Hijacking the command center of the cell: nuclear parasites in deep-sea mussels
Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology reveal how a bacterial parasite thrives inside the nuclei of deep-sea mussels
2024-09-06
(Press-News.org)
Most animals live in intimate relationships with bacteria. Some of these bacteria live inside the cells of their hosts, but only very few are able to live inside cell organelles (structures inside the cell, like organs in the body). One group of bacteria have figured out how to colonize the nuclei of their hosts, a remarkable feat given that the nucleus is the control center of the cell.
To date, nothing is known about the molecular and cellular processes that these intranuclear bacteria use to infect and reproduce in animal hosts. A group of scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology in Bremen, Germany, now presents the first in-depth analysis of an intranuclear parasite of animals in a study published in Nature Microbiology.
How to massively reproduce within a cell without killing it
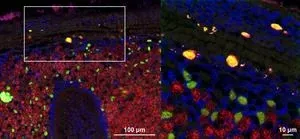
This intranuclear parasite, Candidatus Endonucleobacter, infects the nuclei of deep-sea mussels from hydrothermal vents and cold seeps around the world. A single bacterial cell penetrates into the mussels' nucleus and then reproduces to over 80,000 cells, causing the nucleus to swell to 50 times its original size. “We wanted to understand how the bacterium infects and reproduces inside nuclei, and in particular how these bacteria acquire the nutrients they need for their massive replication, yet keep their host cells from dying,“ says Niko Leisch, co-senior author together with Nicole Dubilier from the Symbiosis Department at the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology.
Using a suite of molecular and imaging methods, the scientists revealed that Ca. Endonucleobacter lives on sugars, lipids and other cell components from its host. It does not digest its host nucleic acids, like many other intranuclear bacteria. This feeding strategy ensures that the host cell functions long enough to provide Ca. Endonucleobacter with the nutrients it needs to reproduce to such massive numbers.
Arms race for the control of the cell
A common response of animal cells to infection is apoptosis – a suicide program that cells initiate when they are damaged or infected by bacteria or viruses. “Interestingly, these bacteria have come up with a sophisticated strategy to keep their host cells from killing themselves,” says first author Miguel Ángel González Porras. “They produce proteins that suppress apoptosis called inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs).” An arms race for the control of cell death then ensues: As the bacteria produce more and more IAPs, the host cell ramps up its production of proteins that induce apoptosis. Eventually, after the parasite has had enough time to multiply in masses, the host cell ruptures, releasing the bacteria and allowing them to infect new host cells.
Nicole Dubilier adds: “The discovery of IAPs in Ca. Endonucleobacter was one of the most surprising results of our study, because these proteins are only known from animals and a few viruses, but have never been found in bacteria.” The authors' analyses of the evolutionary relationships of the IAPs revealed that the parasite likely acquired these genes from its host through horizontal gene transfer (HGT). While HGT from bacteria to eukaryotes is well known, only very few examples of HGT in the opposite direction – as the authors now found – are known.
Implications from evolution to medicine
“Our discovery expands our understanding of host-microbe interactions and highlights the complex strategies parasites have evolved to thrive in their hosts”, explains Nicole Dubilier. These findings could have broader implications for studying parasitic infections and immune evasion strategies in other organisms. “Our research sheds light on an overlooked mechanism of genetic exchange — HGT from eukaryotes to bacteria — potentially influencing how we understand microbial evolution and pathogenesis. Moreover, our study offers insights into apoptosis regulation, which is relevant to cancer research and cell biology,” Niko Leisch concludes.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-06
Thermogenesis is a process by which organisms generate internal heat. Although it is usually associated with animals, some plants have also developed this ability. This metabolic process allows certain parts of the plant, such as flowers and inflorescences, to raise their temperature above that of the surrounding environment. Today, these plants, which include cycads and some angiosperms (flowering plants), rely on insects for pollination. The heat they generate helps volatilize and disperse floral fragrances and other chemical compounds that attract insects such as beetles, flies, and ...
2024-09-06
They’re tiny drug-delivery systems 1000 times smaller than a human hair, but while nanomedicines have long been hailed as the future for treating debilitating and life-threatening diseases, their journey from lab to patient has many challenges.
