(Press-News.org) EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 11 A.M. ET FRIDAY, SEPTEMBER 6. 2024
Individuals involved in the criminal legal system have a high rate of opioid use disorder (OUD) and a high risk of overdose death compared to the general population, yet the most effective treatments—medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD)—are underutilized in criminal legal settings where treatment is mandated as part of a person’s probation or parole. Medications are often not provided due to stigma or lack of adequate funding for evidence-based care. According to a study published today in JAMA Health Forum, use of these lifesaving medications has increased only modestly in criminal legal settings in recent years, despite national, state and local efforts, and progress has varied widely across the country. Only six states successfully delivered MOUDs to at least 50% of people referred to treatment by the criminal legal system in 2021, a rate comparable to what people treated in non-criminal legal settings receive.
“One of the groups at the highest risk of opioid overdose death is people leaving jails and prisons. If we want to save lives, we have to do a better job of connecting people to the most effective treatments when they are released from incarceration,” said says J. Travis Donahoe, Ph.D., M.P.H., assistant professor of health policy and management at the University of Pittsburgh School of Public Health. “While there has been some progress in closing the gap, those gains have been uneven. States that have been the most successful—such as Massachusetts and New Jersey—can serve as models for states that are lagging behind.”
END
Disparity in access to medications for opioid use disorder persist in criminal legal settings
2024-09-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Age-related changes in male fibroblasts increase treatment-resistant melanoma
2024-09-06
Age-related changes in the fibroblasts, cells that create the skin’s structure, contribute to the development of aggressive, treatment-resistant melanoma in males, according to research in mice by the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
The study was published online Sept. 6 in Cell.
The risk of developing melanoma, a potentially deadly skin cancer, increases with age. Men are more at risk than women, and tend to develop more aggressive, hard-to-treat melanomas, particularly at advanced ages, says Ashani Weeraratna, Ph.D., the Bloomberg ...
COVID-19 and rates of cancer diagnosis in the US
2024-09-06
About The Study: This population-based cross-sectional study of U.S. cancer incidence trends found that rates of diagnosis improved in 2021 but continued to be lower than expected, adding to the existing deficit of diagnosed cases from 2020. Particular attention should be directed at strategies to immediately increase cancer screenings to make up lost ground.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Krystle A. Lang Kuhs, PhD, MPH, email krystle.kuhs@uky.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.32288)
Editor’s Note: Please see ...
New research from Swansea University shines a light on how solar power and farming can coexist
2024-09-06
Scientists from Swansea University have developed a new tool to help identify optimal photovoltaic (PV) materials capable of maximising crop growth while generating solar power.
In a recent study published in Solar RRL, academics from the University’s Department of Physics have been exploring the effect of semi-transparent PV materials placed over crops – an exemplary application of agrivoltaics (solar panels combined with agricultural settings).
As part of this work, the team has developed an innovative freeware tool that predicts the light transmission, absorption, and power generation of different PV materials nearly anywhere on the globe using ...
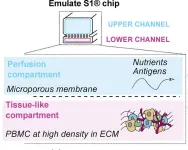
Artificial lymphoid organs could help predict efficacy of booster vaccines
2024-09-06
Researchers at the Institut Pasteur in France have developed artificial “lymphoid organ-chips” that recreate much of the human immune system’s response to booster vaccines. The technology, described in an article to be published September 6 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), could potentially be used to evaluate the likely effectiveness of new protein and mRNA-based booster vaccines for COVID-19 and other infectious diseases.
The rapid mutation and evolution of SARS-CoV-2 and other viruses ...
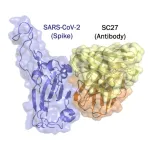
One antibody to neutralize them all?
2024-09-06
SAN ANTONIO -- A monoclonal antibody appears effective at neutralizing the numerous variants of SARS-CoV-2, as well as related viruses in animals that could pose a threat if they were to begin spreading in people. The antibody, called SC27, was recently described in Cell Reports Medicine.
The finding opens the possibility of broader, more effective treatments to work against current and future COVID variants.
Monoclonal antibody SC27 was identified, developed and provisionally patented by a team of researchers led ...
How context-specific factors control gene activity
2024-09-06
Every cell in our body contains the same DNA, yet liver cells are different from brain cells, and skin cells differ from muscle cells. What determines these differences? It all comes down to gene regulation; essentially how and when genes are turned on and off to meet the cell’s demands. But gene regulation is quite complex, especially because it is itself regulated by other parts of DNA.
Gene regulators: Enhancers, transcription factors
There are two important components that control gene regulation: the first are enhancers, which are short bits of DNA that increase the likelihood that a ...
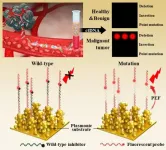
Detects cancer genes with ultra-high sensitivity!
2024-09-06
Dr. Min-young Lee and Dr. Sung-gyu Park of the Advanced Bio and Healthcare Materials Research Division at KIMS have developed a technology that can detect cancer mutant genes in blood with the world's highest sensitivity of 0.000000001% based on plasmonic nanomaterials for optical signal amplification. The team tested blood samples from lung cancer patients (stages 1-4) and healthy individuals for EGFR mutations and achieved a diagnostic accuracy of 96%.
Previously utilized genetic analysis technologies had low analytical sensitivity to detect mutated genes compared to normal genes, making it difficult to accurately diagnose early-stage cancer patients. ...
Study suggests US droughts, rainy extremes becoming more severe
2024-09-06
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Severe drought in the American Southwest and Mexico and more severe wet years in the Northeast are the modern norm in North America, according to new research – and the analysis suggests these seasonal patterns will be more extreme in the future.
The middle of the United States, meanwhile, can expect bigger swings between wetter wet periods – high-rainfall years known as pluvials – and drier summers through the rest of this century, the study predicts.
Researchers at The Ohio State University say the findings, based on modern precipitation data, historical tree rings and climate models ...
Quality assurance in histopathology laboratories
2024-09-06
The medical field is inherently susceptible to errors, with laboratory tests being no exception. In histopathology laboratories, where tests are considered the gold standard for diagnosing various diseases, errors can significantly impact patient outcomes. Quality Control (QC) and Quality Assurance (QA) programs are essential in minimizing these errors and ensuring the generation of accurate and reliable reports. The complex, multistep nature of histopathology work, combined with the subjective nature of many diagnostic interpretations, ...
Causing environmental damage should be a criminal offense, say 72% of people surveyed in G20 countries
2024-09-06
Nearly three out of four people (72%) surveyed across 18 G20 countries1 support making it a criminal offence for government or leaders of large businesses to approve or permit actions which cause serious damage to nature and climate, finds major new research. This finding is part of the latest Global Commons Survey 2024, conducted by Ipsos UK and commissioned by Earth4All and the Global Commons Alliance (GCA).
The research follows recent landmark legislative changes, including in Belgium where ecocide was recognised as a federal crime earlier this year. Related laws ...