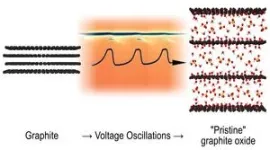
(Press-News.org) A reaction that puzzled scientists for 50 years has now been explained by researchers at Umeå University. Rapid structural snapshots captured how graphite transforms into graphite oxide during electrochemical oxidation, revealing intermediate structures that appear and disappear over time. The researchers describe this as a new type of oscillating reaction.
Oscillating chemical reactions are fascinating to watch and important for developing an understanding of how complex systems work, both in chemistry and in nature. Classical visual examples of such reactions show how the colors of a solution change back and forth, cycling through different states and producing a final product after each cycle.
Umeå researchers recently published a study in the scientific journal Angewandte Chemie, reporting a rather different and new type of oscillating reaction during electrochemical oxidation of graphite.
“It has been known for 50 years that some voltage oscillations spontaneously occur when a charge is applied to a graphite electrode immersed in sulphuric acid solution. The end product of this reaction is graphite oxide, a material consisting of layers of graphene oxide. However, what happens to the structure of the material during the reaction at every oscillation cycle had remained a complete mystery,” says Alexandr Talyzin, Professor in the Department of Physics at Umeå University.
Thanks to new synchrotron methods, researchers can record X-ray diffraction scans in a matter of a few seconds, providing snapshots of the material’s structure changes during oxidation. Surprisingly, the experiments revealed an intermediate phase with a specific structure that appears at one part of the cycle, disappears in the next stage and then reappears, repeating the cycle.
”Soon we realised that we had observed a new – to the best of our knowledge – type of oscillating reaction. What began as a detailed study of a particular chemical reaction suddenly appeared to be a lot more interesting from the point of view of fundamental chemistry. Bartosz Gurzeda, the first author of the study, also recorded a beautiful video showing periodic changes in the appearance of a sample every few minutes,” says Alexandr Talyzin.
Oscillation reactions are happening inside all living beings but were once considered impossible in inorganic chemistry. This discovery expands our knowledge of chemical kinetics and reaction mechanisms and could lead to the development of new theories and models in chemistry.
The first theory explaining oscillating reactions earned Ilya Prigogine the Nobel Prize in 1977 and became a fundamental part of non-equilibrium thermodynamics, showing how order can emerge from chaos.
“We hope that new theories will be developed to explain this new type of oscillating reaction, which may lead to the discovery of new similar examples,” says Alexandr Talyzin.
END
Graphite oxidation experiments reveal new type of oscillating chemical reaction
2024-09-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How does a tiny shrimp find its way home in a vast ocean? Study finds it’s down to their cave’s special smell
2024-09-17
Homing is an animal’s ability to navigate towards an original location, such as a breeding spot or foraging territory. Salmon and racing pigeons are famous for homing, but similar behaviors occur in groups as diverse as bees, frogs, rats, and sea turtles. There, homing individuals are known or suspected to rely on landmarks, the Earth’s magnetic field, or the sky’s pattern of polarized light to find their way back.
Another group known to display homing are cave-dwelling mysid shrimp, also known as possum shrimp for the pouches in which females carry ...
‘Marine identity’ can help restore the ocean
2024-09-17
People’s deep connection with the ocean – their “marine identity” – can help us reset society’s relationship with the seas, new research led by Dr Pamela Buchan, from the University of Exeter, suggests.
A diverse, international group of marine researchers and practitioners met to discuss marine identity – based on testimony and photos from multiple countries.
The group included Diz Glithero of the Canadian Ocean Literacy Coalition, Dr Emma McKinley of Cardiff University who helped deliver the workshop, and others from across Europe, Africa, Indonesia, North America, and Australasia.
They found many common themes, including traditions ...
Evidence shows that estrogen blocker treatment does not increase the risk of coronary heart disease in breast cancer patients
2024-09-17
New evidence shows that extended estrogen suppression treatment using an aromatase inhibitors for hormone receptor-positive postmenopausal breast cancer is safe; it does not increase the risk of coronary artery calcification, a sign of active coronary atherosclerosis, as some prior studies had indicated. An article in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier, details the findings from a retrospective, cross-sectional observational study that investigated the association between the duration of aromatase inhibitor treatment and the severity of coronary artery calcification in postoperative breast cancer patients.
