(Press-News.org) It turns out that a particular gene has a great influence on longevity, a new study from the University of Copenhagen concludes. This may pave the way for new treatment.
Sleep, fasting, exercise, green porridge, black coffee, a healthy social life …
There is an abundance of advice out there on how to live a good, long life. Researchers are working hard to determine why some people live longer than others, and how we get the most out of our increasingly long lives.
Now researchers from the Center for Healthy Aging, Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine at the University of Copenhagen have made a breakthrough. They have discovered that a particular protein known as OSER1 has a great influence on longevity.
”We identified this protein that can extend longevity (long duration of life, red.). It is a novel pro-longevity factor, and it is a protein that exists in various animals, such as fruit flies, nematodes, silkworms, and in humans,” says Professor Lene Juel Rasmussen, senior author behind the new study.
Because the protein is present in various animals, the researchers conclude that new results also apply to humans:
”We identified a protein commonly present in different animal models and humans. We screened the proteins and linked the data from the animals to the human cohort also used in the study. This allows us to understand whether it is translatable into humans or not,” says Zhiquan Li, who is a first author behind the new study and adds:
“If the gene only exists in animal models, it can be hard to translate to human health, which is why we, in the beginning, screened the potential longevity proteins that exist in many organisms, including humans. Because at the end of the day we are interested in identifying human longevity genes for possible interventions and drug discoveries.”
Paves the way for new treatment
The researchers discovered OSER1 when they studied a larger group of proteins regulated by the major transcription factor FOXO, known as a longevity regulatory hub.
“We found 10 genes that, when - we manipulated their expression - longevity changed. We decided to focus on one of these genes that affected longevity most, called the OSER1 gene,” says Zhiquan Li.
When a gene is associated with shorter a life span, the risk of premature aging and age-associated diseases increases. Therefore, knowledge of how OSER1 functions in the cells and preclinical animal models is vital to our overall knowledge of human aging and human health in general.
“We are currently focused on uncovering the role of OSER1 in humans, but the lack of existing literature presents a challenge, as very little has been published on this topic to date. This study is the first to demonstrate that OSER1 is a significant regulator of aging and longevity. In the future, we hope to provide insights into the specific age-related diseases and aging processes that OSER1 influences,” says Zhiquan Li.
The researchers also hope that the identification and characterization of OSER1 will provide new drug targets for age-related diseases such as metabolic diseases, cardiovascular and neuro degenerative diseases.
“Thus, the discovery of this new pro-longevity factor allows us to understand longevity in humans better,” says Zhiquan Li.
END
Newly discovered gene may influence longevity
2024-09-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
SwRI signs MOU with Blade Energy Partners to support carbon dioxide sequestration research
2024-09-04
SAN ANTONIO — September 4, 2024 — Southwest Research Institute has signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with Blade Energy Partners, establishing a new research collaboration focused on advancing carbon dioxide storage technology to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) refers to the practices of capturing CO2 from its industrial sources or the atmosphere, transport it using pipelines and other means, using it as alternative fuel or other industrial applications, and storing it for later use. The drive to meet net-zero greenhouse gas emissions goals and ...
Integrated design and fabrication of pneumatic soft robot actuators in a single casting step
2024-09-04
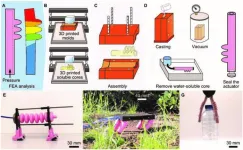
A research paper by scientists at University of Coimbra proposed an integrated approach targeting the design and fabrication of pneumatic soft actuators in a single casting step. Molds and sacrificial water-soluble hollow cores are printed using fused filament fabrication.
The new research paper, published on Jul. 17 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, presented an integrated process for the design and fabrication of soft robot actuators in a single casting. The author proved the availability, versatility, and effectiveness of the proposed methods, contributing to accelerating the design and fabrication of soft robots.
Bio-inspired soft robots have already shown the ability to handle ...
Underwater resection of neuroendocrine tumors of the gastrointestinal tract
2024-09-04
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract are a rare and heterogeneous group of malignancies arising from the neuroendocrine cell system. These tumors are more commonly encountered in the stomach, appendix, small bowel, rectum, and pancreas. Over the past few decades, the incidence of GI NETs has increased due to improved diagnostic capabilities and an aging population. The management of these tumors requires a careful assessment of various factors, including the site, size, grading, depth of invasion, and local lymphadenopathy, as they significantly impact prognosis and treatment ...
