(Press-News.org)
If this galaxy is typical, then the study, published today in Nature Astronomy, indicates that our galaxy is already interacting with its closest neighbour, Andromeda.
Where does a galaxy end and deep space begin? It seems like a simple question until you look more closely at the gas that surrounds galaxies, known as the circumgalactic medium.
The halo of gas surrounding the stellar disc accounts for about 70% of the mass of the galaxy – excluding dark matter – but until now has remained something of a mystery. In the past we have only been able to observe the gas by measuring the light from a background object, such as a quasar, that is absorbed by the gas.
That limits the picture of the cloud to a pencil-like beam.
A new study, however, has observed the circumgalactic medium of a star-bursting galaxy 270 million light years away, using new deep imaging techniques that were able to detect the cloud of gas glowing outside of the galaxy 100,000 light years into space, as far as they were able to look.
To envisage the vastness of that cloud of gas, consider that the galaxy’s starlight – what we would typically view as the disc – extends just 7,800 light years from its centre.
The current study observed the physical connection of hydrogen and oxygen from the centre of the galaxy far into space and showed that the physical conditions of the gas changed.
“We found it everywhere we looked, which was really exciting and kind of surprising,” says Associate Professor Nikole M. Nielsen, lead author of the paper, and a researcher with Swinburne University, and ASTRO 3D and an Assistant Professor at the University of Oklahoma.
Other authors of the paper came from Swinburne, the University of Texas at Austin, the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, the University of California, San Diego, and Durham University.
“We’re now seeing where the galaxy's influence stops, the transition where it becomes part of more of what’s surrounding the galaxy, and, eventually, where it joins the wider cosmic web and other galaxies. These are all usually fuzzy boundaries,” says Dr Nielsen.
“But in this case, we seem to have found a fairly clear boundary in this galaxy between its interstellar medium and its circumgalactic medium.”
The study observed stars ionizing gas with their photons within the galaxy.
“In the CGM, the gas is being heated by something other than typical conditions inside galaxies, this likely includes heating from the diffuse emissions from the collective galaxies in the Universe and possibly some contribution is due to shocks,” says Dr Nielsen.
“It's this interesting change that is important and provides some answers to the question of where a galaxy ends,” she says.
The discovery has been made possible thanks to the Keck Cosmic Web Imager (KCWI) on the 10-meter Keck telescope in Hawaii, which contains an integral field spectrograph and is one of the most sensitive instruments of its kind in operation.
“These one-of-a-kind observations require the very dark sky that is only available at the Keck Observatory on Mauna Kea,” said one of the paper’s authors, Swinburne’s Associate Professor Deanne Fisher.
ASTRO 3D scientists gained access to KCWI through Swinburne University.
“Swinburne’s Partnership with the W. M. Keck Observatory has allowed our team to really push the boundaries of what is possible,” says another author, Associate Professor Glenn Kacprzak. “KCWI has really changed the game on how we can now measure and quantify the diffuse gas around galaxies.”
Thanks to the instrument, rather than making a single observation providing a single spectrum of the gas in the galaxy, scientists can now obtain thousands of spectra simultaneously with one image from KCWI.
“It is the very first time that we have been able to take a photograph of this halo of matter around a galaxy,” says Professor Emma Ryan-Weber, the Director of ASTRO 3D.
The study adds another piece to the puzzle that is one of the big questions in astronomy and galaxy evolution – how do galaxies evolve? How do they get their gas? How do they process that gas? Where does that gas go.
“The circumgalactic medium plays a huge role in that cycling of that gas,” says Dr Nielsen. “So, being able to understand what the CGM looks like around galaxies of different types – ones that are star-forming, those that are no longer star-forming, and those that are transitioning between the two –we can observe differences in this gas, which might drive the differences within the galaxies themselves, and changes in this reservoir may actually be driving the changes in the galaxy itself.”
The study speaks directly to the ASTRO 3D’s mission. “It helps us understand how galaxies build mass over time,” says Professor Ryan-Weber.
The findings could also hold implications for how different galaxies interact and how they might impact each other.
“It’s highly likely that the CGMs of our own Milky Way and Andromeda are already overlapping and interacting,” says Dr Nielsen.
END
Dark matter is the invisible force holding the universe together – or so we think. It makes up around 85% of all matter and around 27% of the universe’s contents, but since we can’t see it directly, we have to study its gravitational effects on galaxies and other cosmic structures. Despite decades of research, the true nature of dark matter remains one of science’s most elusive questions.
According to a leading theory, dark matter might be a type of particle that barely ...
