(Press-News.org) “Bystander” mice that briefly watched other mice be harmed show fewer signs of behavioral despair when faced with their own harmful event, compared to mice who do not observe their fellow mice being harmed. The negative emotional contagion experienced by the bystander mice appears to build resilience against a depressive-like state, according to new research by Sarah Mondoloni and colleagues. Mondoloni et al. demonstrate that resilience in these mice requires an increase in serotonin release in a part of the brain called the lateral habenula. “These findings support the notion that, as is the case in humans, graded trauma can be resilience-promoting, enabling individuals to cope with future challenges,” the researchers write. They also note that their findings may refine the current model of the key neuronal circuits involved in depression. The negative emotional contagion in bystander mice was produced when they watched their cagemates receive a mild foot shock, prior to their own shock experience. The researchers suggest that serotonin release helps produce bystander resilience by reducing neuronal bursting in the lateral habenula. This type of neuronal hyperactivity underlies depressive behaviors in the mice. In a related Perspective, Martin Metzger and Jose Donato Jr. say the findings “have great potential relevance to be incorporated into the treatment of major depression, post-traumatic stress disorder and addiction.”
END
Emotional contagion promotes resilience via serotonin release in mice
Summary author: Becky Ham
2024-09-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tiny glass beads indicate volcanism on the Moon 120 million years ago
2024-09-05
There were volcanic eruptions on the Moon as recently as 120 million years ago, according to a new analysis of a lunar sample collected by the Chang’e‑5 mission. Samples collected by the Apollo, Luna and Chang’e‑5 missions have previously shown there was widespread basaltic volcanism on the Moon extending from about 4.4 to 2.0 billion years ago. The new findings demonstrate that volcanism persisted much longer than was previously suspected, at least on smaller, more localized scale. Bi-Wen Wang, Qian W.L. Zhang and colleagues sorted through more than 3000 tiny glass beads they recovered from a lunar sample collected by Chang’e‑5, examining the bead’s ...
Injected fibroblasts transform to give thin skin a tough new identity
2024-09-05
The thick and tough skin on our palms and soles, called volar skin, stands up well under high-pressure conditions. This type of skin would be welcome on the limb stumps of amputees, since these points of contact with prostheses are covered in thin, non-volar skin that can be damaged over time. Now, Sam Lee and colleagues demonstrate that an injection of volar fibroblasts into non-volar skin in a group of human volunteers can promote volar features in the thin skin that last up to five months. Based on their analysis, Lee et al. are now enrolling amputees in a phase 2 clinical trial to further explore volar fibroblasts as a future ...
Novel study reveals how aging immune system fuels cancer growth, potentially opening new avenues for prevention
2024-09-05
New York, NY [September 5, 2024]—A novel study by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai addresses a critical yet under-explored question in cancer research: Why is aging the biggest risk factor for cancer? The study reveals how an aging immune system spurs tumor growth, offering new insights into cancer prevention and treatment, especially for older adults.
Details on the findings were reported in the September 5 Online First Release of Science [DOI:10.1126/science.adn0327]. In preclinical models, the research team found that anakinra, a drug typically used for inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, can be repurposed to block harmful signals between ...
Researchers prove 120-million-year-old volcanism on moon
2024-09-05
Extensive geologic evidence of ancient volcanic activity can be found on the Moon, but how long this volcanism persisted has been unclear. However, Prof. LI Qiuli’s Lab at the Institute of Geology and Geophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IGGCAS) has recently identified three volcanic glass beads from lunar soil samples collected by the Chang’e-5 mission. Their research shows that the beads were formed 123±15 million years ago (Ma), thus representing the youngest lunar ...
State-by-state data boosts bird conservation planning
2024-09-05
ITHACA, N.Y. – New data summaries from the Cornell Lab of Ornithology’s eBird platform will help state wildlife planners assess the status of bird populations that live in or pass through their state – a crucial tool in protecting species.
A team of data scientists at eBird, the participatory science platform, has packaged summaries covering every bird species, in every state, and made them available online for free. These data summaries will help states prepare their federally required ...
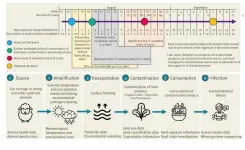
Study on E. coli outbreak in the UK demonstrates increasing impact of climate change on public health and food security
2024-09-05
A study published in Eurosurveillance to investigate an outbreak of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) O157:H7 in the UK identified contaminated lettuce as the most likely source of the infection, and determined that heavy rainfall and flooding may have carried STEC from animal faeces to the lettuce crops. More heavy rainfall events are expected due to climate change in the future, leading to increased impacts on health and food security.
Ahead of Field Epidemiology Day 2024, this study demonstrates the value of field investigations in quickly responding to outbreaks, improving preparedness, and protecting public health, and possible ...
Using 3D imaging to transform plastic waste recycling
2024-09-05
In a global first, University of Waterloo researchers have used 3D imaging technology to understand the fine details of microplastics, paving the way for more effective methods of plastic waste recycling.
Micro and nanoplastics, tiny particles of plastic that come from the breakdown of larger plastic items, have become an exponentially worsening environmental crisis. Due to their difficulties in safely decomposing, plastic pollution poses significant threats to ecosystems, wildlife and human health.
Scientists have struggled to understand the exact process of ...
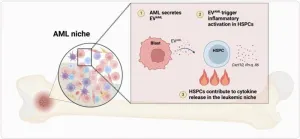
Case for inflammatory memory for hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in AML niche
2024-09-05
“In this research perspective, we discuss recent work from our lab describing an active role of HSPCs in AML and the potential implications.”
BUFFALO, NY- September 5, 2024 – A new research perspective was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on September 4, 2024, entitled, “Trained and ready - the case for an inflammatory memory for hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in the AML niche.”
As noted in the abstract of this paper, lifelong hematopoiesis is sustained by the crosstalk between hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) and specialized bone marrow ...
For many animals sleep is a social activity, but it’s usually studied as an individual process
2024-09-05
Group sleeping can impact when animals sleep, how long they sleep for, and how deeply they sleep. For example, groups of meerkats time their sleep according to “sleep traditions”; olive baboons sleep less when their group size increases; bumblebees suppress sleep in the presence of offspring; and co-sleeping mice can experience synchronized REM sleep. To fully understand both sleep and animal social structures, we need to pay more attention to the “social side” of sleep, animal behaviorists argue in an opinion paper publishing September 5 in the Cell Press journal ...
Human brain cancers fire electrical impulses – researchers reveal unexpected hybrid cell spiking the signals
2024-09-05
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children’s Hospital have uncovered a new cell type in the human brain.
The study published in Cancer Cell reveals that a third of the cells in glioma, a type of brain tumor, fire electrical impulses. Interestingly, the impulses, also called action potentials, originate from tumor cells that are part neuron and part glia, supporting the groundbreaking idea that neurons are not the only cells that can generate electric signals in the brain. The scientists also discovered ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Emotional contagion promotes resilience via serotonin release in miceSummary author: Becky Ham