(Press-News.org) The superior colliculus is a midbrain region that is traditionally thought to help animals orient themselves toward important locations in space, like directing their eyes and head toward a bright flash of light. New research from the University of Chicago shows that this part of the brain also plays a role in complex cognitive tasks like visual categorization and decision making.
In the new study, published in Nature Neuroscience, scientists measured the information contained in patterns of brain cell activity across multiple brain regions involved in visual category decisions. The researchers monitored activity in the superior colliculus (SC) and part of the posterior parietal cortex (PPC), a region of the cerebral cortex that is important for visual categorical decisions. To their surprise, they saw that activity in the SC was even more involved than the PPC in guiding the subjects’ category decisions, suggesting that it helps coordinate higher-order cognitive processes traditionally thought to take place in the neocortex.
“This is a really surprising place to find these kinds of cognitive signals because this area of the brain is traditionally associated with simpler spatial orienting behaviors and even reflexive functions,” said David Freedman, PhD, Professor of Neurobiology and the Neuroscience Institute at UChicago and senior author of the new study. "We have this evolutionarily ancient brain structure that seems to be even more involved in complex cognitive decisions than the cortical areas we studied in our experiments.”
An ancient brain region with surprising powers
All animals, from fish and reptiles to mammals like primates and humans, need to quickly distinguish and categorize objects in their field of vision. Is the object moving toward them an obstacle or a threat? Is that thing darting by a predator or prey?
The SC is a region in the brain that is evolutionarily conserved across all vertebrates, even those without a more sophisticated neocortex. It helps orient movements of the head and eyes toward visual stimuli, and it was traditionally believed to kick off reflexive motor actions by relaying inputs from upstream brain regions. However, recent research has shown that it is also involved in complex tasks like selecting an orientation point and paying attention to stimuli at different spatial locations.
Freedman and his team have been studying other cortical areas with strong anatomical connections to the SC for years. These adjacent areas are involved in flexible and cognitively demanding decision-making tasks, and the researchers wanted to see if the SC is involved in more abstract thinking too. For the latest study, they trained monkeys to perform a visual decision-making task in which they viewed images on a computer screen. The animals received fruit juice rewards for pushing a button at the right times to assign images to the correct categories.
While the subjects performed the task, the researchers recorded brain cell activity in the SC and the lateral intraparietal area (LIP), part of the PPC that Freedman’s lab previously showed is involved in category decisions during these kinds of tasks. Since the task required the subjects to maintain their gaze in one spot and indicate their choices by a hand movement, the experimental design singled out brain activity needed for categorization—not the eye or head movements usually thought to be the SC’s job.
The researchers saw lots of activity in the SC that encoded the categories of the images the animals were looking at, and this activity took place more strongly than in the PPC. They also performed an experiment in which they injected a drug to temporarily numb the SC during the same task. While this didn’t impair most of the subjects’ motor and visual functions, it dramatically affected their ability to correctly categorize the images until the effects of the drug wore off.
“Our results show us that this area is really important for the task,” Freedman said. “Even in tasks where the animals don't need to move their eyes or direct their attention to different places, the superior colliculus is involved in these more complex cognitive behaviors.”
That special “oomph” for problem-solving
Freedman said it’s not just surprising to find this activity in the SC; it could mean something about why this brain region is being recruited to solve such complex tasks. Since it is present across all vertebrates, from primitive sharks to modern humans, it was one of the earliest brain regions that evolved to help process visual inputs and generate corresponding movements. But in this new study, it’s also involved in decidedly non-spatial functions. Could this be a sign that spatial processing provides a special “oomph” to problem-solving?
Freedman pointed out the kind of eye movements and hand gestures that humans make when we’re asked to recall something or make decisions. If someone asks what you had for dinner last night, for example, your eyes often drift upward, as if the answer were written on the ceiling. Or when weighing a decision between two choices, you might move your hands up and down like two sides of a balance scale.
“Some of this data might be telling us is that the reason we're making these kinds of spatial gestures and eye movements is because the spatial parts of the brain are getting recruited into helping us perform these non-spatial cognitive functions,” said first author Barbara Peysakhovich, PhD, a former graduate student in Freedman’s lab now a postdoctoral researcher at Harvard.
Or, we’ve all had the experience of struggling to understand something written in text—like a long press release about a neuroscience study—but having it instantly click into place when the same information is presented in a graphic.
“They say a picture is worth 1,000 words—even a very simple spatial diagram can rapidly convey so much more information than you can possibly describe,” Freedman said. “It’s like the brain has created this beautiful mental graph paper which it can use to solve both spatial and non-spatial problems.”
