AI helps distinguish dark matter from cosmic noise
2024-09-06
(Press-News.org)
Dark matter is the invisible force holding the universe together – or so we think. It makes up around 85% of all matter and around 27% of the universe’s contents, but since we can’t see it directly, we have to study its gravitational effects on galaxies and other cosmic structures. Despite decades of research, the true nature of dark matter remains one of science’s most elusive questions.
According to a leading theory, dark matter might be a type of particle that barely interacts with anything else, except through gravity. But some scientists believe these particles could occasionally interact with each other, a phenomenon known as self-interaction. Detecting such interactions would offer crucial clues about dark matter’s properties.
However, distinguishing the subtle signs of dark matter self-interactions from other cosmic effects, like those caused by active galactic nuclei (AGN) – the supermassive black holes at the centers of galaxies – has been a major challenge. AGN feedback can push matter around in ways that are similar to the effects of dark matter, making it difficult to tell the two apart.
In a significant step forward, astronomer David Harvey at EPFL’s Laboratory of Astrophysics has developed a deep-learning algorithm that can untangle these complex signals. Their AI-based method is designed to differentiate between the effects of dark matter self-interactions and those of AGN feedback by analyzing images of galaxy clusters – vast collections of galaxies bound together by gravity. The innovation promises to greatly enhance the precision of dark matter studies.
Harvey trained a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) – a type of AI that is particularly good at recognizing patterns in images – with images from the BAHAMAS-SIDM project, which models galaxy clusters under different dark matter and AGN feedback scenarios. By being fed thousands of simulated galaxy cluster images, the CNN learned to distinguish between the signals caused by dark matter self-interactions and those caused by AGN feedback.
Among the various CNN architectures tested, the most complex - dubbed “Inception” – proved to also be the most accurate. The AI was trained on two primary dark matter scenarios, featuring different levels of self-interaction, and validated on additional models, including a more complex, velocity-dependent dark matter model.
Inception achieved an impressive accuracy of 80% under ideal conditions, effectively identifying whether galaxy clusters were influenced by self-interacting dark matter or AGN feedback. It maintained is high performance even when the researchers introduced realistic observational noise that mimics the kind of data we expect from future telescopes like Euclid.
What this means is that Inception – and the AI approach more generally – could prove incredibly useful for analyzing the massive amounts of data we collect from space. Moreover, the AI’s ability to handle unseen data indicates that it’s adaptable and reliable, making it a promising tool for future dark matter research.
AI-based approaches like Inception could significantly impact our understanding of what dark matter actually is. As new telescopes gather unprecedented amounts of data, this method will help scientists sift through it quickly and accurately, potentially revealing the true nature of dark matter.
Reference
D. Harvey. A deep-learning algorithm to disentangle self-interacting dark matter and AGN feedback models. Nature Astronomy 06 September 2024. DOI: 10.1038/s41550-024-02322-8
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-06
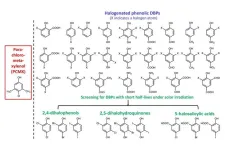
A widely used disinfectant worldwide, chloroxylenol, has been associated with eco-toxicological threats in water environments due to its relatively high chemical stability and massive consumption. Researchers at the School of Engineering of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have discovered a promising alternative known as 2,6-dichlorobenzoquinone (2,6-DCQ), which works more effectively in combating certain common bacteria, fungi and viruses, and can be rapidly degraded and detoxified in receiving waters.
This groundbreaking study is led by Prof. ZHANG Xiangru from HKUST's ...
2024-09-06
In some places around the globe, the lights never go off. Streetlights, roadway lighting, and illuminated signs can deter crime, make roads safer, and enhance landscaping. Undisrupted light, however, comes with ecological, behavioral, and health consequences.
In the US, some states have legislation in place to reduce light pollution; however, levels of light at night remain high in many parts of the country. Now, researchers there have investigated correlations between outside nightly light pollution and Alzheimer's disease (AD).
“We show that in the US there is a positive ...
