$1 million grant to fund research of nerve regeneration in multiple sclerosis patients
Multiple sclerosis is a disease of the brain and spinal cord caused by the loss of myelin. It affects more than 2.8 million people worldwide.
2024-09-18
(Press-News.org)
The National Multiple Sclerosis Society (USA) has awarded a grant of 1 million dollars to Dr. Isabel Pérez-Otaño, who leads the Plasticity and Remodeling of Neural Circuits laboratory at the Institute for Neurosciences (IN), a joint center of the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) and the Miguel Hernández University (UMH) of Elche. The grant is part of the NMSS 'Pathways to Cure' program that funds innovative therapeutic approaches to treat multiple sclerosis (MS). The team will work on identifying mechanisms that mediate a special kind of brain plasticity, known as myelin plasticity. The goal is to find ways to stimulate myelin plasticity to regenerate affected nerve fibers in MS patients.
MS is a chronic neurological condition that affects the central nervous system. It is caused by the destruction of myelin, a protective sheath that insulates nerve fibers and ensures rapid, efficient communication between neurons. When myelin is damaged, the flow of information between the brain and the rest of the body is disrupted, leading to a wide range of debilitating symptoms. These can include vision impairment, loss of coordination, difficulty walking, and cognitive challenges such as memory loss and trouble concentrating.
Studies suggest that MS has an autoimmune origin. While advances have been made in halting the immune system’s attack on oligodendrocytes—the cells that produce myelin—current treatments lose efficacy as the disease progresses. At present, no therapies exist that can restore lost or damaged myelin. “Our brains have an inherent repair mechanism called remyelination, which is activated after damage to form new myelin sheaths. But this repair capacity fails with age and disease progression, leading to irreversible disability,” explains Pérez-Otaño.
Pérez-Otaño’s research brings renewed hopeI. Oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs) are abundant in the brain and spinal cord of MS patients, and offer an unmatched opportunity for generating new oligodendrocytes and promoting myelin repair. The challenge is to find ways to enhance their responses and improve their ability to form myelin.
The team led by the researcher at the IN has discovered a brain receptor that could help activate these stem cells and unlock the plasticity of myelin. The research will focus on developing gene therapy or pharmacological approaches and test their ability to bring back efficient myelination in mouse models. Additionally, the team is exploring the potential of combining gene therapy with pharmacological treatments and rehabilitation strategies to further enhance myelin repair after injury.
The project will be done in collaboration with international leading experts in the field, including Professor Thora Karadottir at the Cambridge Center for Myelin Repair (UK), Professor Anna Williams at the University of Edinburgh (UK), and researcher Juan Antonio García León from the University of Málaga (Spain). All bring wold-class expertise in myelin repair and the study of human MS patients. A breakthrough from this research could not only transform the treatment landscape for MS but may also have wide-ranging implications for other neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer´s or Huntington´s disease, where myelin failure has been implicated.
You can collaborate with the National Multiple Sclerosis Society (USA) at the following link:
https://donate.nationalmssociety.org/index.cfm?fuseaction=cms.page&id=8508&&donate=529
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-18
[Strasbourg, 18th September 2024]
A new online tool designed to assess the equity of scholarly communication models is launched today at the OASPA 2024 conference. The “How Equitable Is It” tool, developed by a multi-stakeholder Working Group, comprising librarians, library consortia representatives, funders and publishers, and convened by cOAlition S, Jisc and PLOS, aims to provide a framework for evaluating scholarly communication models and arrangements on the axis of equity.
The tool, which was inspired by the “How Open Is It?” framework, is targeted at institutions, library consortia, ...
2024-09-18
Preschool teachers have different views on finger counting. Some teachers consider finger counting use in children to signal that they are struggling with math, while others associate its use as advanced numerical knowledge. In a new Child Development study, researchers at the University of Lausanne in Switzerland and Lea.fr, Editions Nathan in Paris, France, explored whether a finger counting strategy can help kindergarten-aged children solve arithmetic problems.
Adults rarely use their fingers to calculate a small sum (e.g., 3+2) as such behaviors could be attributed to pathological difficulties in mathematics or cognitive impairments. However, young children between ...
