(Press-News.org) About The Study: The population attributable fraction of dementia from vision impairments ranged from 4.9%-19.0%. While not proving a cause-and-effect relationship, these findings support inclusion of multiple objective measures of vision impairments, including contrast sensitivity and visual acuity, to capture the total potential impact of addressing vision impairment on dementia.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jason R. Smith, ScM, email jsmit491@jhu.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.3131)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaophthalmology/fullarticle/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.3131?guestAccessKey=26113c66-f05b-4dbc-958d-dbef32ef78a1&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=090524
END
Vision impairment and the population attributable fraction of dementia in older adults
JAMA Ophthalmology
2024-09-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Balloon angioplasty vs medical management for intracranial artery stenosis
2024-09-05
About The Study: In patients with symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis, balloon angioplasty plus aggressive medical management, compared with aggressive medical management alone, statistically significantly lowered the risk of a composite outcome of any stroke or death within 30 days or an ischemic stroke or revascularization of the qualifying artery after 30 days through 12 months. The findings suggest that balloon angioplasty plus aggressive medical management may be an effective treatment for symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis, although the risk of stroke or ...
Cannabis laws and utilization of medications for the treatment of mental health disorders
2024-09-05
About The Study: This cross-sectional study of commercially insured patients suggests that there may have been meaningful heterogeneous associations between cannabis policy and state and between cannabis policy and drug class (e.g., decreases in dispensing of benzodiazepines but increases in dispensing of antidepressants and antipsychotics). This finding suggests additional clinical research is needed to understand the association between cannabis use and mental health. The results have implications for patient substance use and mental health–related outcomes.
Corresponding Author: To ...
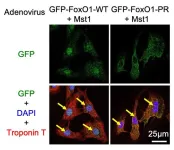
New avenues for treating heart failure: uncovering a protective mechanism in the cardiac myocytes
2024-09-05
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identify Mst1–FoxO1–C/EBP-ß signaling pathway that promotes heart cell survival
Tokyo, Japan – Understanding the mechanisms behind cell death and survival is crucial when it comes to conditions like heart failure, which affects millions of people worldwide. Now, researchers from Japan have identified a mechanism which protects cardiac myocytes against ischemia, or a lack of blood supply.
In this study published online on 25 July 2024 in Nature Communications, researchers from the Tokyo Medical and Dental ...
Shedding light on how oral bacteria can aggravate rheumatoid arthritis
2024-09-05
Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) researchers investigate the molecular mechanisms that link periodontal disease to rheumatoid arthritis
Tokyo, Japan – Periodontal disease, which affects the gums and tissues that surround the teeth, is one of the most prevalent dental conditions worldwide. Most often caused by the formation and accumulation of bacterial biofilm around the teeth, periodontal disease can ultimately lead to tooth loss if left unattended. Interestingly, the inflammatory effects of periodontal bacteria can go well beyond the mouth, leading to systemic effects. Over the past few decades, clinical studies have revealed that the periodontal ...
Regenstrief to host semiannual LOINC® conference in Washington, D.C., Sept. 17-20
2024-09-05
Regenstrief Institute will host its semiannual LOINC® conference September 17-20, 2024, in Washington, D.C.
LOINC, a global healthcare terminology standard, will be the subject of the three-day conference during which experts worldwide will collaborate during presentations across three points of emphasis: implementation and policy, innovation and mapping.
Keynote presenters will be:
Wednesday, September 18 – Jesse Ehrenfeld, M.D., MPH, the president of the American Medical Association.
Thursday, September ...
Cause, potential treatments ID'd for persistent COVID-19 lung problems
2024-09-05
Arthritis drugs already available for prescription have the potential to halt lingering lung problems that can last months or years after COVID-19 infections, new research from the University of Virginia School of Medicine and Cedars-Sinai suggests.
By examining damaged human lungs and developing an innovative new lab model, the scientists identified faulty immune processes responsible for the ongoing lung issues that plague an increasing number of people after they’ve otherwise recovered from COVID-19. These lasting harms of COVID infection, ...
Pregnant women exposed to PFAS may be at risk for obesity, heart disease later in life
2024-09-05
WASHINGTON—Women with higher levels of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) during pregnancy may experience long-term weight gain and heart problems later in life, according to new research published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
PFAS are manmade chemicals found in food packaging, cookware, clothes, drinking water, personal care products and many other consumer goods. These endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) can interfere with hormones and cause health issues such as obesity, infertility and cancer.
“Our study supports the idea that pregnancy may be ...
Skin fungus colonization accelerates breast cancer tumor growth
2024-09-05
Washington, D.C. — A common skin fungus, Malassezia globosa may invade deep tissues through the skin or by other means, then cause tumor growth, according to a new study. The study results were reported in mBio, an open access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
“It is important to take care of skin not only for beauty, but also for health,” said corresponding study author Qi-Ming Wang, Ph.D., a professor in the School of Life Sciences, Institute of Life Sciences and Green Development, Hebei University, Hebei, China. “As ...
New study in JNCCN supports chemotherapy option that reduces side effects for people with gastrointestinal cancers
2024-09-05
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [September 5, 2024] — New research just-published online by JNCCN—Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network finds that for many commonly used treatment regimens targeting metastatic gastrointestinal (GI) cancers, such as FOLFOX, FOLFIRI, or FOLFIRINOX, it is possible to administer 5-FU solely through continuous infusion, minus the bolus (quick-delivery via intravenous push) component, without negatively affecting patient outcomes.
The study reviewed results from 11,765 patients across 280 cancer clinics who were diagnosed with ...
Study shows long term-effects of immigration on Chinese Americans’ cardiovascular health
2024-09-05
A new UCLA-led study found that cardiovascular disease risk among Chinese American immigrants increases with length of residence and varies by location in the U.S. The study, which leveraged data from the MESA (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis) cohort, sponsored by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), observed the heart health of 746 Chinese Americans in both Los Angeles and Chicago over a period of roughly 18 years. The study found that participants who resided in Chicago showed lower mortality levels from heart disease compared to those who lived in Los Angeles.
“This is the first long-term prospective study in nearly two decades to investigate the effects of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Vision impairment and the population attributable fraction of dementia in older adultsJAMA Ophthalmology