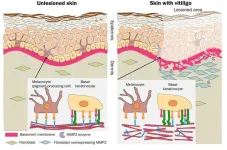
Loss of skin’s pigment-producing cells could be related to basement membrane disruption
Suppression of an enzyme might allow melanocytes to recover
2024-09-09
(Press-News.org)
Skin pigmentation disorders affect people across the world. One of them, vitiligo, is said to have a worldwide incidence of 1-2%. What causes the loss of pigmentation in vitiligo has long been unclear, but an Osaka Metropolitan University-led team has uncovered clues to the mechanism behind the disorder.
In findings published in The Journal of Pathology, Graduate School of Medicine Specially Appointed Associate Professor Lingli Yang, the corresponding author, and researchers including Specially Appointed Professor Ichiro Katayama found that disruptions to the basement membrane zone between the epidermis and dermis could be making it harder for pigment-producing cells to adhere to the affected zone.
They also discovered an overexpression of an enzyme in vitiligo-affected skin. Too much of this enzyme, matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2), might be causing the disturbance to the basement membrane.
An experiment using model mice with vitiligo-like depigmentation showed recovery of pigment-producing cells when MMP2 was suppressed.
“The results of this study potentially provide a new method for the treatment of vitiligo,” Professor Yang suggested. “In particular, by suppressing MMP2, the hope is that pigment-producing cells will return to the skin.”
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-09
Solving the problem of error is essential for the practical application of quantum computing technologies that surpass the performance of digital computers. Information input into a qubit, the smallest unit of quantum computation, is quickly lost and error-prone. No matter how much we mitigate errors and improve the accuracy of qubit control, as the system size and computation scale increase, errors accumulate and algorithms become impossible to perform. Quantum error correction is a way to solve this problem. As the race for global supremacy in quantum technology intensifies, most major companies and research groups leading the development of quantum ...
2024-09-09
Humans will build Artificial Intelligence (AI) which surpasses our own capabilities once we crack the ‘neural code’, says an AI technology analyst.
Eitan Michael Azoff, a specialist in AI analysis, argues that humans are set to engineer superior intelligence with greater capacity and speed than our own brains.
What will unlock this leap in capability is understanding the ‘neural code’, he explains. That’s how the human brain encodes sensory information, and how it ...
2024-09-09
Targeting vaccination programs for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) to older adults with underlying health conditions is a cost-effective way to reduce disease, according to a new modelling study https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240452 in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
RSV infections cause major illness, especially in infants and older adults, and rates of infection increase with age. There are now vaccines available to prevent disease caused by RSV in adults, and vaccination campaigns may reduce the incidence in older adults and associated ...
2024-09-09
About The Study: The findings of this cohort study showed a significant recent downward trend in both melanoma incidence and melanoma mortality in the age group 30 to 49 years in Sweden. The reasons for these declines are unclear but may include UV protection, public health campaigns, changing population demographics, and the introduction of effective melanoma treatment. None of these possibilities were evaluated; further study is needed.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hildur Helgadottir, MD, PhD, email hildur.helgadottir@sll.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
2024-09-09
The risk of skin cancer, malignant melanoma, now appears to be decreasing in Sweden - at least in those under 50, according to a new study.
“We can see a trend break in young adults around 2015 where the incidence curves are falling,” says first author Hildur Helgadottir, senior consultant and associate professor of oncology at the Department of Oncology-Pathology, Karolinska Institutet.
She and her research colleagues have analyzed data from the Swedish Melanoma Registry and followed melanoma incidence and mortality for different age segments over time. This means that they have compared individuals in a certain age range at one ...
2024-09-09
The chatbot ChatGPT performed better than trainee doctors in assessing complex cases of respiratory disease in areas such as cystic fibrosis, asthma and chest infections in a study presented at the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Congress in Vienna, Austria [1].
The study also showed that Google’s chatbot Bard performed better than trainees in some aspects and Microsoft’s Bing chatbot performed as well as trainees.
The research suggests that these large language models (LLMs) could be used to support trainee doctors, nurses and general practitioners to triage patients more quickly and ease pressure on health services.
The ...
2024-09-09
Night owls have a higher BMI, larger waists, more hidden body fat and are almost 50% more likely to develop type 2 diabetes (T2D) than those who go to bed earlier, new research to be presented at the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Madrid, Spain (9-13 September), has found.
Lead researcher Dr Jeroen van der Velde, of Leiden University Medical Centre, Leiden, Netherlands, says: “Previous studies have indicated that a late chronotype – preferring to go to bed late and wake up later – is associated with an unhealthy lifestyle. Late chronotypes are ...
2024-09-09
Altitude changes during commercial flights may affect the blood glucose levels of people with type 1 diabetes who are treated with insulin pump therapy, according to new research to be presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of The European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), Madrid (9-13 Sept).
“We investigated the effect atmospheric pressure changes during flight can have on insulin pumps following concerns that glucose levels may drop below the normal ranges during or immediately after flights,” explained lead author Dr Ka Siu Fan from the Royal Surry County Hospital and University ...
2024-09-09
New research being presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Madrid, Spain (9-13 September), shows that eating fruit, oats and rye in childhood is associated with a higher risk of developing type 1 diabetes (T1D). Eating berries, however, is linked to lower odds of developing the condition.
T1D is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing islet cells in the pancreas. This prevents the body from producing enough of the hormone insulin to properly regulate blood sugar levels.
What triggers the immune system’s attack is unknown but is thought to involve a combination ...
2024-09-09
Patients who are being treated with systemic glucocorticoids are more than twice as likely to develop diabetes as those not receiving the treatment, the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Madrid, Spain (9-13 September) will hear.
Glucocorticoids (sometimes known as steroids) fight inflammation and are used to treat a wide range of inflammatory and autoimmune conditions, including asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, cancers and other medical problems.
While they can be very effective in decreasing inflammation, glucocorticoids have many adverse effects including ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Loss of skin’s pigment-producing cells could be related to basement membrane disruption
Suppression of an enzyme might allow melanocytes to recover