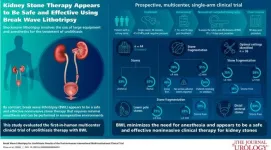
(Press-News.org) September 11, 2024 — A noninvasive ultrasound technology called Break Wave™ lithotripsy (BWL) offers a safe and effective new option for treatment of urinary stones, reports a clinical trial in the October issue of The Journal of Urology®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"In this initial experience, BWL provided a high treatment success rate, using a portable technology that can be used in a range of settings, without the need for anesthesia" comments lead author Ben H. Chew, MD, MSc, of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada.
Alternative approach to noninvasive treatment of urinary stones
Urinary stones are a common clinical problem and a major reason for emergency department (ED) visits. Treatment options include surgery (ureteroscopy) or, for some patients, extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy (SWL), which uses high-pressure ultrasound waves to fragment stones so they can pass through the urinary system. Although SWL is noninvasive and effective, it has some disadvantages: the equipment is large and expensive, and the procedure usually requires some kind of anesthesia and a surgical suite.
Rather than shockwaves, BWL uses low-pressure ultrasound waves to target and fragment urinary stones. Break Wave lithotripsy is delivered using a smaller and less costly mobile unit, allowing treatment to be performed in a range of locations outside of an operating room. In 2022, the BWL system received Breakthrough Device Designation from the US Food and Drug Administration.
Dr. Chew and colleagues report the "first-in-human" clinical trial of BWL. The study included 44 patients at five hospitals across North America with stones located in the kidney (57% of patients) or ureter (43%). All patients chose to undergo BWL after discussion of other options (ureteroscopy or conventional SWL). Stones were treated for a total of 30 minutes under real-time ultrasound targeting.
BWL may lower costs and provide more timely care for urinary stones
Break Wave lithotripsy was effective, with evidence of fragmentation in 88% of patients. After treatment, most patients had fragments small enough to pass through the urinary system: four millimeters or less in 70% of patients and two millimeters or less in 51%. On follow-up CT scans, 49% of patients were completely stone-free.
After the first several cases, 36 patients were treated with "optimized" ultrasound dose settings, achieving a fragmentation rate of 92%. Seventy-five percent of patients had fragments measuring four millimeters or less, while 58% were completely stone-free. As expected, success rates were higher for patients with stones located in the distal ureter, compared to stones in the lower pole of the kidney. Complications were generally mild, with no serious adverse events.
Through 90 days' follow-up, only seven percent of patients required further treatment for the target stone. In most patients, BWL could be performed without anesthesia – either with no medications or only a mild pain reliever. In four patients with severe, acute pain, BWL was successfully carried out in the ED.
In this initial clinical study, BWL appears to be a safe and effective new option for treatment of urinary stones. Treatment can be conveniently performed in the ED, medical office, or other settings, without the need for anesthesia or sedation. Dr. Chew comments: "The BWL technique – together with other developing technologies such as ultrasonic propulsion – has the potential to provide effective, noninvasive treatment for patients with kidney and ureteral stones, reducing resource burdens and enabling more timely care."
Read Article: Break Wave Lithotripsy for Urolithiasis: Results of the First-in-Human International Multi-Institutional Clinical Trial
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers and students in effective decision-making and outcomes across healthcare. We support clinical effectiveness, learning and research, clinical surveillance and compliance, as well as data solutions. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health.
###
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (EURONEXT: WKL) is a global leader in information, software solutions and services for professionals in healthcare; tax and accounting; financial and corporate compliance; legal and regulatory; corporate performance and ESG. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2023 annual revenues of €5.6 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 21,400 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
For more information, visit www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on LinkedIn, Facebook, YouTube and Instagram.
END
New noninvasive technique provides effective treatment for urinary stones
'Break Wave' lithotripsy has high success rate in first in-human trial, reports Journal of Urology
2024-09-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers uncover new infection-fighting molecules through “molecular de-extinction”
2024-09-11
A new study led by Cesar de la Fuente, PhD, Presidential Assistant Professor of Psychiatry, Microbiology, Chemistry, Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and Bioengineering at the University of Pennsylvania, has uncovered sequences for infection-fighting molecules in the genomic data of extinct species. This most recent study in the emerging field of “molecular de-extinction”, pioneered by Prof. de la Fuente, offers the potential to develop new antimicrobial treatments in the fight against rising antibiotic resistance.
The study, published in Cell Reports Physical Science, analyzed genomic data from the extinct moa, a flightless bird from New Zealand, ...
Keeping mold out of future space stations
2024-09-11
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Mold can survive the harshest of environments, so to stop harmful spores from growing on future space stations, a new study suggests a novel way to prevent its spread.