The study, “Primate superior colliculus is causally engaged in abstract higher-order cognition,” was supported by funding from National Institutes of Health (grants R01EY019041, U19NS107609, 1F31MH124395, F30EY033648, F31 EY029155) and the Department of Defense Vannevar Bush Faculty Fellowship (N000141912001). Additional authors include Barbara Peysakhovich, Ou Zhu, Stephanie M. Tetrick, Vinay Shirhatti, Alessandra A. Silva, Sihai Li, Matthew C. Rosen, and W. Jeffrey Johnston from UChicago and Guilhem Ibos from UChicago and Institut de Neurosciences de la Timone, Aix-Marseille Université, France.
END
Activity in brain system that controls eye movements highlights importance of spatial thinking
New research from UChicago shows that the superior colliculus, a brain region that controls eye movements, also plays an important role in higher cognitive functions like categorization and decision making
2024-09-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New research reenvisions Earth’s mantle as a relatively uniform reservoir
2024-09-19
Lavas from hotspots—whether erupting in Hawaii, Samoa or Iceland—likely originate from a worldwide, uniform reservoir in Earth’s mantle, according to an evaluation of volcanic hotspots published today in Nature Geoscience.
The findings indicate Earth’s mantle is far more chemically homogenous than scientists previously thought—and that lavas only acquire their unique chemical “flavours” enroute to the surface.
“The discovery literally turns our view of hotspot lavas and the mantle upside down,” said Dr. Matthijs Smit, associate professor ...
Global warming leads to drier and hotter Amazon: reducing uncertainty in future rainforest carbon loss
2024-09-19
The Amazon, often called the "lungs of the planet", is the world’s largest tropical forest, playing a crucial role in the global climate system due to its vast carbon storage. While it is typically warm and humid all year round, continued climate change poses the threat of more frequent and severe droughts and heat extremes. A new study, published in Nature Communications delves into future projections of the Amazon carbon cycle, focusing specifically on the impacts driven by climate change.
Scientists use the latest generation of Earth system models from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project which contributed to ...
Low-carbon ammonia offers green alternative for agriculture and hydrogen transport
2024-09-19
A new way of making ammonia by harnessing the unique power of liquid metal could lead to significant cuts in carbon emissions caused by production of the widely-used chemical.
Ammonia is used in fertiliser to grow much of our food, but also plays a role in clean energy as a carrier to safely transport hydrogen.
The global production of ammonia, however, comes at a high environmental cost: it consumes over 2% of global energy and produces up to 2% of global carbon emissions.
RMIT Research Fellow and study ...
New mechanism uncovered for the reduction of emu wings
2024-09-19
Researchers have uncovered a fascinating mechanism behind the reduction and asymmetry of emu wing bones. The wings not only show significant shortening, but the skeletal elements also fuse asymmetrically, a phenomenon traced back to the absence of muscle formation in the distal regions of the wings. During development, this lack of muscle leads to insufficient mechanical stress, which is crucial for proper bone formation. The team identified muscle progenitor cells with a unique dual identity, combining characteristics of both somite1-derived myogenic and lateral plate mesoderm2 cells. These ...
Zeroing in on the genes that snakes use to produce venom
2024-09-19
Only about ten percent of the world’s roughly 4,000 snake species have venom strong enough to seriously hurt a human, but that’s enough for snake bites to be an important public health concern. To help better understand how snakes make their venom and how venoms differ from one species to another, researchers developed a new way to zero in on the genes that snakes use in venom production. Their work was published in the journal Molecular Ecology Resources.
“We’ve developed a tool that can tell us which venom-producing genes are present across an entire snake family in one fell swoop,” says Sara Ruane, the Assistant Curator of Herpetology in the ...
Maynooth University study reveals impact of homework on student achievement in maths and science
2024-09-19
· Daily homework of up to 15 minutes most effective for maths achievement
· Homework assigned three to four times a week benefits science performance
· Short duration homework just as effective as longer assignments
Researchers at Maynooth University’s Hamilton Institute and Department of Mathematics and Statistics in Ireland have unveiled significant findings on the role of homework in student achievement. The research, led by Prof Andrew Parnell, Nathan McJames and Prof Ann O’Shea, used a new AI model to analyse data from the Trends in International Mathematics and Science ...
