(Press-News.org) CHICAGO (Sept 13, 2024)—Menopause is a natural life transition occurring when many women are at the “top of their game.” Unsupported menopause symptoms drive up employer healthcare costs and cause roughly $1.8 billion in missed workdays. To help employers retain these valued workers and build cultures of well-being, The Menopause Society launched Making Menopause Work™ based on new science-based Consensus Recommendations. The Recommendations are published online in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
“More employers—from large corporations to small organizations—are supporting workers during menopause,” Dr. Stephanie Faubion, medical director of The Menopause Society and director of the Mayo Clinic Center for Women’s Health, said today at The Menopause Society’s Annual Meeting in Chicago.
“But more menopause-supportive workplaces are urgently needed,” Faubion continued. “Women ages 50 and older are the fastest-growing demographic group, making essential contributions to society, families, communities, and the paid and unpaid workforces. This is a moment of tremendous opportunity.”
The Menopause Society builds on its 35-year, science-based track record with the creation of Making Menopause Work. The program—which includes a free Employer Guide, an assessment, planning tools, and other resources, with an employer designation program to come—incorporates recommendations based on new scientific consensus recommendations from a multidisciplinary panel of leading medical, legal, and human resource experts.
“Employers need to take menopause symptoms seriously and also know that they’re manageable and temporary,” said Jill K. Bigler, labor attorney at Epstein Becker Green and a member of the advisory panel for the Consensus Recommendations. “Making Menopause Work is a smart, strategic move for employers. It safeguards workers’ opportunities for leadership and financial security. It retains workers and productivity. And it builds a multigenerational workplace where midlife employees hold institutional knowledge, bring calm under stress, and make wise decisions.”
Understanding menopause and creating menopause-responsive workplaces
Menopause, the end of menstrual periods, usually occurs between ages 45 and 55; although perimenopause can start as early as age 35. Symptoms are different for each person. For some, periods become irregular and then stop. Others may experience hot flashes, difficulty sleeping, memory problems, mood disturbances, vaginal dryness, or weight gain.
The Society’s Consensus Recommendations cite a survey by the Society for Women’s Health Research showing that two out of five people had considered looking for or had found a new job because of menopause symptoms. Not only do employers risk losing talent and revenues when they ignore menopause, they also face greater costs for healthcare as well as the cost of replacing and training workers.
Creating a supportive workplace culture is the first step in turning these numbers around. The Employer Guide supports employers, managers, and supervisors to do this, including opening conversations for those who want it, understanding how to hear and support people’s needs, and recognizing menopause as a normal part of life for half the population.
From there, the Employer Guide helps employers update policies, benefits, and environments, including offering the following:
Health insurance plans that include adequate and affordable coverage for menopause-related care
Access to adequate bathrooms and flexible breaks to use them—vital for people with heavy or unpredictable bleeding
Improved ventilation and updated uniforms with breathable, flexible fabrics—a game changer for people experiencing hot flashes
Quiet work environments and flexible deadlines, which improve focus for people experiencing insomnia, anxiety, or brain fog
Peer support networks, employee resource groups and employee assistance programs, which can help people know they’re not going through menopause alone
Employers or employees interested in learning more about this important initiative should visit menopause.org/workplace.
The Menopause Society (formerly The North American Menopause Society) is the leading nonprofit organization dedicated to empowering health care professionals to improve the health of women during the menopause transition and beyond. Employers who support Making Menopause Work become part of a movement that includes more than 2,000 health care professionals who have earned The Menopause Society’s Certified Practitioner (MSCP) credential, along with tens of thousands of people who rely on The Menopause Guidebook, the most complete consumer menopause resource available.
END
The Menopause Society launches Making Menopause Work™ Initiative
Unique educational and designation initiative based on new science-based Consensus Recommendations to help employers retain workers and recoup $1.8 billion in lost workdays by supporting menopausal women in the workplace
2024-09-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Exploring ternary metal sulfides as electrocatalyst for carbon dioxide reduction reactions
2024-09-13
One of the most promising avenues for actively reducing CO2 levels in the atmosphere is recycling it into valuable chemicals via electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reactions. With a suitable electrocatalyst, this can be achieved under mild conditions and at a low energy cost. Many types of electrocatalysts are being actively investigated, but most suffer from either low electrocatalytic activity, poor selectivity, or low stability.
Metal sulfides might hold the huge potential solution to this puzzle. By combining ionic and covalent characteristics, this unique family of materials offers good catalytic activity and energy efficiency. The ternary metal system is expected to be a better ...
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide
2024-09-13
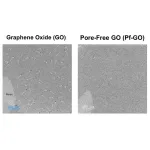
Kumamoto University’s research team, led by Assistant Professor Kazuto Hatakeyama and Professor Shintaro Ida of Institute of Industrial Nanomaterials, has announced a groundbreaking development in hydrogen ion barrier films using graphene oxide (GO) that lacks internal pores. This innovative approach promises significant advancements in protective coatings for various applications.