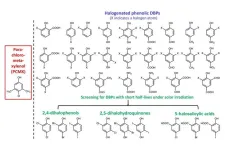
A widely used disinfectant worldwide, chloroxylenol, has been associated with eco-toxicological threats in water environments due to its relatively high chemical stability and massive consumption. Researchers at the School of Engineering of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have discovered a promising alternative known as 2,6-dichlorobenzoquinone (2,6-DCQ), which works more effectively in combating certain common bacteria, fungi and viruses, and can be rapidly degraded and detoxified in receiving waters.
This groundbreaking study is led by Prof. ZHANG Xiangru from HKUST's ...
In some places around the globe, the lights never go off. Streetlights, roadway lighting, and illuminated signs can deter crime, make roads safer, and enhance landscaping. Undisrupted light, however, comes with ecological, behavioral, and health consequences.
In the US, some states have legislation in place to reduce light pollution; however, levels of light at night remain high in many parts of the country. Now, researchers there have investigated correlations between outside nightly light pollution and Alzheimer's disease (AD).
“We show that in the US there is a positive ...
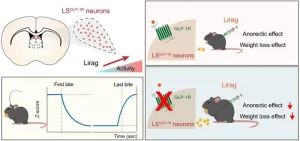
A research group led by Prof. ZHU Yingjie from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), has revealed the essential role of lateral septum (LS) neurons in mediating anorectic and weight-lowering effects of the anti-obesity drug— liraglutide in mice.
The study was published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation on Sep. 03.
Obesity is now among the top ten chronic diseases worldwide, causing a range of health issues and increasing the medical burden. Anti-obesity medications have shown greater efficacy than lifestyle changes and diet, with lower risks and fewer side effects ...
From August 7 to 10, the Third SynBio Challenges were held at the Guangming Tianan Cloud Park International Conference Center in Shenzhen, China.
The event was co-organized by Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Chinese Society of Biotechnology, Shenzhen University of Advanced Technology (SUAT), Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology (iSynBio), Shenzhen Synthetic Biology Association, and the Shenzhen Industrial Innovation Center for Engineering Biology.
The SynBio Challenges aim to provide a platform for students to engage in exchange and competition within the synthetic biology ...
Cruciferous vegetables, including broccoli, cabbage, kale, and cauliflower have been found to lower blood pressure, in comparison to root and squash vegetables, in middle-aged and older Australian adults with elevated blood pressure.
In a randomised, controlled, crossover trial, researchers from Edith Cowan University (ECU) found that consuming four serves a day of cruciferous vegetables resulted in a significant reduction in blood pressure, compared with four serves a day of root and squash vegetables including carrot, potato, sweet ...
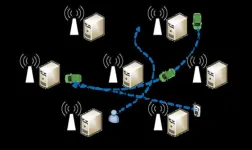
Dynamic service migration is a key technology in Mobile Edge Computing(MEC). In a multi-user service migration scenario, the states of all users are combined into a global state, which leads to the instability of the system and ignores the influence of multiple users. It is more and more challenging to design an effective migration strategy to balance migration costs and latency in a multi-user distributed environment.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Degan ZHANG published their new research on 15 August 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
Considering ...
Scientists at Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah (the U), the National Cancer Institute-designated cancer center for the Mountain West, have made a significant breakthrough in predicting the prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), a particularly aggressive disease. Their research, published in JCO Precision Oncology as part of the TOWARDS study, has led to the development of a new mechanism that accurately forecasts the aggressiveness of TNBC. This advancement could revolutionize the way doctors treat TNBC, allowing them to identify higher-risk patients and tailor precise treatments.
Currently, TNBC lacks reliable methods to predict recurrence after ...
SEQUIM, Wash.—Officials gathered at the Sequim campus of the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory today to dedicate DOE’s first hybrid-electric research vessel, RV Resilience.
The event marks the start of a new era of marine energy research at PNNL-Sequim, part of DOE’s Office of Science national laboratory system and Resilience’s new home port. Speakers at the dedication included U.S. Sen. Maria Cantwell, U.S. Rep. Derek Kilmer, Washington State Rep. Steve Tharinger and representatives from DOE and PNNL.
“DOE is focused on ...
ROCHESTER, Minn. — About 8 to 10 million Americans over age 40 have an overabundance of cloned white blood cells, or lymphocytes, that hamper their immune systems. Although many who have this condition — called monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis (MBL) — do not experience any symptoms, a new study shows they may have an elevated risk for several health complications, including melanoma, a form of skin cancer. The findings, by Mayo Clinic researchers, are published in a new paper in the Journal ...