(Press-News.org) Figshare, a leading provider of institutional repository infrastructure that supports open research, is pleased to announce that the University of Limpopo has chosen Figshare to facilitate the collection, management, sharing and preservation of its research data.
The University of Limpopo – one of the top public universities in South Africa offering undergraduate and postgraduate qualifications, and a variety of short learning programmes – will become the 20th institution in the country using Figshare as their data repository.
Using Figshare, The University of Limpopo will be able to encourage collaboration amongst their research community and network. This will drive interdisciplinary research discovery, the cross-pollination of ideas and further knowledge sharing. With Figshare, they will now have the infrastructure required to ensure research data will be managed in line with best practices throughout the research lifecycle as part of the University’s commitment to research excellence.
Importantly, the repository will also facilitate compliance with the University’s own open research guidance and mandates but also enable researchers to easily adhere to research sharing obligations set out in a growing number of funder policies.
“The motto 'Finding Solutions for Africa' expresses the commitment to provide high-quality academic programmes and research outcomes that are socially relevant and responsive, giving meaningful expression to the motto.
“Choosing Figshare gives the University of Limpopo the advantage of having a sustainable platform for our research data to be well managed, discoverable and citable. The repository will promote research work by enabling access to data used for its cutting-edge research to support further studies on a global scale,” said Khomotso Maphopha, Executive Director: LIS.
Mark Hahnel, Figshare Founder and Digital Science’s VP of Open Research, said: “It’s wonderful to see the University of Limpopo become the 20th institution using Figshare in South Africa. We’re thrilled to be able to support their research excellence initiatives and strategies with Figshare infrastructure and their commitment to making research data management a priority for their research community is admirable. It’s exciting to see the global Figshare community continue to grow with leading institutions such as the University of Limpopo.”
About the University of Limpopo
The University of Limpopo was established in 1960 as the University College of the North and later retained the name University of Limpopo (UL) after the unbundling of the MEDUNSA campus from UL in 2015. The University is situated in the Limpopo Province, South Africa and has grown into a world-class university with a commitment towards offering approved and accredited high-quality programmes. The University Envisions its future as one in which “the provision and quality of programmes, students’ graduate attributes, academics, culture and services are poised towards finding solutions for Africa”.
About Figshare
Figshare, a Digital Science Solution, is a provider of institutional repository infrastructure. Our solutions help institutions share, showcase and manage their research outputs in a discoverable, citable, reportable and transparent way. We support institutions in meeting the growing demands for research to become open, freer, FAIRer and more connected. We provide the flexibility and control for you to create research management workflows that work for you. We take care of implementation, updates, security and maintenance – ensuring you and your researchers can always depend on your repository, leaving you to focus on what really matters; research and its impact on the world.
About Digital Science
Digital Science is an AI-focused technology company providing innovative solutions to complex challenges faced by researchers, universities, funders, industry and publishers. We work in partnership to advance global research for the benefit of society. Through our brands – Altmetric, Dimensions, Figshare, IFI CLAIMS Patent Services, metaphacts, OntoChem, Overleaf, ReadCube, Scismic, Symplectic, and Writefull – we believe when we solve problems together, we drive progress for all. Visit digital-science.com and follow @digitalsci on X or on LinkedIn.
Media contacts
Simon Linacre, Head of Content, Brand & Press, Digital Science: Mobile +44 7484 381477, s.linacre@digital-science.com
David Ellis, Press, PR & Social Manager, Digital Science: Mobile +61 447 783 023, d.ellis@digital-science.com
END
The University of Limpopo chooses Figshare to support its research excellence strategy
2024-09-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
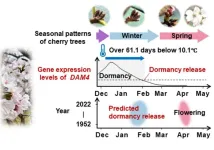
A new forecasting model based on gene activity predicts when Japan’s cherry buds awake from dormancy
2024-09-19
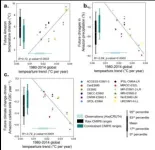
Fukuoka, Japan – Japan in spring is famous for its cherry blossoms, or sakura, which begin flowering in the southern region of Kyushu and blaze upwards to the remote north of Hokkaido. The most abundant cherry tree cultivar, Somei Yoshino, is the iconic symbol of spring, as the cloned trees flower simultaneously at each site, creating a fleeting explosion of white-pink blossom that enraptures locals and tourists alike. The flowering forecasts of Somei Yoshino are poured over for months before flowering, as visitors plan their trips and locals ...
New organic thermoelectric device that can harvest energy at room temperature
2024-09-19
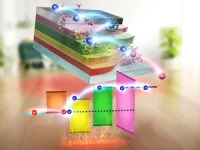
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers have developed a new organic thermoelectric device that can harvest energy from ambient temperature. While thermoelectric devices have several uses today, hurdles still exist to their full utilization. By combining the unique abilities of organic materials, the team succeeded in developing a framework for thermoelectric power generation at room temperature without any temperature gradient. Their findings were published in the journal Nature Communications.