2024-09-06
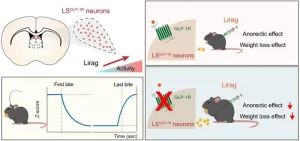
A research group led by Prof. ZHU Yingjie from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), has revealed the essential role of lateral septum (LS) neurons in mediating anorectic and weight-lowering effects of the anti-obesity drug— liraglutide in mice.
The study was published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation on Sep. 03.
Obesity is now among the top ten chronic diseases worldwide, causing a range of health issues and increasing the medical burden. Anti-obesity medications have shown greater efficacy than lifestyle changes and diet, with lower risks and fewer side effects ...
2024-09-06
From August 7 to 10, the Third SynBio Challenges were held at the Guangming Tianan Cloud Park International Conference Center in Shenzhen, China.
The event was co-organized by Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Chinese Society of Biotechnology, Shenzhen University of Advanced Technology (SUAT), Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology (iSynBio), Shenzhen Synthetic Biology Association, and the Shenzhen Industrial Innovation Center for Engineering Biology.
The SynBio Challenges aim to provide a platform for students to engage in exchange and competition within the synthetic biology ...
2024-09-06
Cruciferous vegetables, including broccoli, cabbage, kale, and cauliflower have been found to lower blood pressure, in comparison to root and squash vegetables, in middle-aged and older Australian adults with elevated blood pressure.
In a randomised, controlled, crossover trial, researchers from Edith Cowan University (ECU) found that consuming four serves a day of cruciferous vegetables resulted in a significant reduction in blood pressure, compared with four serves a day of root and squash vegetables including carrot, potato, sweet ...
2024-09-06
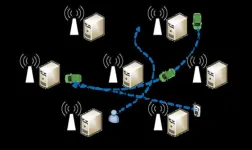
Dynamic service migration is a key technology in Mobile Edge Computing(MEC). In a multi-user service migration scenario, the states of all users are combined into a global state, which leads to the instability of the system and ignores the influence of multiple users. It is more and more challenging to design an effective migration strategy to balance migration costs and latency in a multi-user distributed environment.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Degan ZHANG published their new research on 15 August 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
Considering ...
2024-09-06
Scientists at Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah (the U), the National Cancer Institute-designated cancer center for the Mountain West, have made a significant breakthrough in predicting the prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), a particularly aggressive disease. Their research, published in JCO Precision Oncology as part of the TOWARDS study, has led to the development of a new mechanism that accurately forecasts the aggressiveness of TNBC. This advancement could revolutionize the way doctors treat TNBC, allowing them to identify higher-risk patients and tailor precise treatments.
Currently, TNBC lacks reliable methods to predict recurrence after ...
2024-09-06
SEQUIM, Wash.—Officials gathered at the Sequim campus of the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory today to dedicate DOE’s first hybrid-electric research vessel, RV Resilience.
The event marks the start of a new era of marine energy research at PNNL-Sequim, part of DOE’s Office of Science national laboratory system and Resilience’s new home port. Speakers at the dedication included U.S. Sen. Maria Cantwell, U.S. Rep. Derek Kilmer, Washington State Rep. Steve Tharinger and representatives from DOE and PNNL.
“DOE is focused on ...
2024-09-06
ROCHESTER, Minn. — About 8 to 10 million Americans over age 40 have an overabundance of cloned white blood cells, or lymphocytes, that hamper their immune systems. Although many who have this condition — called monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis (MBL) — do not experience any symptoms, a new study shows they may have an elevated risk for several health complications, including melanoma, a form of skin cancer. The findings, by Mayo Clinic researchers, are published in a new paper in the Journal ...
2024-09-06
PHILADELPHIA— The vision of people with a rare inherited condition that causes them to lose much of their sight early in childhood was 100 times better after they received gene therapy to address the genetic mutation causing it. Some patients even experienced a 10,000-fold improvement in their vision after receiving the highest dose of the therapy, according to researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania who co-led the clinical trial published in The Lancet.
“That 10,000-fold improvement ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] AI helps distinguish dark matter from cosmic noise