Now, new findings from a global team of expert scientists in academia and industry has generated world-first research quality standards that will help slash costs and reduce the time it takes to develop advanced nanomedicine treatments and make them available for patients.
Published in Nature Nanotechnology today, and led by the University of South Australia’s Dr Paul Joyce and the University ...
2024-09-06
If this galaxy is typical, then the study, published today in Nature Astronomy, indicates that our galaxy is already interacting with its closest neighbour, Andromeda.
Where does a galaxy end and deep space begin? It seems like a simple question until you look more closely at the gas that surrounds galaxies, known as the circumgalactic medium.
The halo of gas surrounding the stellar disc accounts for about 70% of the mass of the galaxy – excluding dark matter – but until now has remained something of a mystery. In the past we have only been able to observe the gas by measuring the light from a background object, ...
2024-09-06
Dark matter is the invisible force holding the universe together – or so we think. It makes up around 85% of all matter and around 27% of the universe’s contents, but since we can’t see it directly, we have to study its gravitational effects on galaxies and other cosmic structures. Despite decades of research, the true nature of dark matter remains one of science’s most elusive questions.
According to a leading theory, dark matter might be a type of particle that barely ...
2024-09-06
A widely used disinfectant worldwide, chloroxylenol, has been associated with eco-toxicological threats in water environments due to its relatively high chemical stability and massive consumption. Researchers at the School of Engineering of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have discovered a promising alternative known as 2,6-dichlorobenzoquinone (2,6-DCQ), which works more effectively in combating certain common bacteria, fungi and viruses, and can be rapidly degraded and detoxified in receiving waters.
This groundbreaking study is led by Prof. ZHANG Xiangru from HKUST's ...
2024-09-06
In some places around the globe, the lights never go off. Streetlights, roadway lighting, and illuminated signs can deter crime, make roads safer, and enhance landscaping. Undisrupted light, however, comes with ecological, behavioral, and health consequences.
In the US, some states have legislation in place to reduce light pollution; however, levels of light at night remain high in many parts of the country. Now, researchers there have investigated correlations between outside nightly light pollution and Alzheimer's disease (AD).
“We show that in the US there is a positive ...
2024-09-06
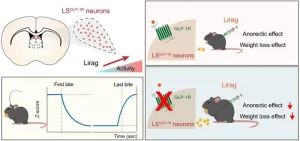
A research group led by Prof. ZHU Yingjie from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), has revealed the essential role of lateral septum (LS) neurons in mediating anorectic and weight-lowering effects of the anti-obesity drug— liraglutide in mice.
The study was published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation on Sep. 03.
Obesity is now among the top ten chronic diseases worldwide, causing a range of health issues and increasing the medical burden. Anti-obesity medications have shown greater efficacy than lifestyle changes and diet, with lower risks and fewer side effects ...
2024-09-06
From August 7 to 10, the Third SynBio Challenges were held at the Guangming Tianan Cloud Park International Conference Center in Shenzhen, China.
The event was co-organized by Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Chinese Society of Biotechnology, Shenzhen University of Advanced Technology (SUAT), Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology (iSynBio), Shenzhen Synthetic Biology Association, and the Shenzhen Industrial Innovation Center for Engineering Biology.
The SynBio Challenges aim to provide a platform for students to engage in exchange and competition within the synthetic biology ...
2024-09-06
Cruciferous vegetables, including broccoli, cabbage, kale, and cauliflower have been found to lower blood pressure, in comparison to root and squash vegetables, in middle-aged and older Australian adults with elevated blood pressure.
In a randomised, controlled, crossover trial, researchers from Edith Cowan University (ECU) found that consuming four serves a day of cruciferous vegetables resulted in a significant reduction in blood pressure, compared with four serves a day of root and squash vegetables including carrot, potato, sweet ...
2024-09-06
Dynamic service migration is a key technology in Mobile Edge Computing(MEC). In a multi-user service migration scenario, the states of all users are combined into a global state, which leads to the instability of the system and ignores the influence of multiple users. It is more and more challenging to design an effective migration strategy to balance migration costs and latency in a multi-user distributed environment.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Degan ZHANG published their new research on 15 August 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
Considering ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Hijacking the command center of the cell: nuclear parasites in deep-sea mussels
Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology reveal how a bacterial parasite thrives inside the nuclei of deep-sea mussels