performance than those who reported no concussions.
The study, a collaboration ...
Spurring more biofilm growth for efficient wastewater treatment
2024-09-04
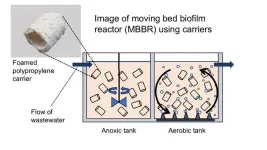
For the sake of the environment and our quality of life, effective treatment of wastewater plays a vital role. A biological method to treat sewage using moving, biofilm-covered plastic items known as carriers has been gaining prominence, and an Osaka Metropolitan University-led team has found ways to make the process more efficient.
The moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) process purifies wastewater by putting these carriers in motion to get the biofilm’s microorganisms into greater contact with organic matter and other impurities. The more biofilm that can be attached ...
In world 1st, high-quality feline iPSCs generated without genetic footprint
2024-09-04
A common image of cats today comes in the form of cute cat memes online, but these furry felines commonly experience kidney disease. Amid advances in medicine to improve people’s quality of life, an Osaka Metropolitan University-led team has, for the first time in the world, generated high-quality feline induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which have the potential to help companion animals and humans alike.
Human iPSCs have been generated using just four genes known as transcription factors, but feline iPSCs have been difficult to generate. Graduate School of Veterinary Science Professor Shingo Hatoya led the team in introducing six transcription factors via the Sendai virus ...
How Sub-Saharan Africa can achieve the SDGs by 2100: A new report by Earth4All
2024-09-04
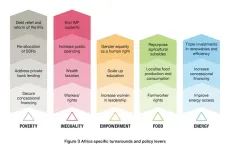
In the best-case scenario, called the "Giant Leap," Sub-Saharan Africa could see poverty drop from 500 million to 25 million people, hunger nearly eradicated, and universal access to education, clean water, and sustainable electricity. On the other hand, the "Too Little Too Late" scenario paints a grim picture where poverty rises to 900 million, hunger still affects 180 million, and over a billion people lack clean water. The Too Little Too Late scenario is based on existing policies in the region. These two scenarios highlight the critical importance of action this decade to drive five extraordinary turnarounds in the areas of poverty, inequality, ...
New research shows regular mobile phone use can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases, especially in smokers and people with diabetes
2024-09-04
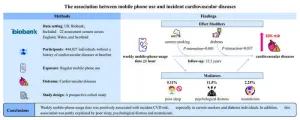
Philadelphia, September 4, 2024 – A new study has found that regular mobile phone use was positively associated with incident cardiovascular diseases risk, especially in current smokers and individuals with diabetes. In addition, this association was partly attributed to poor sleep, psychological distress, and neuroticism. The article in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier, details the results of this large-scale prospective cohort study.
Yanjun Zhang, MD, Division of Nephrology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, explains, "Mobile phone use is a ubiquitous exposure in modern society, so exploring its impact on health has ...
Can you identify the new threat attracting Gen Z to nicotine use?
2024-09-04
COLUMBUS, Ohio – About half of adults can identify cigarettes and e-cigarettes, but just one in four would recognize oral nicotine pouches, and these easily available products are growing increasingly popular among teens and young adults, according to a recent study commissioned by The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James).
Oral nicotine pouches are small packets filled with a flavored powder containing nicotine and other chemicals that are tucked between the lip and gums. ...
Generation and multiplexing of double-polarized terahertz vortex combs
2024-09-04
Introduction
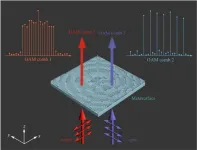
As a new degree of freedom, the orbital angular momentum of electromagnetic waves exceeds the traditional frequency, phase, and amplitude, and is expected to promote the infinite expansion of channel capacity. Recently, a team of research professor Chao-Hai Du from Peking University and Professor Xiaofei Zang's research group from the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology have carried out in-depth cooperation. Based on the research foundation of both sides in the field of terahertz and metasurface, a new method of generating polarization-multiplexed terahertz vortex combs using all-silicon metasurface has been ...
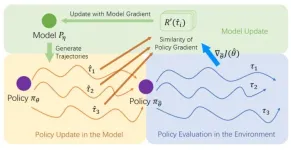
A unified objective for dynamics model and policy learning in model-based reinforcement learning
2024-09-04
Recently, model-based reinforcement learning has been considered a crucial approach to applying reinforcement learning in the physical world, primarily due to its efficient utilization of samples. However, the supervised learned model, which generates rollouts for policy optimization, leads to compounding errors and hinders policy performance. To address this problem, the research team led by Yang YU published their new research on 15 August 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education ...
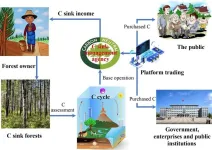
How to solve the challenges faced by the carbon sequestration function of Chinese plantations in the future?
2024-09-04
Since the first industrial revolution, the rapid development of the human economy and society has directly exacerbated the process of CO2 emission from human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, industrial processes, agriculture, and land use activities. With the continuous increase of global greenhouse gas concentration dominated by CO2, the greenhouse effect is becoming more and more obvious, and the trend of global warming is becoming more and more serious. To cope with the continuous warming of the global climate and mitigate ...