(Press-News.org) Outdoor light at night could be a significant risk factor in Alzheimer’s disease, according to new research from Rush.
While light pollution is associated with increased risk of some disorders and diseases, this is the first time it had been associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
The study was conducted at Rush University System for Health and published in Frontiers in Neuroscience.
“Our research shows that there is an association in the U.S. between Alzheimer’s disease prevalence and exposure to light at night, particularly in those under the age of 65,” said lead investigator, Robin Voigt-Zuwala, PhD, an associate professor at Rush. “Nightly light pollution — a modifiable environmental factor — may influence risk for Alzheimer’s.”
High U.S. light levels
While legislation in some states aims to reduce light pollution, levels of nighttime light remain high in many parts of the country.
In studying light pollution maps, researchers looked at the lower 48 states and incorporated medical data associated with Alzheimer’s disease risk factors and divided the groups by light intensity. In the five groups, they found that light intensity was correlated with Alzheimer’s disease prevalence even when some well-established disease factors were not.
While the cause is unknown, higher nighttime light intensity was associated with a greater Alzheimer’s disease prevalence than any other risk factor examined in the study for those under the age of 65, suggesting that younger people may be more sensitive to the effects of light exposure at night.
“Certain genes can influence early-onset Alzheimer’s, and these same genes may cause increased vulnerability to the effects of nighttime light exposure,” Voigt-Zuwala explained. “Additionally, younger people are more likely to live in urban areas and have lifestyles that may increase exposure to light at night.”
Reducing light exposure
Exposure to light influences the body’s natural sleep-wake pattern, which is called a circadian rhythm. Exposure to light at night can disrupt a person’s circadian rhythm, which can promote inflammation and make a person less resilient and more prone to disease. Researchers did not examine light inside the home at night or how it might impact health.
Voigt-Zuwala said, “The good news is that simple changes can be made with minimal effort to reduce exposure to light at night — adding black out curtains or sleeping with an eye mask.”
The research results are limited to a subset of the population and further testing is needed to better understand the connection between evening outdoor light and Alzheimer’s disease.
END
Light pollution a new Alzheimer’s risk factor
Outdoor light exposure in the evening may be a risk factor for Alzheimer’s in people under age 65, Rush study finds
2024-09-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Clovis people used Great Lakes camp annually 13,000 years ago
2024-09-11
Graphics // Photos
The earliest humans to settle the Great Lakes region likely returned to a campsite in southwest Michigan for several years in a row, according to a University of Michigan study.
Until recently, there was no evidence that people from the Clovis period had settled the Great Lakes region. Clovis people appeared in North America about 13,000 years ago, during the geologic epoch called the Pleistocene. During the Pleistocene, sheets of glaciers covered much of the world, including Michigan, making the land inhospitable for human settlers. But a 2021 U-M study confirmed that Clovis people built ...
Can having a stroke change your sleep?
2024-09-11
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 11, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – People who have had a stroke may be more likely to sleep too much or too little compared to those without prior stroke, according to a study published in the September 11, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that stroke causes abnormal sleep; it only shows an association.
“Sleeping the right amount is considered essential for ideal brain and heart health,” said study author Sara Hassani, ...
Microscale robot folds into 3D shapes and crawls
2024-09-11
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University researchers have created microscale robots less than 1 millimeter in size that are printed as a 2D hexagonal “metasheet” but, with a jolt of electricity, morph into preprogrammed 3D shapes and crawl.
The robot’s versatility is due to a novel design based on kirigami, a cousin of origami, in which slices in the material enable it to fold, expand and locomote.
The team’s paper, “Electronically Configurable Microscopic Metasheet Robots,” published Sept. 11 in Nature Materials. The paper’s co-lead authors are postdoctoral ...