Researchers created a predictive approach for modeling unintended microbial growth in critical spaces and applied it to life on the International Space Station.
An analysis of dust samples obtained from the space station found that repeated elevated humidity exposures for even a short time can lead to rapid microbial growth and composition changes in dust that make it easier for microbes, ...
"It feels like I'm moving my own hand". A research team from the Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna in Pisa has developed the prosthesis of the future, the first in the world with magnetic control
2024-09-11
Pisa, 11 september. It is the first magnetically controlled prosthetic hand, that allows amputees to reproduce all movements simply by thinking and to control the force applied when grasping fragile objects. No wires, no electrical connection, only magnets and muscles to control the movements of the fingers and enable everyday activities such as opening a jar, using a screwdriver, picking up a coin.
A research team from the BioRobotics Institute of the Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna in Pisa, coordinated by Prof. Christian Cipriani, has ...
Self-medicating gorillas and traditional healers provide clues for new drug discovery
2024-09-11
Four plants consumed by wild gorillas in Gabon and used by local communities in traditional medicine show antibacterial and antioxidant properties, find Leresche Even Doneilly Oyaba Yinda from the Interdisciplinary Medical Research Center of Franceville in Gabon and colleagues in a new study publishing September 11 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
Wild great apes often consume medicinal plants that can treat their ailments. The same plants are often used by local people in traditional medicine.
To investigate, researchers observed the behavior of western lowland gorillas (Gorilla gorilla ...
Trust in police declined among Black Chicago residents after Jacob Blake shooting
2024-09-11
Survey data collected from Chicago, Illinois at the time of the 2020 police shooting of Jacob Blake in nearby Wisconsin shows that trust in police plummeted among Black residents after the shooting. Jonathan Ben-Menachem and Gerard Torrats-Espinosa of Columbia University in New York, U.S., present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on September 11, 2024.
For young minority men in the U.S., police violence has become a leading cause of death. Prior research has explored how police violence and misconduct might reduce trust in police, but most studies have been limited in ...
Quitting smoking reduces risk of atrial fibrillation
2024-09-11
Quitting cigarettes can significantly lower a person’s risk of atrial fibrillation (AFib) compared to those who continue to smoke, according to a study published today in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology. The findings show that the benefits of quitting start right away, suggesting that it is possible to reverse the risk of negative health outcomes.
“The findings provide a compelling new reason to show current smokers that it’s not too late to quit and that having smoked in the past doesn’t ...
How many people have A-Fib? Three times more than we thought
2024-09-11
Atrial fibrillation, a rapid, irregular heart beat that can lead to stroke or sudden death, is three times more common than previously thought, affecting nearly 5% of the population, or 10.5 million U.S. adults, according to new estimates from UC San Francisco.
A-Fib, as the condition is commonly known, has been on the rise for at least the past decade, driven by the aging of the population, along with increasing rates of hypertension, diabetes and obesity. Earlier projections had estimated that 3.3 million U.S. adults ...
Groundbreaking achievement: NSF Daniel K. Inouye solar telescope produces its first magnetic field maps of the sun’s corona
2024-09-11
Summary: The U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope, the world’s most powerful solar telescope, operated by the NSF National Solar Observatory (NSO), achieved a major breakthrough in solar physics by successfully producing its first detailed maps of the Sun’s coronal magnetic fields. This milestone, led by NSO Associate Astronomer Dr. Tom Schad, was recently published in Science Advances, and promises to enhance our understanding of the Sun's atmosphere and how its changing conditions lead to impacts on Earth's technology-dependent society. The corona, or the Sun’s ...
Landmark study reveals how antibiotics contribute to inflammatory bowel disease risk
2024-09-11
In a landmark study published today in Science Advances, Dr. Shai Bel and his research team at the Azrieli Faculty of Medicine of Bar-Ilan University have uncovered crucial insights into how antibiotic use increases the risk of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
The study demonstrates that antibiotics interfere with the protective mucus layer in the intestine, a discovery that could reshape our understanding of antibiotic effects and IBD development.
IBD, which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, affects approximately 1% of the global population. This debilitating condition is ...
Neuromorphic platform presents huge leap forward in computing efficiency
2024-09-11
In a landmark advancement, researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have developed a brain-inspired analog computing platform capable of storing and processing data in an astonishing 16,500 conductance states within a molecular film. Published today in the journal Nature, this breakthrough represents a huge step forward over traditional digital computers in which data storage and processing are limited to just two states.
Such a platform could potentially bring complex AI tasks, like training Large Language Models (LLMs), to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] New noninvasive technique provides effective treatment for urinary stones'Break Wave' lithotripsy has high success rate in first in-human trial, reports Journal of Urology