(Press-News.org) Perceptual recognition of numerical characters, like Arabic numerals, is indispensable for our daily activities in the modern society. Studying the perceptual and neural mechanisms that endow us with the ability to understand those characters is an important scientific topic. In this project, researchers explored a bistable perceptual phenomenon of a specially designed character named occluded digital numeral, to get a deeper understanding of the mechanisms underpinning the perceptual recognition of numbers.
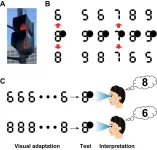
The digital numeral is a special version of number fonts designed for application in electronic products like traffic countdown timers, digital calculators, and many other LED broadcasting panels. Sometimes, an accidental partial occlusion of these characters (Fig. 1A) results in an intriguing perceptual phenomenon, that one digital numeral can be recognized as having multiple, usually two, semantic meanings (Fig. 1B).
“Because of the simple design of digital numerals, a partial occlusion causes visual ambiguities. In other words, the visual input does not contain enough information for us to make a unique semantic interpretation of the occluded numerical character,” said Dr. Junxiang Luo of the National Institute for Physiological Sciences, a researcher who led this project.
Researchers then performed a behavioral experiment on healthy human participants using visual adaptation tasks. This task paradigm examined how the exposure to specific types of visual input bias perception. Specifically, they found that after long-time presentation of normal digital numerals to the visual system, participants tended to report seeing a unique number biased away from the adaptation numeral (Fig. 1C).
“Visual adaptation selectively reduces the neural sensitivity of a certain visual processing stage to a certain category of visual stimuli, so by evaluating how much the interpretation biases away from the bistable state after adaptation to different types of visual information, we have a chance to know at which visual processing level that the perceptual recognition of numerals may happen,” said Dr. Luo.
The researchers selected a series of candidate adaptation stimuli. They demonstrated that the bistability does not depend on either low-level visual information such as simple visual features, or high-level information such as semantics, and these results suggest a contribution of midlevel visual processing that encodes complex shapes and symbolic number forms.
The perceptual phenomenon discovered in this psychophysical study has the potential to be extended to physiological studies in the future, in which researchers can compare brain activity among different perceptual interpretations of the same occluded numerals. “We hope to extend this study using some physiological methods to get a deeper understanding and more precise localization of the brain areas which generate the perceptual bistability,” said Dr. Luo.
The results are published in Journal of Vision on September 17th, 2024. Dr. Isao Yokoi and Professor Hiromasa Takemura of the National Institute for Physiological Sciences and Dr. Serge Dumoulin of the Spinoza Centre for Neuroimaging also contributed this research.
END
What numbers do you see? A new bistable perceptual phenomenon on symbolic numbers
Researchers from the National Institute for Physiological Sciences in Japan found that partial occlusion of digital numerals induces bistable interpretations of their semantic meanings. Moreover, long-time visual exposure to normal numerals biases percept
2024-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Quantum speedup and limitations on matroid property problems
2024-09-18
Quantum computers show advantages over classical computers in some problems, such as unordered data base searching and prime factorization. Finding more problems that can take quantum speedup has become one of the focus problems in quantum computing. Before this, there is no research work on the quantum query complexity and quantum algorithm for matroid problems. It is interesting and meaningful to search for structures that can take quantum advantage in matroid problems.
In order to study the possibility and limitation of acceleration of quantum computing in matroid problems, a ...
Unravelling an ancient European extinction mystery: Disappearance of dwarf megafauna on palaeolithic Cyprus
2024-09-18
Scientists have unravelled a mystery about the disappearance of dwarf hippos and elephants that once roamed the picturesque landscape on the Mediterranean island of Cyprus before palaeolithic humans arrived.
Cyprus only had two species of megafauna present during the Late Pleistocene — the 500-kg dwarf elephant (Palaeoloxodon cypriotes), and the 130-kg dwarf hippo (Phanourios minor), but both species disappeared soon after humans arrived around 14,000 years ago.
In examining the reasons behind the extinction of these prehistoric animals, research funded by the European Regional Development Fund and the Republic of Cyprus through the Research and Innovation Foundation ...
Highly-sensitive beaks could help albatrosses and penguins find their food
2024-09-18
Researchers have discovered that seabirds, including penguins and albatrosses, have highly-sensitive regions in their beaks that could be used to help them find food. This is the first time this ability has been identified in seabirds.