Thermoelectric devices, or thermoelectric ...
Activity in brain system that controls eye movements highlights importance of spatial thinking
2024-09-19
The superior colliculus is a midbrain region that is traditionally thought to help animals orient themselves toward important locations in space, like directing their eyes and head toward a bright flash of light. New research from the University of Chicago shows that this part of the brain also plays a role in complex cognitive tasks like visual categorization and decision making.
In the new study, published in Nature Neuroscience, scientists measured the information contained in patterns of brain cell activity across multiple brain regions involved in visual category decisions. The researchers monitored activity in the superior colliculus (SC) and part of the posterior parietal ...
New research reenvisions Earth’s mantle as a relatively uniform reservoir
2024-09-19
Lavas from hotspots—whether erupting in Hawaii, Samoa or Iceland—likely originate from a worldwide, uniform reservoir in Earth’s mantle, according to an evaluation of volcanic hotspots published today in Nature Geoscience.
The findings indicate Earth’s mantle is far more chemically homogenous than scientists previously thought—and that lavas only acquire their unique chemical “flavours” enroute to the surface.
“The discovery literally turns our view of hotspot lavas and the mantle upside down,” said Dr. Matthijs Smit, associate professor ...
Global warming leads to drier and hotter Amazon: reducing uncertainty in future rainforest carbon loss
2024-09-19
The Amazon, often called the "lungs of the planet", is the world’s largest tropical forest, playing a crucial role in the global climate system due to its vast carbon storage. While it is typically warm and humid all year round, continued climate change poses the threat of more frequent and severe droughts and heat extremes. A new study, published in Nature Communications delves into future projections of the Amazon carbon cycle, focusing specifically on the impacts driven by climate change.
Scientists use the latest generation of Earth system models from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project which contributed to ...
Low-carbon ammonia offers green alternative for agriculture and hydrogen transport
2024-09-19
A new way of making ammonia by harnessing the unique power of liquid metal could lead to significant cuts in carbon emissions caused by production of the widely-used chemical.
Ammonia is used in fertiliser to grow much of our food, but also plays a role in clean energy as a carrier to safely transport hydrogen.
The global production of ammonia, however, comes at a high environmental cost: it consumes over 2% of global energy and produces up to 2% of global carbon emissions.
RMIT Research Fellow and study ...
New mechanism uncovered for the reduction of emu wings
2024-09-19
Researchers have uncovered a fascinating mechanism behind the reduction and asymmetry of emu wing bones. The wings not only show significant shortening, but the skeletal elements also fuse asymmetrically, a phenomenon traced back to the absence of muscle formation in the distal regions of the wings. During development, this lack of muscle leads to insufficient mechanical stress, which is crucial for proper bone formation. The team identified muscle progenitor cells with a unique dual identity, combining characteristics of both somite1-derived myogenic and lateral plate mesoderm2 cells. These ...
Zeroing in on the genes that snakes use to produce venom
2024-09-19
Only about ten percent of the world’s roughly 4,000 snake species have venom strong enough to seriously hurt a human, but that’s enough for snake bites to be an important public health concern. To help better understand how snakes make their venom and how venoms differ from one species to another, researchers developed a new way to zero in on the genes that snakes use in venom production. Their work was published in the journal Molecular Ecology Resources.
“We’ve developed a tool that can tell us which venom-producing genes are present across an entire snake family in one fell swoop,” says Sara Ruane, the Assistant Curator of Herpetology in the ...
Maynooth University study reveals impact of homework on student achievement in maths and science
2024-09-19
· Daily homework of up to 15 minutes most effective for maths achievement
· Homework assigned three to four times a week benefits science performance
· Short duration homework just as effective as longer assignments
Researchers at Maynooth University’s Hamilton Institute and Department of Mathematics and Statistics in Ireland have unveiled significant findings on the role of homework in student achievement. The research, led by Prof Andrew Parnell, Nathan McJames and Prof Ann O’Shea, used a new AI model to analyse data from the Trends in International Mathematics and Science ...
Reducing floodplain development doesn’t need to be complex
2024-09-19
A new paper in Oxford Open Climate Change, published by Oxford University Press, uncovers evidence suggesting that, contrary to expectations, most U.S. cities are not doing too badly in avoiding development in areas prone to flooding, and those that are effective appear to be applying existing tools and strategies well, rather than doing anything particularly novel.
Despite billions of dollars of investments and widespread mitigation efforts, the costs of disasters in the United States have grown dramatically. ...