(Press-News.org) Prescribing rates for stimulants that treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) have increased significantly over the past decade, with some of the largest increases reported during the COVID-19 pandemic. A new study of adult emergency department admissions at Mass General Brigham, led by McLean Hospital researchers, found that individuals who are taking high doses of amphetamine (e.g. Adderall) face more than a five-fold increased risk for developing psychosis or mania. Findings were published September 12th in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Overall, individuals with past-month prescription amphetamine use had a greater likelihood of new-onset psychosis or mania than individuals without past-month use. The risk was highest in those taking 30 mg or more of dextroamphetamine (which corresponds to 40 mg of Adderall), according to the study.
Previous studies have linked stimulants to psychosis and mania risk; however, information had been lacking on whether dosing impacted risk.
“Stimulant medications don’t have an upper dose limit on their labels, and our results show that it is clear that dose is a factor in psychosis risk and should be a chief consideration when prescribing stimulants,” said lead study author Lauren Moran, MD, a pharmacoepidemiology researcher at McLean Hospital. “This is a rare but serious side effect that should be monitored by both patients and their doctors whenever these medications are prescribed.”
Moran said the study was born out of her past clinical observations as an inpatient psychiatrist. She and her McLean colleagues would regularly see patients coming in experiencing first episodes of psychosis, and their medical records would reveal they were prescribed high doses of stimulants by their doctors.
Researchers reviewed electronic health records of Mass General Brigham patient encounters between 2005 and 2019, focusing on adults aged 16 to 35, the typical age of onset for psychosis and schizophrenia. All patients were admitted to McLean Hospital following referrals from other hospitals in the Mass General Brigham healthcare system. The researchers identified 1,374 cases of individuals presenting with first-episode psychosis or mania, compared to 2,748 control patients with a psychiatric hospitalization for other conditions like depression or anxiety. They conducted a comparison analysis of stimulant use over the preceding month and accounted for other factors, including substance use, in order to isolate the effects of stimulants.
They found the attributable risk percentage among those exposed to any prescription amphetamine was nearly 63% and for high dose amphetamine was 81%. These findings suggest that among people who take prescription amphetamine, 81% of cases of psychosis or mania could have been eliminated if they were not on the high dose. While a significant dose-related risk increase was seen in patients taking high doses of amphetamine, no significant risk increase was seen with methylphenidate (Ritalin) use, which is consistent with previous research, including a 2019 study led by Moran.
While the study does not prove causality, the researchers note there is a plausible biological mechanism in neurobiological changes that include a release of higher levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine from amphetamines, that parallel dopaminergic changes observed in psychosis.
Limitations of the study include inconsistencies with how electronic health records are kept. Additionally, with the research taking place in a psychiatric hospital in the Boston area that sees many patients with psychosis, it may make these findings less generalizable to other parts of the country.
Moran said the findings need not create alarm but should lead to extra caution when these medications are prescribed, especially for those who have risk factors for psychosis and mania.
“There’s limited evidence that prescription amphetamines are more effective in high doses,” said Moran. “Physicians should consider other medications our study found to be less risky, especially if a patient is at high risk for psychosis or mania.”
Authorship: In addition to Moran, Mass General Brigham co-authors included Joseph P. Skinner, BA (BWH), Ann K. Shinn MD, MPH (McLean), Kathryn Nielsen (McLean), Vinod Rao, MD, PhD (MGH), Trevor Taylor, MD, MPH (MGH), Talia R. Cohen (McLean), Cemre Erkol, MD (McLean), Jaisal Merchant, MA (McLean), Christin A. Mujica, MA (McLean), Roy H. Perlis, MD, MSc, (MGH) and Dost Ongur, MD, PhD (McLean).
Funding: This work was funded by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), R01 MH122427.
Disclosures: Perlis received personal fees from Genomind, Burrage Capital, Psy Therapeutics Inc, Circular Genomics Inc, and Vault Health unrelated to the submitted work. Dr. Ongur received honorariums for scientific presentations to Neumora Inc. and Guggenheim LLC unrelated to the submitted work. Dr. Moran is employed by Sage Therapeutics (unrelated to this work and after study completed and submitted for publication). All other authors report no financial relationships with commercial interests.
Paper cited: Moran, LV et al. “Risk of Incident Psychosis and Mania with Prescription Amphetamines,” American Journal of Psychiatry. DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.20230329
###
About McLean
McLean Hospital has a continuous commitment to put people first in patient care, innovation and discovery, and shared knowledge related to mental health. It is consistently named the #1 freestanding psychiatric hospital in the United States by U.S. News & World Report, and is #1 in America for psychiatric care in 2023-24. McLean Hospital is the largest psychiatric affiliate of Harvard Medical School and a member of Mass General Brigham. To stay up to date on McLean, follow us on Facebook, YouTube, and LinkedIn.
