(Press-News.org) Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) researchers uncover the genetic link in patients with polycystic kidney disease lacking family history
Tokyo, Japan – Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an intractable disorder that causes fluid-filled cysts to grow in the kidneys. It is typically seen in adults. As one of the most prevalent hereditary kidney diseases, the autosomal dominant form of PKD is usually caused by mutations in the PKD1 and PKD2 genes. However, one out of ten patients with this condition typically exhibit no family history of the disease and lack mutations in these well-known genes. This raises an important question about the other genetic factors that may be contributing to PKD in these cases.
In a study published online on 16 July 2024 in Kidney International Reports, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) addressed a key gap in understanding PKD. They performed a comprehensive genetic analysis of patients with PKD focusing exclusively on those without a family history of polycystic kidneys.
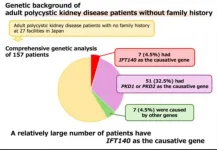
A total of 157 adult patients were recruited in the study from 2014 to 2023, coming from 27 Japanese institutions. These patients underwent genetic testing using next-generation sequencing, covering up to 92 genes depending on the panel used for the assay. These genes were all associated with inherited kidney cystic diseases.
The results pinpointed a potential cause for PKD in a part of the cohort. “Our comprehensive genetic analysis revealed that seven patients (4.5%) had mutations in the IFT140 gene, a recently identified gene associated with PKD,” says Dr. Eisei Sohara from TMDU, while discussing the results. This was in stark contrast to previous findings on IFT40. “The proportion of monoallelic loss-of-function IFT140 variants in this cohort was higher than that in previously reported cohorts with polycystic kidneys who had a positive family history,” he adds.
To shed further light on this issue, the researchers analyzed various relevant clinical characteristics of the patients. Interestingly, the kidneys of patients with mutations in the ITF140 gene were usually in a better state than those with PKD1 in terms of kidney function and cyst size. “Because the phenotype of polycystic kidneys caused by the IFT140 gene is mild, parental kidney disease may be overlooked. Therefore, patients without a positive family history are more likely to carry pathogenic variants in IFT140,” highlights Dr. Takayasu Mori from TMDU. Explaining further, he says, “Patients with IFT140-related polycystic kidneys are also likely to be underdiagnosed because of relatively high glomerular filtration rate, smaller kidney volume, and atypical kidney cysts.”
Overall, the results of this study help paint a clearer picture of the genetic landscape surrounding autosomal dominant PKD, which affects over 30,000 people in Japan alone. “Our findings may impact clinical practice, including diagnosis, drug therapy selection, and genetic counseling for adult PKD patients without a family history,” concludes Dr. Takuya Fujimaru from TMDU.
In summary, this breakthrough research could revolutionize diagnostics and treatment, offering hope for significantly improved outcomes. With continued innovation, the promise of enhanced patient care for patients with PKD could soon become a reality.
###
The article, “Importance of IFT140 in Patients with Polycystic Kidney Disease Without a Family History,” was published in Kidney International Reports at DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.06.021
END
Genetic analysis sheds light on the role of IFT140 in polycystic kidney disease
2024-09-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists use AI to detect chronic high blood pressure in people’s voice recordings
2024-09-10
NEW YORK/TORONTO – September 10, 2024 – Researchers at Klick Labs unveiled a cutting-edge, non-invasive technique that can predict chronic high blood pressure (hypertension) with a high degree of accuracy using just a person's voice. Just published in the peer-reviewed journal IEEE Access, the findings hold tremendous potential for advancing early detection of chronic high blood pressure and showcase yet another novel way to harness vocal biomarkers for better health outcomes.
The ...
NIH Kids First Program announces the release of three new pediatric research datasets exploring childhood rare disease
2024-09-10
WHO: The Gabriella Miller Kids First Pediatric Research Program (Kids First), an initiative of the National Institutes of Health (NIH)
WHAT: Kids First announces the release of three comprehensive new pediatric research datasets exploring childhood cancers and congenital disorders. New publicly available datasets include:
CHILDHOOD CANCERS
Gabriella Miller Kids First (GMKF) Pediatric Research Program in Susceptibility to Ewing Sarcoma Based on Germline Risk and Familial History of Cancer.