An international team of researchers, led by the University of Cambridge, studied over 350 species of modern birds and found that seabirds have a high density of sensory receptors and nerves at the tip of their beaks, which has been previously identified in specialised tactile foragers such as ducks.
The researchers say this touch-sensitive region could have come from a common ancestor, and further work is needed to determine ...
Self-reporting of health may lead to underestimation of health inequalities in England
2024-09-17
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL TUESDAY 17 SEPTEMBER 23:15 UK TIME (BST).
Self-reporting of health may lead to underestimation of health inequalities in England
Peer reviewed | Observational study | People
A first-of-its kind analysis of data collected from England’s annual health survey found that of the people who reported their health as ‘poor’, those living in areas of high deprivation are likely to have worse health than those living in the least deprived areas.
This could mean that we are ...
New research shows how oral cancer cells avoid immune system
2024-09-17
Macquarie University researchers have discovered new information about how oral cancer cells may block the body's immune response. This could lead to better treatments for this aggressive disease.
Their research, published in the Journal of Oral Biosciences this month, looked at protein interactions in oral cancer cells that might stop our immune cells from attacking these tumours.
Oral cancer is the sixth most common cancer in Australia and the most common in India. Advanced forms of oral cancer are hard to treat, with patients typically surviving less than 12 months.
Lead author Dr Rajdeep Chakraborty from Applied Biosciences ...
Abnormal electrolyte levels in people with eating disorders may increase risk of death, poor health outcomes
2024-09-17
Ottawa, ON, September 17, 2024 – A new study published in The Lancet Psychiatry found that 32% of individuals with an eating disorder had abnormal electrolyte levels, which were associated with a higher risk of death from any cause.
The study, led by researchers at ICES and The Ottawa Hospital, found that electrolyte abnormalities were also linked to the development of other serious health conditions, including chronic kidney disease, bone fracture, bowel obstruction, and acute kidney injury.
This is one of the first large, population-based studies to identify an important risk factor for mortality and poor health outcomes in individuals ...
No major concerns about risks to offspring for would-be dads taking epilepsy meds
2024-09-17
Would-be dads taking drugs to stop their epilepsy seizures—and valproate in particular—should be largely reassured that the available evidence on the developmental risks to their offspring doesn’t justify any major concerns, concludes a systematic review of relevant studies published online in the Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
The available evidence is scarce and inconsistent, but most studies indicate no heightened risk, the findings show, casting doubt on the stance taken by the UK drugs regulator, the MHRA, in particular, say ...
Fifth of GPs using AI despite lack of guidance or clear work policies, UK survey suggests
2024-09-17
A fifth of family doctors (GPs) seem to have readily incorporated AI into their clinical practice, despite a lack of any formal guidance or clear work policies on the use of these tools, suggest the findings of an online UK-wide snapshot survey, published in the open access journal BMJ Health & Care Informatics.
Doctors and medical trainees need to be fully informed about the pros and cons of AI, especially because of the inherent risks of inaccuracies (‘hallucinations’), algorithmic biases, and the potential to compromise patient privacy, ...
Novel triplet regimen yields promising response in advanced-phase chronic myeloid leukemia
2024-09-17
HOUSTON ― According to researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, 80% of patients with previously untreated or relapsed/refractory advanced-phase chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) – including both accelerated or myeloid blast phases of the disease – or Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute myeloid leukemia (AML) achieved a bone marrow remission when treated with a novel combination of decitabine, venetoclax and ponatinib.
Findings from the Phase II clinical trial, published today in The Lancet Haematology, represent an important step forward for patients ...
‘Scuba-diving’ lizards use bubble to breathe underwater and avoid predators
2024-09-17
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Presenting the world’s smallest (and scrappiest) scuba diver: A species of semi-aquatic lizard produces a special bubble over its nostrils to breathe underwater and avoid predators, according to new research from Binghamton University, State University of New York.
Lindsey Swerk, an assistant research professor of biological sciences at Binghamton University, studies water anoles, a type of semi-aquatic lizard found in the tropical forests of southern Costa Rica. She had previously documented the lizards using a bubble underwater. When these lizards feel threatened by a predator, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] What numbers do you see? A new bistable perceptual phenomenon on symbolic numbersResearchers from the National Institute for Physiological Sciences in Japan found that partial occlusion of digital numerals induces bistable interpretations of their semantic meanings. Moreover, long-time visual exposure to normal numerals biases percept