Microglial responses to hypernatremia: new insights into brain health
2024-09-04
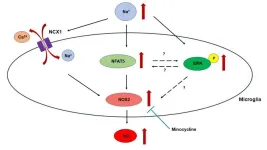
Microglia are the brain’s immune cells known to play a vital role in maintaining neural function and responding to potential threats. However, when the brain is subjected to hyperosmotic stress—a condition characterized by elevated extracellular sodium levels, the microglial response can become exaggerated, leading to potentially harmful effects. Understanding the mechanisms behind this heightened response is crucial for the treatment of hypernatremia-induced neurological dysfunctions.
To ...
Breaking the link between obesity and atrial fibrillation with a new cellular target
2024-09-04
A cellular link between obesity and atrial fibrillation — a heart condition that afflicts over 33 million people worldwide — presents a promising target for new therapies, researchers from the University of Illinois Chicago report.
Obesity is among the leading causes of atrial fibrillation, an irregular heart rhythm that can lead to heart failure and stroke. But scientists still don’t know how high levels of body fat cause this heart condition.
In a new study published in The Journal of Clinical Investigation, UIC researchers identified a cellular pathway essential to obesity-induced ...
New research has potential to speed up forensic analysis in sexual assault cases
2024-09-04
A team of researchers has developed a radical new technique for analyzing evidence in sexual assault cases. The new approach could streamline the forensics pipeline and reduce delays in the processing of DNA evidence.
The research is described in a paper published today in the journal Advanced Science.
There are almost half a million sexual assaults in Canada every year with many more going unreported. The new approach could mitigate one of the reasons victims are reluctant to report assaults: the perception that ...
Banning friendships can backfire: moms who ‘meddle’ make bad behavior worse
2024-09-04
Delinquent activities almost always occur outside of the home and away from adult supervision, so it is only natural for parents to blame peers for their child’s bad behavior. Not surprisingly, many parents also assume that they can prevent future problems by limiting contact with suspicious peers.
However, a new study cautions parents – especially meddling moms – to resist the temptation to prohibit friendships because doing so only makes a bad situation worse. How can this be?
Results from a new longitudinal study of middle school youth, published in The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, indicates that maternal disapproval of friends in ...
AIM-HI Accelerator Fund announces the 2024 Women’s Venture Competition winners
2024-09-04
ROCKVILLE, MD (September 4, 2024) The AIM-HI Accelerator Fund is pleased to announce that the 2024 Women’s Venture Competition’s first prize winner with distinction goes to HDAX Therapeutics led by its CEO and Co-Founder, Nabanita Nawar, Ph.D, and the Second Prize Winner goes to ARMA BIO, led by Co-Founder & CSO, Paraskevi Giannakakou, Ph.D.
The 2024 AIM-HI Women’s Venture Competition Committee reviewed more than 50 applications from 10 countries, including Canada, Ghana, India, Israel, Norway, Romania, Singapore, Spain, Thailand, ...
Scientists use magnetic nanotech to safely rewarm frozen tissues for transplant
2024-09-04
Every day, people die waiting for an organ transplant. Time is at a premium, not just for those awaiting organs, but also for the organs themselves, which can deteriorate rapidly during transportation. Looking to extend the viability of human tissues, researchers report in ACS’ Nano Letters their efforts to facilitate completely freezing, rather than cooling and then thawing, potentially life-saving organs. They demonstrate a magnetic nanoparticle’s successful rewarming of animal tissues.
As of August 2024, more than 114,000 people are on the U.S. national transplant ...
Why dinosaur collagen might have staying power
2024-09-04
Dinosaurs continue to fascinate people, but that’s not their only enduring quality: Collagen in their skeletons remains intact for millions of years, despite containing chemical bonds that should only persist for about 500 years. Now, scientists report in ACS Central Science that the unique tenacity of this protein may result from a molecular structure that shields these vulnerable bonds from attack by water that’s present in the environment.
Collagen is the most abundant protein in animals. It’s found in skin and connective tissues, such as cartilage and bones. Fragments of collagen have been ...