Lights, camera, action! Coronavirus spike proteins can be selectively detected in 5 minutes
Light-induced immunoassay coated with novel coronavirus spike proteins found highly sensitive even with weak light like a laser pointer
2024-09-19
(Press-News.org)
Like moths to a flame, microbes can also be moved by light. Using this knowledge, researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University’s Research Institute for Light-induced Acceleration System (RILACS) have demonstrated a method to detect the presence of viruses quickly and using only a small sample.
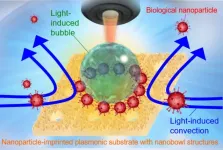
The research team led by OMU Professor Takuya Iida, the director of RILACS, and Associate Professor Shiho Tokonami, the deputy director, report in npj Biosensing on a light-induced immunoassay. Using laser irradiation for less than 1 minute, a nanoparticle-imprinted plasmonic substrate with a series of nanobowl structures (500 nm in diameter for each) could be coated with antibodies for the spike proteins of the novel coronavirus. A 5-milliwatt laser, as low power as commercial laser pointers, could then form bubbles on the biochip that drew virus-mimicking nanoparticles, thereby accelerating the selective detection of the particles.
Because light-induced convection helps move the nanoparticles around so that they end up assembling at the stagnant region between the substrate surface and the bottom of the bubble, a high concentration of the particles was not required. In under 5 minutes, the entire process, from substrate coating to detection, could be completed.
“This study shows that we can shorten the cumbersome antibody coating process and perform rapid and highly sensitive protein detection,” Professor Iida proclaimed. “We believe our findings can contribute to the early diagnosis of not only the novel coronavirus, but possibly also various infectious diseases, cancer, even dementia.”
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-19
Part of many people’s pandemic experience included working from home. Even after lockdowns, videoconferencing remains a big part of life as people continue to work remotely, connect with families and friends online, and attend virtual events hosted on videoconferencing platforms.
Spending hours on video calls, however, can be exhausting and manifest as physical, emotional, or cognitive tiredness – a phenomenon known as videoconferencing fatigue (VF). Now, researchers in Singapore have asked if a relationship between virtual backgrounds and VF exists and ...
2024-09-19
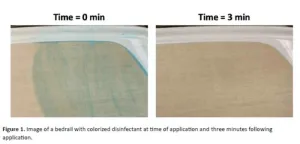
With the Use of Visual Cues, Hospital Rooms Get Nearly 70% Cleaner
New study shows that a simple color additive in disinfectant wipes dramatically improved room cleanliness and even reduced time needed for cleaning
Arlington, Va. — September 19, 2024 — A new study published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) reports a comparison of hospital room cleanliness using standard disinfectant wipes versus wipes with a color additive that allows users to see which surfaces have been sanitized. With the color additive, rooms ...
2024-09-19
In the last decade, auxiliary information has been widely used to address data sparsity. Due to the advantages of feature extraction and the no-label requirement, autoencoder-based methods addressing auxiliary information have become quite popular. However, most existing autoencoder-based methods discard the reconstruction of auxiliary information, which poses a huge challenge for better representation learning and model scalability.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Zhu YI published their new research on 15 August 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
The team proposed a novel representation ...
2024-09-19
Cucumber is a common vegetable on people’s table because of its crisp and refreshing characteristics. In order to meet the market demand throughout the year, cucumber is now mainly planted in facility greenhouses. However, the loss of soil nutrients and the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms are inevitable in successive years of cultivation. Cucumber corynespora leaf spot, also known as cucumber target spot disease, is a major foliar disease that causes cucumber yield reduction, and its pathogen is the Corynespora cassiicola. The pathogen harms cucumber leaves, causing irregular spots and affecting the photosynthesis ...
2024-09-19
Globally, more than 13,000 plant species, equivalent to the entire native flora of Europe, have been naturalized outside their native ranges. A recent study, jointly conducted by scientists from China and the USA, has provided new insights about biodiversity, exotic invasion, and their relationship to climate change.
Published in Nature Plants, the research uncovers the climatic niche mechanisms that shape both the vulnerability of native ecosystems and the invasiveness of exotic species in a warming world.
A long-standing debate exists over the impact of exotic species on native ecosystems and ...
2024-09-19
The Arctic frequently experiences temperatures that support the formation of mixed-phase clouds that contain supercooled liquid droplets and ice crystals. The composition of such clouds plays a crucial role in the region's energy balance and climate system. Clouds with more liquid last longer and reflect more sunlight than those with more ice crystals.
With Arctic warming, meteorologists have been interested in determining the effect of rising temperatures on cloud composition and its broader effect on the region. Climate models generally predict that as the Arctic warms, clouds in the region will ...
2024-09-19
A researcher from the University of Southampton (UK) has found evidence that the treeless, rugged, grassland landscape of the Falkland Islands was home to a lush, diverse rainforest up to 30 million years ago.
A study by Dr Zoë Thomas, leading an international team of scientists, reveals that the South Atlantic archipelago was once covered in cool, wet woodland – similar to the present day rainforests found in Tierra del Fuego, off the tip of South America.
The scientists conducted the research after clues to the whereabouts of buried remains of the ancient forest reached them via word-of-mouth in the tight knit community of Port Stanley, the Falklands’ ...
2024-09-19
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON PRESS RELEASE
Peer reviewed/Systematic review and meta-analysis/People
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL Thursday 19th September at 00:01 UTC (01:01 BST)
Dizziness in older adults is linked to higher risk of future falls
Researchers say it’s not just a normal part of ageing
The first meta-analysis of its kind has shown a conclusive link between older adults experiencing spells of dizziness and a dramatically elevated risk of falling.
Dizziness is a term used to describe sensations such as vertigo, imbalance, light-headedness, and disorientation. It is common in older adults, affecting one in three of those aged 65 years and older. For the first time, dizziness ...
2024-09-18
Some triptans are a more effective treatment for acute migraines than newer, more expensive drugs, finds an analysis of the latest evidence published by The BMJ today.
Triptans work by narrowing blood vessels in the brain and preventing the release of chemicals that cause pain and inflammation.
The findings show that four triptans - eletriptan, rizatriptan, sumatriptan, and zolmitriptan - were better at relieving migraine pain than the recently marketed and more expensive drugs lasmiditan, rimegepant, and ubrogepant, which were comparable to paracetamol ...
2024-09-18
Researchers found that a medicine called ferric carboxymaltose given in drip through the vein works faster and better than an iron tablet taken by mouth for the treatment of anaemia – and it is as safe as the tablet. The findings were published in Lancet Global Health.
Anaemia (low blood level) is a common cause of ill-health or death in mothers and their babies, especially in sub-Saharan Africa and South-East Asia where more than four out of ten pregnant women have the condition. A sizeable proportion of pregnant women in Nigeria proceed to giving birth while still anaemic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Lights, camera, action! Coronavirus spike proteins can be selectively detected in 5 minutes
Light-induced immunoassay coated with novel coronavirus spike proteins found highly sensitive even with weak light like a laser pointer