Principal Investigators: Joshua D. Schiffman, MD. Huntsman Cancer Institute, ...
Pressure sensing by muscles is a promising new target for treatments
2024-09-10
A new study from Umeå University, Sweden, shows that the body's muscles sense mechanical pressure. This new discovery has important implications for movement neuroscience and may improve the design of training and rehabilitation to relieve stiff muscles.
"The results provide an important piece of the puzzle in understanding what information our nervous system receives from muscles," says Michael Dimitriou, associate professor at the Department of Medical and Translational Biology, ...
Women with asthma are more likely to miscarry and need fertility treatment
2024-09-10
Women who are being treated for asthma are more likely to miscarry and need fertility treatment to get pregnant, according to a large study presented at the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Congress in Vienna, Austria [1]. However, the study also suggests that most women with asthma are able to have babies.
The study was presented by Dr Anne Vejen Hansen from the department of respiratory medicine at Copenhagen University Hospital, Denmark.
She said: “Asthma is common in women of reproductive age. Previous ...
MD Anderson Research Highlights Special Edition: ESMO 2024
2024-09-10
ABSTRACTS: 510MO, 618MO, 1821MO, 71MO, 995MO
BARCELONA, Spain ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights provides a glimpse into recent basic, translational and clinical cancer research from MD Anderson experts. This special edition features upcoming oral presentations by MD Anderson researchers at the 2024 European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress focused on clinical advances across a variety of cancer types.
In addition to the studies summarized below, forthcoming press releases will feature the following oral presentations:
Initial results from a first-in-human ...
Appalachian State University chooses Figshare as its new institutional repository platform
2024-09-10
Figshare, a leading provider of institutional repository infrastructure that supports open research, is pleased to announce that Appalachian State University has chosen Figshare as its new institutional repository platform to share, showcase and manage its research outputs.
Appalachian State University (App State) – part of the University of North Carolina System – chose Figshare as its new repository platform to replace the NC DOCKS consortial repository, which was created in 2007 and is slated to shut down at the end of 2024. The team at App State wanted to ...
Drug treatment shows promise for dangerous snoring condition, obstructive sleep apnea
2024-09-10
Patients taking sulthiame, a drug currently in use for epilepsy, experienced a reduction in their symptoms of obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA), according to results of a clinical trial presented at the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Congress in Vienna, Austria [1].
Patients with OSA often snore loudly, their breathing starts and stops during the night, and they may wake up several times. Not only does this cause tiredness, but it can also increase the risk of high blood pressure, stroke, heart disease and type 2 diabetes. OSA is very common, but many people do not ...
Experimental blood test predicts risk for developing COPD, other severe respiratory diseases
2024-09-10
A scientific team supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has created a preclinical blood test to identify adults most likely to develop severe respiratory conditions, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The blood test analyzes 32 proteins that scientists determined accurately predicted an adult with an increased likelihood for requiring medical care for or dying from severe respiratory illness. The risk score was based on lung health data collected from nearly 2,500 U.S. adults over a 30-year period. The findings were published ...
Girls may start puberty early due to chemical exposure
2024-09-10
WASHINGTON—Girls exposed to certain endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) may be more likely to start puberty early, according to new research published in Endocrinology, the flagship basic science journal of the Endocrine Society. EDCs mimic, block or interfere with hormones in the body's endocrine system.
There has been an alarming trend toward early puberty in girls, suggesting the influence of chemicals in our environment. Early puberty is associated with an increased risk of psychosocial problems, obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and breast cancer.
“We conducted a comprehensive screen of 10,000 environmental compounds ...
Innovative delivery, access to care necessary to increase health equity for rural patients with heart disease
2024-09-10
The American College of Cardiology’s Quality Summit 2024 will feature several poster presentations regarding rural health delivery and access to care that offer insights into innovative strategies to increase health equity for all heart disease patients. Research examines door-in-door-out and door-to-balloon (D2B) times for heart attack patients at critical access hospitals, improving door-to-thrombolytics for heart attack patients at rural hospitals, remote cardiac rehabilitation to increase access, and improving communications technology for EMS with STEMI patients in rural areas.
“Rurality creates unique challenges in delivering high quality cardiovascular ...