Coronary ...
Survey shows 25% of adults consider weight loss drug use without prescription
2024-09-17
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Injectable weight loss drugs are popular right now but can be hard to get because they are in short supply or too expensive without insurance. The result is that some people are skipping the doctor’s office and reaching out to potentially unreliable sources such as unlicensed online pharmacies or telehealth sites, which could expose patients to risks.
A new national survey from The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center reveals 1 in 4 (25%) of 1,006 adults surveyed would consider using an injectable weight loss medication without consulting their doctor. The reasons ...
New treatment extends ovarian function in older mice
2024-09-17
Medication to reduce ovarian scarring helps extends overall health of reproductive system
Freezing eggs only addresses age-related infertility, not ovarian hormone loss. New treatment would ‘fix the root of the issue’
Findings also have implications for developing treatments for ovarian cancer
CHICAGO --- A woman’s ovaries are like a factory where eggs grow and produce hormones that regulate everything from menstruation and pregnancy to bone density and mood. As she and her factory age, production dwindles, and by the time she hits menopause ...
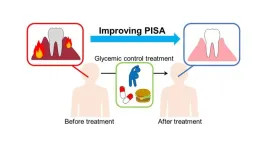
Getting to the root of the problem: Intensive diabetes treatment reduces gum disease inflammation
2024-09-17
Osaka, Japan – While the link between diabetes and periodontal disease is known, the impact of diabetes treatment on periodontal health is less well understood. Recent research published in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism demonstrates that periodontal inflammation can be positively affected just by receiving intensive diabetes treatment.
It is widely believed that there is an interrelationship between diabetes and periodontal disease. While it has been shown that treatment of periodontal disease improves blood ...
Researchers take power and efficiency of biological sensing to record level
2024-09-17
University of Arizona researchers have developed a new biological sensing method that can detect substances at the zeptomolar level – an astonishingly miniscule amount.
This level of sensing, immediately useful for drug testing and other research, has the potential to make new drug discoveries possible. Eventually, the advance could lead to portable sensors that can detect environmental toxins or chemical weapons, monitor food quality or screen for cancer.
A paper describing the results was published in the journal Nature Communications on Aug. 28.
Judith Su, associate professor of biomedical engineering and optical ...
Under-plant mirrors improve endangered plant survival and growth
2024-09-17
The most endangered plant species in the Mariana Islands, the legume tree Serianthes nelsonii, faces persistent threats in its recovery. These have been identified as a short lifespan of habitat seedlings and rapid death of saplings transplanted from conservation nurseries.
The Plant Physiology Laboratory at the University of Guam addressed this conundrum by improving growth and survival of Serianthes seedlings through strategically placed mirrors beneath deeply shaded seedlings to increase available ambient light. The resulting paper has been published ...
Widespread evidence for packaging-related chemicals in humans
2024-09-17
About this study: A new review is the first to reveal the extent of human exposure to food contact chemicals (FCC), with 3,601 chemicals used in food packaging and other food contact articles having been found in human bodies. The authors say this review also highlights significant gaps in biomonitoring and toxicity data.
---
In a new study, published in the Journal of Exposure Science and Environmental Epidemiology, scientists describe the widespread human exposure to food contact chemicals (FCCs). The research reveals which chemicals ...
Hardship early in life can affect health and longevity – even for marmots
2024-09-16
Key takeaways
The cumulative adversity index for people quantifies numerous measures of hardship, such as poverty and stress to understand health and longevity over the individual’s lifespan.
A similar tool could help scientists who study and want to conserve animal populations by identifying the most influential stressors to mitigate.
UCLA biologists have created the first cumulative adversity index for yellow-bellied marmots. They found that as in humans, adversity early on had lifelong consequences and reduced their life expectancy.
Adversity early in life can have permanent health consequences for people — even if their circumstances improve dramatically later on. ...