2024-09-18
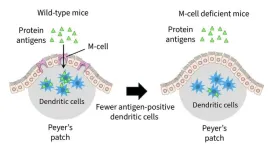
Researchers led by Hiroshi Ohno at the RIKEN Center for Integrative medical sciences (IMS) in Japan have discovered that food antigens like milk proteins help keep tumors from growing in our guts, specifically the small intestines. Experiments revealed how these proteins trigger the intestinal immune system, allowing it to effectively stop the birth of new tumors. The study was published in the scientific journal Frontiers in Immunology on Sep. 18.
Food antigens get a lot of negative press because they are the source of allergic reactions to foods such as peanuts, shellfish, bread, eggs, and ...
2024-09-18
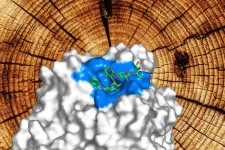
Researchers want to transform the natural and abundant resource wood into useful materials, and central to that is a molecular machine found in fungi that decomposes the complex raw material into its basic components. A Kobe University researcher and his team now were the first to come up with a test feed for the fungal molecular machine that allows them to observe its close-to-natural action, opening the door to improving it and to putting it to industrial application.
Biochemical engineers want to transform the abundant and renewable material wood into bioplastics, medically relevant chemicals, food additives or fuel. ...
2024-09-18
PHILADELPHIA – Today, the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) released the 14th edition of its annual Cancer Progress Report. This comprehensive report provides the latest statistics on cancer incidence, mortality, and survivorship. It also outlines how basic, translational, and clinical cancer research and cancer-related population sciences—largely supported by federal investments in the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the National Cancer Institute (NCI), the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the Centers for Disease ...
2024-09-18
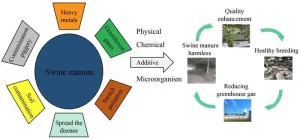
Most of the heavy metals in pig manure originate from feed additives, such as copper and zinc. When these heavy metals are introduced into agricultural soil, they can significantly increase the heavy metal content in crops, posing a threat to both the environment and human health. While pig manure is rich in nitrogen, an essential nutrient for crop growth, a substantial amount of nitrogen is lost in gaseous form during the composting process, impacting the quality of the compost. Moreover, this process results in the emission of ...
2024-09-18
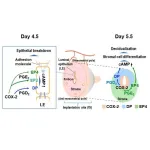
A team from Kumamoto University has uncovered a new mechanism that could revolutionize infertility care by promoting embryo implantation. The discovery focuses on prostaglandin (PG) receptors in the uterus that enhance the critical process of decidualization, which is necessary for a successful pregnancy. This finding opens the door to developing new fertility treatments that target these receptors.
Prostaglandins are bioactive lipids known for their role in body’s response to injury by causing fever and pain, but they are also crucial in reproductive ...
2024-09-18
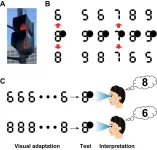
Perceptual recognition of numerical characters, like Arabic numerals, is indispensable for our daily activities in the modern society. Studying the perceptual and neural mechanisms that endow us with the ability to understand those characters is an important scientific topic. In this project, researchers explored a bistable perceptual phenomenon of a specially designed character named occluded digital numeral, to get a deeper understanding of the mechanisms underpinning the perceptual recognition of numbers.
The digital numeral is a special version of number fonts designed for application in electronic products ...
2024-09-18
Quantum computers show advantages over classical computers in some problems, such as unordered data base searching and prime factorization. Finding more problems that can take quantum speedup has become one of the focus problems in quantum computing. Before this, there is no research work on the quantum query complexity and quantum algorithm for matroid problems. It is interesting and meaningful to search for structures that can take quantum advantage in matroid problems.
In order to study the possibility and limitation of acceleration of quantum computing in matroid problems, a ...
2024-09-18
Scientists have unravelled a mystery about the disappearance of dwarf hippos and elephants that once roamed the picturesque landscape on the Mediterranean island of Cyprus before palaeolithic humans arrived.
Cyprus only had two species of megafauna present during the Late Pleistocene — the 500-kg dwarf elephant (Palaeoloxodon cypriotes), and the 130-kg dwarf hippo (Phanourios minor), but both species disappeared soon after humans arrived around 14,000 years ago.
In examining the reasons behind the extinction of these prehistoric animals, research funded by the European Regional Development Fund and the Republic of Cyprus through the Research and Innovation Foundation ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] $1 million grant to fund research of nerve regeneration in multiple sclerosis patients
Multiple sclerosis is a disease of the brain and spinal cord caused by the loss of myelin. It affects more than 2.8 million people worldwide.