END
With flu season just around the corner and COVID-19 cases on the rise, a new nationwide survey from The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center reveals hesitancy around vaccines this fall. The new data comes just as this year’s flu shot rolls out and following the FDA’s approval of an updated round of COVID-19 vaccines.
The national poll of 1,006 people found more than one-third (37%) have gotten vaccines in the past but do not plan to this year. The same percent of respondents said they don’t need any of the vaccines surveyed in the poll, including flu, COVID-19, pneumococcal and respiratory ...
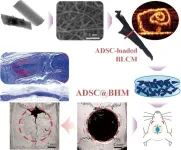
Scientists from Sun Yat-sen University's School of Biomedical Engineering have developed groundbreaking tubular scaffolds made from electrospun membranes, which significantly enhance bone regeneration in critical skull defects. These scaffolds, designed to mimic natural bone structures, create an ideal environment for adipose-derived stem cells (rADSCs) to thrive and accelerate healing. By integrating advanced materials like polycaprolactone, PLGA, and nano-hydroxyapatite, the researchers achieved remarkable results in both lab and animal studies, ...
Nobel laureate Pierre Agostini, winner of the 2023 prize in physics, will headline a special two-day event hosted by the University of Tokyo on Sept. 26-27. The keynote lecture by Agostini, renowned for this pioneering work in attosecond science, will be part of a larger symposium bringing together researchers from around the world to celebrate the university’s planned Attosecond Laser Facility (ALFA), and discuss the latest developments and future directions of attosecond science.
Have you taken a photo of a fast-moving animal or vehicle and noticed how blurry the subject can be? This is likely because the faster a moving subject is, the faster the camera’s shutter needs ...
Toronto, ON, September 11, 2024 — A single dose of the Modified vaccinia Ankara-Bavarian Nordic (MVA-BN) was 58% effective in protecting again mpox infection, according to a new study published in BMJ.
Researchers from ICES, Public Health Ontario, and the MAP Centre for Urban Health Solutions at St. Michael’s Hospital of Unity Health Toronto have conducted a target trial emulation to estimate the effectiveness of the mpox vaccine.
During the mpox outbreak in 2022, Ontario, Canada introduced the vaccine ...
One dose of modified vaccinia Ankara-Bavarian Nordic (MVA-BN) smallpox vaccine is moderately effective in preventing mpox infection and should be made available to communities at risk, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
With mpox infections rising again across the globe, the researchers say these findings “strengthen the evidence that MVA-BN is effective at preventing mpox infection and should be made available and accessible to communities at risk.”
No randomised clinical trials of vaccination against mpox have been conducted. Estimates of the effectiveness of a single dose of vaccination from observational studies range from ...
More than half of the experts on the UK government’s nutrition advisory panel have links to the food industry, reveals an investigation by The BMJ today.
At least 11 of the 17 members of the Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (SACN) have conflicts of interest with the likes of Nestle, sugar manufacturer Tate and Lyle, and the world’s largest ice cream producer, Unilever, reports freelance journalist Sophie Borland.
And at least six out of the 11 members of SACN’s Subgroup on Maternal and Child Nutrition have ties to food firms, including baby food manufacturers and formula milk brands.
SACN ...
Giving higher doses per fraction of radiation therapy over a shorter time after breast cancer surgery significantly reduces the risk of side effects and improves quality of life compared with a conventional schedule, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
Although survival and recurrence rates were similar, this approach, known as hypofractionation, is safer, more convenient for patients, and reduces costs for healthcare systems, and should be the preferred treatment option, say the researchers.
Conventional fractionation radiation therapy has been the standard of care for most patients with breast ...
Obesity treatments are being restricted by cash poor local services across England with many patients being denied specialist drugs, surgery and support, an investigation by The BMJ has found.
Patients in nearly half the country can’t get appointments with specialist teams for weight loss support and care, including treatment with drugs such as semaglutide. And in nearly one in five local health areas, patients don’t have access to a bariatric surgery service, reports Elisabeth Mahase.
The government estimates that obesity costs the NHS in England around £6.5bn a year and is the second biggest preventable cause ...
Laughter may be as effective as eye drops in improving symptoms of dry eye disease, finds a clinical trial from China published by The BMJ today
The researchers suggest that laughter exercise could be an initial treatment for relieving symptoms of dry eye disease.
Dry eye disease (DED) is a chronic condition estimated to affect around 360 million individuals worldwide. Common symptoms include uncomfortable, red, scratchy or irritated eyes.
Evidence suggests that laughter therapy alleviates depression, anxiety, stress, and chronic pain, while strengthening immune ...
Earth will only remain able to provide even a basic standard of living for everyone in the future if economic systems and technologies are dramatically transformed and critical resources are more fairly used, managed and shared, according to an international research team including scientists from The Australian National University (ANU).
The report, published in The Lancet Planetary Health, outlines how cities and businesses have the power to play a crucial role and become the “stewards” of critical Earth ...