Reducing floodplain development doesn’t need to be complex
2024-09-19
A new paper in Oxford Open Climate Change, published by Oxford University Press, uncovers evidence suggesting that, contrary to expectations, most U.S. cities are not doing too badly in avoiding development in areas prone to flooding, and those that are effective appear to be applying existing tools and strategies well, rather than doing anything particularly novel.
Despite billions of dollars of investments and widespread mitigation efforts, the costs of disasters in the United States have grown dramatically. ...
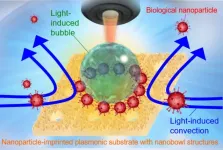
Lights, camera, action! Coronavirus spike proteins can be selectively detected in 5 minutes
2024-09-19
Like moths to a flame, microbes can also be moved by light. Using this knowledge, researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University’s Research Institute for Light-induced Acceleration System (RILACS) have demonstrated a method to detect the presence of viruses quickly and using only a small sample.
The research team led by OMU Professor Takuya Iida, the director of RILACS, and Associate Professor Shiho Tokonami, the deputy director, report in npj Biosensing on a light-induced immunoassay. Using ...
Your Zoom background could influence how tired you feel after a video call
2024-09-19
Part of many people’s pandemic experience included working from home. Even after lockdowns, videoconferencing remains a big part of life as people continue to work remotely, connect with families and friends online, and attend virtual events hosted on videoconferencing platforms.
Spending hours on video calls, however, can be exhausting and manifest as physical, emotional, or cognitive tiredness – a phenomenon known as videoconferencing fatigue (VF). Now, researchers in Singapore have asked if a relationship between virtual backgrounds and VF exists and ...
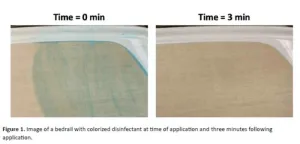
With the use of visual cues, hospital rooms get nearly 70% cleaner
2024-09-19
With the Use of Visual Cues, Hospital Rooms Get Nearly 70% Cleaner
New study shows that a simple color additive in disinfectant wipes dramatically improved room cleanliness and even reduced time needed for cleaning
Arlington, Va. — September 19, 2024 — A new study published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) reports a comparison of hospital room cleanliness using standard disinfectant wipes versus wipes with a color additive that allows users to see which surfaces have been sanitized. With the color additive, rooms ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The long standing commercialization challenge of lithium batteries, often called the dream battery, has been solved.
New method to remove toxic PFAS chemicals from water
The nanozymes hypothesis of the origin of life (on Earth) proposed
Microalgae-derived biochar enables fast, low-cost detection of hydrogen peroxide
Researchers highlight promise of biochar composites for sustainable 3D printing
Machine learning helps design low-cost biochar to fight phosphorus pollution in lakes
Urine tests confirm alcohol consumption in wild African chimpanzees
Barshop Institute to receive up to $38 million from ARPA-H, anchoring UT San Antonio as a national leader in aging and healthy longevity science
Anion-cation synergistic additives solve the "performance triangle" problem in zinc-iodine batteries
Ancient diets reveal surprising survival strategies in prehistoric Poland
Pre-pregnancy parental overweight/obesity linked to next generation’s heightened fatty liver disease risk
Obstructive sleep apnoea may cost UK + US economies billions in lost productivity
Guidelines set new playbook for pediatric clinical trial reporting
Adolescent cannabis use may follow the same pattern as alcohol use
Lifespan-extending treatments increase variation in age at time of death
From ancient myths to ‘Indo-manga’: Artists in the Global South are reframing the comic
Putting some ‘muscle’ into material design
House fires release harmful compounds into the air
Novel structural insights into Phytophthora effectors challenge long-held assumptions in plant pathology
Q&A: Researchers discuss potential solutions for the feedback loop affecting scientific publishing
A new ecological model highlights how fluctuating environments push microbes to work together
Chapman University researcher warns of structural risks at Grand Renaissance Dam putting property and lives in danger
Courtship is complicated, even in fruit flies
Columbia announces ARPA-H contract to advance science of healthy aging
New NYUAD study reveals hidden stress facing coral reef fish in the Arabian Gulf
36 months later: Distance learning in the wake of COVID-19
Blaming beavers for flood damage is bad policy and bad science, Concordia research shows
The new ‘forever’ contaminant? SFU study raises alarm on marine fiberglass pollution
Shorter early-life telomere length as a predictor of survival
Why do female caribou have antlers?
[Press-News.org] Activity in brain system that controls eye movements highlights importance of spatial thinkingNew research from UChicago shows that the superior colliculus, a brain region that controls eye movements, also plays an important role in higher cognitive functions like categorization and decision making