In their study, the research team successfully synthesized and developed a thin film from a new form of graphene oxide that does not contain pores. Traditionally, ...
Urbanization has impacted the population genetic structure of the Eurasian red squirrel in Japan within a short period of 30 years
2024-09-13
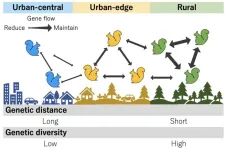
Since many kinds of wildlife have started living in urban environments, urban environments have been recognized as places of biodiversity conservation. What kind of factors facilitate or prohibit wildlife from living in urban environments? Understanding the population genetic structure of urban wildlife living would suggest the hint. In this study, we investigated the population genetic structure of Eurasian red squirrels living in urban to rural areas in Obihiro City, Hokkaido, Japan. As a result, we found that ...
Experimental mRNA cancer vaccine shows potential for advanced stage cancer patients in Phase 1 trial
2024-09-13
Interim data from the Phase I dose escalation part of the mRNA cancer immunotherapy (mRNA-4359), show promise in patients with advanced solid cancers.
The investigational mRNA cancer immunotherapy is targeted for patients with lung cancer, melanoma and other solid tumours. Nineteen patients with advanced stage cancers received between one and nine doses of the immunotherapy treatment. Scientists have found the immunotherapy created an immune response against cancer and was well tolerated, with adverse events ...
Rapid new blood diagnostic test for ALS
2024-09-13
(Jackson, Wyoming – Embargoed until Thursday 12 September 2024 8:00 PM EDT)
A highly accurate diagnostic blood test has been developed for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a progressive neurodegenerative disease that effects neurons in the brain and spinal cord.
ALS leads to gradual paralysis, ultimately resulting in the inability to walk, speak, or, in later stages, move. Currently, diagnosis is based on a thorough clinical examination, but it can take up to 12 months to provide a definitive diagnosis, by which time many patients have significantly ...
Ignore antifungal resistance in fungal disease at your peril, warn top scientists
2024-09-12
Without immediate action, humanity will potentially face further escalation in resistance in fungal disease, a renowned group of scientists from the across the world has warned. The commentary - published in The Lancet this week - was coordinated by scientists at The University of Manchester, the Westerdijk Institute and the University of Amsterdam. According to the scientists most fungal pathogens identified by the World Health Organisation - accounting for around 3.8 million deaths a year - are either already resistant or rapidly acquiring resistance to antifungal drugs.
The authors argue that the currently narrow focus on bacteria will not fully combat antimicrobial resistance ...
Increased testing for heart disease indicator needed worldwide
2024-09-12
Review in The Lancet finds that one in five globally are at risk of contracting cardiovascular diseases, because they carry a genetic risk of high levels of a specific lipoprotein, which can be tested for and possibly treated.
20 % of the world population carries a genetic risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks, strokes, and aortic valve stenosis: Increased levels of a lipid particle called lipoprotein(a). It is the most common genetic cause of cardiovascular diseases.
“Lipoprotein(a) is the direct cause of cardiovascular diseases much like cigarettes cause ...
Huge gamma-ray burst collection 'rivals 250-year-old Messier catalogue'
2024-09-12
Huge gamma-ray burst collection 'rivals 250-year-old Messier catalogue'
Royal Astronomical Society press release
RAS PR 24/24
Embargoed until 00:01 BST on Friday 13 September 2024
Hundreds of gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) have been recorded as part of an enormous global effort so extensive it "rivals the catalogue of deep-sky objects created by Messier 250 years ago", astronomers say.
GRBs are the most violent explosions in the Universe, releasing more energy than the Sun would in 10 billion years. They occur when either a massive star dies or two neutron stars merge.
The explosions are so ...
Crude oil decimates sea otter buoyancy
2024-09-12
Sea otters are famed for their luscious pelts, but the fur almost led to their extinction. By 1938, only a tiny population of ~50 remained clinging to the central California coast. Since then, the mammals have battled back; however, the charismatic creatures are still at risk from crude oil spilled by offshore rigs. But no one knew how severely crude oil impacts the buoyancy of sea otter fur or how well it recovers after cleaning. And Kate Riordan from California Polytechnic State University San Luis ...
Semaglutide and tirzepatide lead to better blood sugar control and weight loss in individuals with type 1 diabetes, US study finds
2024-09-12
Semaglutide and tirzepatide treatment lead to significant weight loss and improve blood sugar control in individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D) who are living with overweight or obesity, new research being presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Madrid, Spain (9-13 September) has found.
The two relatively new drugs are approved to treat type 2 diabetes and for weight loss. In type 2 diabetes, they help the body produce more insulin when needed. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
[Press-News.org] The Menopause Society launches Making Menopause Work™ InitiativeUnique educational and designation initiative based on new science-based Consensus Recommendations to help employers retain workers and recoup $1.8 billion in lost workdays by supporting menopausal women in the workplace