For many animals sleep is a social activity, but it’s usually studied as an individual process
2024-09-05
(Press-News.org) Group sleeping can impact when animals sleep, how long they sleep for, and how deeply they sleep. For example, groups of meerkats time their sleep according to “sleep traditions”; olive baboons sleep less when their group size increases; bumblebees suppress sleep in the presence of offspring; and co-sleeping mice can experience synchronized REM sleep. To fully understand both sleep and animal social structures, we need to pay more attention to the “social side” of sleep, animal behaviorists argue in an opinion paper publishing September 5 in the Cell Press journal Trends in Ecology & Evolution.
Although many animals sleep in groups, most sleep studies are conducted under laboratory conditions that only consider one animal at a time. These laboratory sleep studies provide high-resolution information on sleep depth and phase, but they are unable to capture the environmental or social contexts in which sleep usually occurs. To understand the interconnections between sleeping and sociality, the researchers say that we need to study groups of sleeping animals in the wild.
“Social sleep is a research frontier that we believe holds exciting potential for new insights into both sleep science and wild animals’ lives,” write the researchers, who include behavioral ecologists Pritish Chakravarty (@prit_chak) and Margaret Crofoot (@MegCrofoot) of the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior and the University of Konstanz Germany. “We propose a new framework that leverages simultaneous monitoring of the sleep of members of social groups, combined with time-series and social network analyses, to investigate how the social environment shapes (and is shaped by) sleep.”
To study sleep in the wild, the researchers recommend leveraging technologies such as wearable or implantable accelerometers, which provide information on animal movements with video or direct observations of the animals’ behavior. Pairing this sleep data with measurements of the group’s social networks like dominance hierarchies and kinship relationships, for example, could provide important ecological and evolutionary insights into the impact of sleep on the fitness and survival of both individual and groups of animals, the researchers say.
“It is likely that key aspects of group behavior, including coordination, decision-making, and cooperative potential, will be influenced by the sleep of its members,” they write. “By collecting data on sleep and sociality and applying our proposed tools to analyze social sleep, we can begin unraveling the adaptive functions and evolutionary trade-offs of sleep that may not be revealed by studying individual animals alone.”
###
This research was supported by the Max Planck Society, the Packard Foundation, the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, the European Union, the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation), the Agence Nationale de la Recherche, and a Marie Skłodowska-Curie Fellowship.
Trends in Ecology & Evolution, Chakravarty et al., “The sociality of sleep in animal groups” https://cell.com/trends/ecology-evolution/fulltext/S0169-5347(24)00176-9
Trends in Ecology & Evolution (@Trends_Ecol_Evo), published by Cell Press, is a monthly review journal that contains polished, concise, and readable reviews and opinion pieces in all areas of ecology and evolutionary science. It aims to keep scientists informed of new developments and ideas across the full range of ecology and evolutionary biology—from the pure to the applied, and from molecular to global. Visit http://www.cell.com/trends/ecology-evolution. To receive Cell Press media alerts, please contact press@cell.com.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-05
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children’s Hospital have uncovered a new cell type in the human brain.
The study published in Cancer Cell reveals that a third of the cells in glioma, a type of brain tumor, fire electrical impulses. Interestingly, the impulses, also called action potentials, originate from tumor cells that are part neuron and part glia, supporting the groundbreaking idea that neurons are not the only cells that can generate electric signals in the brain. The scientists also discovered ...
2024-09-05
Staging of patients with early pancreatic cancer is inaccurate as much as 80% of the time, according to a new Cedars-Sinai Cancer study published in the peer-reviewed journal JAMA. The finding underscores the urgent need for advancements in diagnostic technology and staging, which could significantly alter early pancreatic cancer treatment and research.
In this study, investigators looked at data from more than 48,000 patients in the National Cancer Database. Based on preoperative imaging, all of the patients in the study had either stage 1 or stage 2 pancreatic cancer.
Following surgery to remove their tumors, more than 78% of stage ...
2024-09-05
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — When overdose rates spiked in Oregon in 2021 after the state decriminalized low-level drug possession, blame quickly turned to the new state law. But a new study by researchers at the Brown University School of Public Health implicates another factor: the introduction of fentanyl into Oregon’s unregulated drug market.
“What's compelling about this analysis is that it follows the path of fentanyl across the country and offers testament to the ...
2024-09-05
About The Study: The population attributable fraction of dementia from vision impairments ranged from 4.9%-19.0%. While not proving a cause-and-effect relationship, these findings support inclusion of multiple objective measures of vision impairments, including contrast sensitivity and visual acuity, to capture the total potential impact of addressing vision impairment on dementia.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jason R. Smith, ScM, email jsmit491@jhu.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.3131)
Editor’s ...
2024-09-05
About The Study: In patients with symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis, balloon angioplasty plus aggressive medical management, compared with aggressive medical management alone, statistically significantly lowered the risk of a composite outcome of any stroke or death within 30 days or an ischemic stroke or revascularization of the qualifying artery after 30 days through 12 months. The findings suggest that balloon angioplasty plus aggressive medical management may be an effective treatment for symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis, although the risk of stroke or ...
2024-09-05
About The Study: This cross-sectional study of commercially insured patients suggests that there may have been meaningful heterogeneous associations between cannabis policy and state and between cannabis policy and drug class (e.g., decreases in dispensing of benzodiazepines but increases in dispensing of antidepressants and antipsychotics). This finding suggests additional clinical research is needed to understand the association between cannabis use and mental health. The results have implications for patient substance use and mental health–related outcomes.
Corresponding Author: To ...
2024-09-05
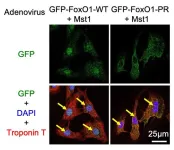
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identify Mst1–FoxO1–C/EBP-ß signaling pathway that promotes heart cell survival
Tokyo, Japan – Understanding the mechanisms behind cell death and survival is crucial when it comes to conditions like heart failure, which affects millions of people worldwide. Now, researchers from Japan have identified a mechanism which protects cardiac myocytes against ischemia, or a lack of blood supply.
In this study published online on 25 July 2024 in Nature Communications, researchers from the Tokyo Medical and Dental ...
2024-09-05
Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) researchers investigate the molecular mechanisms that link periodontal disease to rheumatoid arthritis
Tokyo, Japan – Periodontal disease, which affects the gums and tissues that surround the teeth, is one of the most prevalent dental conditions worldwide. Most often caused by the formation and accumulation of bacterial biofilm around the teeth, periodontal disease can ultimately lead to tooth loss if left unattended. Interestingly, the inflammatory effects of periodontal bacteria can go well beyond the mouth, leading to systemic effects. Over the past few decades, clinical studies have revealed that the periodontal ...
2024-09-05
Regenstrief Institute will host its semiannual LOINC® conference September 17-20, 2024, in Washington, D.C.
LOINC, a global healthcare terminology standard, will be the subject of the three-day conference during which experts worldwide will collaborate during presentations across three points of emphasis: implementation and policy, innovation and mapping.
Keynote presenters will be:
Wednesday, September 18 – Jesse Ehrenfeld, M.D., MPH, the president of the American Medical Association.
Thursday, September ...
2024-09-05
Arthritis drugs already available for prescription have the potential to halt lingering lung problems that can last months or years after COVID-19 infections, new research from the University of Virginia School of Medicine and Cedars-Sinai suggests.
By examining damaged human lungs and developing an innovative new lab model, the scientists identified faulty immune processes responsible for the ongoing lung issues that plague an increasing number of people after they’ve otherwise recovered from COVID-19. These lasting harms of COVID infection, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] For many animals sleep is a social activity, but it’s usually studied as an individual process