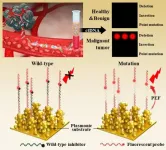
(Press-News.org) Dr. Min-young Lee and Dr. Sung-gyu Park of the Advanced Bio and Healthcare Materials Research Division at KIMS have developed a technology that can detect cancer mutant genes in blood with the world's highest sensitivity of 0.000000001% based on plasmonic nanomaterials for optical signal amplification. The team tested blood samples from lung cancer patients (stages 1-4) and healthy individuals for EGFR mutations and achieved a diagnostic accuracy of 96%.
Previously utilized genetic analysis technologies had low analytical sensitivity to detect mutated genes compared to normal genes, making it difficult to accurately diagnose early-stage cancer patients. In addition, it was difficult to establish a quick treatment strategy and apply it to screening tests due to the high cost and long time required for analysis and the need for special equipment. To overcome these challenges, the research team developed a low-cost analysis technology that can analyze various cancer mutations within the target gene region within 1 hour with an ultra-high sensitivity of 0.000000001%. This technology boasts the world's highest level of sensitivity, which is 100,000 times better than the highest level of 0.0001% among reported technologies, and through this, the possibility of early diagnosis was confirmed using the blood of lung cancer patients.
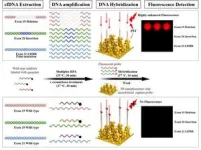
This technology combines nanomaterial technology that significantly improves the fluorescence signal, and primer/probe design that suppresses the fluorescence signal of normal genes, amplifying only the fluorescence signal of cancer mutant genes. This is because the accurate detection of even very small amounts of cancer mutated genes requires not only strong fluorescent signal expression technology but also precise discrimination of fine fluorescent signals. The team fabricated a biochip in the form of a microarray capable of simultaneously detecting three mutant genes of EGFR (deletion, insertion, and point mutations) on a plasmonic substrate made of three-dimensional, high-density gold nanostructures. After evaluating the clinical performance of 43 domestic lung cancer patients (stages 1 to 4) and 40 normal groups, a clinical sensitivity of 93% for lung cancer patients and a clinical specificity of 100% for the normal group were confirmed.
This technology can play an important role in not only early diagnosis and detection of recurrence of cancer, but also in monitoring treatment effectiveness and establishing personalized treatment plans. In addition, liquid biopsy using blood is possible as an alternative to surgical tissue biopsy, reducing the burden on patients and simplifying the examination process. It can also serve as a regular screening test, ultimately improving the quality of cancer management and treatment.
Senior researcher Min-young Lee said,“Because it is capable of comprehensively detecting various cancer mutations with the world’s highest level of ultra-high sensitivity, it can become a leading player in the early cancer diagnosis and treatment/recurrence monitoring market,”and added, “We expect that this will greatly improve the survival rate and quality of life of cancer patients.”
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT’s Nano Materials Technology Development Project (hosted by the Korea Institute of Materials Science). Additionally, the research results were published online on June 26 in the world-renowned academic journal‘Small Science’(IF: 11.1, first author Dr. Ji-young Lee) and were also selected as the cover paper (Inside Front Cover). Currently, the research team is conducting expanded development of early diagnosis technology for various cancers, such as lung cancer, colon cancer, breast cancer, and pancreatic cancer, and is seeking technology transfer companies for commercialization.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
###
About Korea Institute of Materials Science(KIMS)
KIMS is a non-profit government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea. As the only institute specializing in comprehensive materials technologies in Korea, KIMS has contributed to Korean industry by carrying out a wide range of activities related to materials science including R&D, inspection, testing&evaluation, and technology support.
END
Detects cancer genes with ultra-high sensitivity!
The Korea Institute of Materials Science(KIMS) has developed the world's most sensitive technology for detecting cancer mutant genes in blood
2024-09-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study suggests US droughts, rainy extremes becoming more severe
2024-09-06
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Severe drought in the American Southwest and Mexico and more severe wet years in the Northeast are the modern norm in North America, according to new research – and the analysis suggests these seasonal patterns will be more extreme in the future.
The middle of the United States, meanwhile, can expect bigger swings between wetter wet periods – high-rainfall years known as pluvials – and drier summers through the rest of this century, the study predicts.
Researchers at The Ohio State University say the findings, based on modern precipitation data, historical tree rings and climate models ...
Quality assurance in histopathology laboratories
2024-09-06
The medical field is inherently susceptible to errors, with laboratory tests being no exception. In histopathology laboratories, where tests are considered the gold standard for diagnosing various diseases, errors can significantly impact patient outcomes. Quality Control (QC) and Quality Assurance (QA) programs are essential in minimizing these errors and ensuring the generation of accurate and reliable reports. The complex, multistep nature of histopathology work, combined with the subjective nature of many diagnostic interpretations, ...