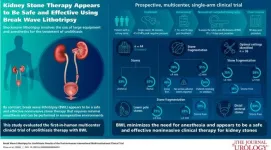
New noninvasive technique provides effective treatment for urinary stones
2024-09-11
September 11, 2024 — A noninvasive ultrasound technology called Break Wave™ lithotripsy (BWL) offers a safe and effective new option for treatment of urinary stones, reports a clinical trial in the October issue of The Journal of Urology®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"In this initial experience, BWL provided a high treatment success rate, using a portable technology that can be used in a range of settings, without the need for anesthesia" comments lead ...
Researchers uncover new infection-fighting molecules through “molecular de-extinction”
2024-09-11
A new study led by Cesar de la Fuente, PhD, Presidential Assistant Professor of Psychiatry, Microbiology, Chemistry, Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and Bioengineering at the University of Pennsylvania, has uncovered sequences for infection-fighting molecules in the genomic data of extinct species. This most recent study in the emerging field of “molecular de-extinction”, pioneered by Prof. de la Fuente, offers the potential to develop new antimicrobial treatments in the fight against rising antibiotic resistance.
The study, published in Cell Reports Physical Science, analyzed genomic data from the extinct moa, a flightless bird from New Zealand, ...
Keeping mold out of future space stations
2024-09-11
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Mold can survive the harshest of environments, so to stop harmful spores from growing on future space stations, a new study suggests a novel way to prevent its spread.
Researchers created a predictive approach for modeling unintended microbial growth in critical spaces and applied it to life on the International Space Station.
An analysis of dust samples obtained from the space station found that repeated elevated humidity exposures for even a short time can lead to rapid microbial growth and composition changes in dust that make it easier for microbes, ...
"It feels like I'm moving my own hand". A research team from the Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna in Pisa has developed the prosthesis of the future, the first in the world with magnetic control
2024-09-11
Pisa, 11 september. It is the first magnetically controlled prosthetic hand, that allows amputees to reproduce all movements simply by thinking and to control the force applied when grasping fragile objects. No wires, no electrical connection, only magnets and muscles to control the movements of the fingers and enable everyday activities such as opening a jar, using a screwdriver, picking up a coin.
A research team from the BioRobotics Institute of the Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna in Pisa, coordinated by Prof. Christian Cipriani, has ...
Self-medicating gorillas and traditional healers provide clues for new drug discovery
2024-09-11
Four plants consumed by wild gorillas in Gabon and used by local communities in traditional medicine show antibacterial and antioxidant properties, find Leresche Even Doneilly Oyaba Yinda from the Interdisciplinary Medical Research Center of Franceville in Gabon and colleagues in a new study publishing September 11 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
Wild great apes often consume medicinal plants that can treat their ailments. The same plants are often used by local people in traditional medicine.
To investigate, researchers observed the behavior of western lowland gorillas (Gorilla gorilla ...
Trust in police declined among Black Chicago residents after Jacob Blake shooting
2024-09-11
Survey data collected from Chicago, Illinois at the time of the 2020 police shooting of Jacob Blake in nearby Wisconsin shows that trust in police plummeted among Black residents after the shooting. Jonathan Ben-Menachem and Gerard Torrats-Espinosa of Columbia University in New York, U.S., present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on September 11, 2024.
For young minority men in the U.S., police violence has become a leading cause of death. Prior research has explored how police violence and misconduct might reduce trust in police, but most studies have been limited in ...
Quitting smoking reduces risk of atrial fibrillation
2024-09-11
Quitting cigarettes can significantly lower a person’s risk of atrial fibrillation (AFib) compared to those who continue to smoke, according to a study published today in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology. The findings show that the benefits of quitting start right away, suggesting that it is possible to reverse the risk of negative health outcomes.
“The findings provide a compelling new reason to show current smokers that it’s not too late to quit and that having smoked in the past doesn’t ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Light pollution a new Alzheimer’s risk factorOutdoor light exposure in the evening may be a risk factor for Alzheimer’s in people under age 65, Rush study finds