Causing environmental damage should be a criminal offense, say 72% of people surveyed in G20 countries
2024-09-06
Nearly three out of four people (72%) surveyed across 18 G20 countries1 support making it a criminal offence for government or leaders of large businesses to approve or permit actions which cause serious damage to nature and climate, finds major new research. This finding is part of the latest Global Commons Survey 2024, conducted by Ipsos UK and commissioned by Earth4All and the Global Commons Alliance (GCA).
The research follows recent landmark legislative changes, including in Belgium where ecocide was recognised as a federal crime earlier this year. Related laws ...
Natural probiotic discovered in UK newborns microbiomes
2024-09-06
Newborn babies have one of three pioneer bacteria in their gut shortly after birth, one of which could be used to develop new personalised infant therapeutic probiotics, researchers show.
In the largest study of UK baby microbiomes to date, researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, University College London (UCL), and the University of Birmingham, used whole genome sequencing to analyse stool samples from 1,288 healthy infants, all under one month old from the UK Baby Biome Study1.
This research, published today (6 September) ...
Hijacking the command center of the cell: nuclear parasites in deep-sea mussels
2024-09-06
Most animals live in intimate relationships with bacteria. Some of these bacteria live inside the cells of their hosts, but only very few are able to live inside cell organelles (structures inside the cell, like organs in the body). One group of bacteria have figured out how to colonize the nuclei of their hosts, a remarkable feat given that the nucleus is the control center of the cell.
To date, nothing is known about the molecular and cellular processes that these intranuclear bacteria use to infect and reproduce in animal hosts. A group of scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology in Bremen, Germany, now presents the first in-depth analysis ...
The heat generated by the tissues of some plants has played a crucial role in the evolutionary history of insect pollination
2024-09-06
Thermogenesis is a process by which organisms generate internal heat. Although it is usually associated with animals, some plants have also developed this ability. This metabolic process allows certain parts of the plant, such as flowers and inflorescences, to raise their temperature above that of the surrounding environment. Today, these plants, which include cycads and some angiosperms (flowering plants), rely on insects for pollination. The heat they generate helps volatilize and disperse floral fragrances and other chemical compounds that attract insects such as beetles, flies, and ...
Global experts help nanomedicines DELIVER on healthcare promise
2024-09-06
They’re tiny drug-delivery systems 1000 times smaller than a human hair, but while nanomedicines have long been hailed as the future for treating debilitating and life-threatening diseases, their journey from lab to patient has many challenges.
Now, new findings from a global team of expert scientists in academia and industry has generated world-first research quality standards that will help slash costs and reduce the time it takes to develop advanced nanomedicine treatments and make them available for patients.
Published in Nature Nanotechnology today, and led by the University of South Australia’s Dr Paul Joyce and the University ...
Galaxies are much much bigger than we thought
2024-09-06
If this galaxy is typical, then the study, published today in Nature Astronomy, indicates that our galaxy is already interacting with its closest neighbour, Andromeda.
Where does a galaxy end and deep space begin? It seems like a simple question until you look more closely at the gas that surrounds galaxies, known as the circumgalactic medium.
The halo of gas surrounding the stellar disc accounts for about 70% of the mass of the galaxy – excluding dark matter – but until now has remained something of a mystery. In the past we have only been able to observe the gas by measuring the light from a background object, ...
AI helps distinguish dark matter from cosmic noise
2024-09-06
Dark matter is the invisible force holding the universe together – or so we think. It makes up around 85% of all matter and around 27% of the universe’s contents, but since we can’t see it directly, we have to study its gravitational effects on galaxies and other cosmic structures. Despite decades of research, the true nature of dark matter remains one of science’s most elusive questions.
According to a leading theory, dark matter might be a type of particle that barely ...
HKUST engineering researchers discover an effective and environment-friendly disinfectant
2024-09-06
A widely used disinfectant worldwide, chloroxylenol, has been associated with eco-toxicological threats in water environments due to its relatively high chemical stability and massive consumption. Researchers at the School of Engineering of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have discovered a promising alternative known as 2,6-dichlorobenzoquinone (2,6-DCQ), which works more effectively in combating certain common bacteria, fungi and viruses, and can be rapidly degraded and detoxified in receiving waters.
This groundbreaking study is led by Prof. ZHANG Xiangru from HKUST's ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
[Press-News.org] Detects cancer genes with ultra-high sensitivity!The Korea Institute of Materials Science(KIMS) has developed the world's most sensitive technology for detecting cancer mutant genes in blood