How do look for microbes in nature that are beneficial to plant?
2024-09-19
(Press-News.org)
Cucumber is a common vegetable on people’s table because of its crisp and refreshing characteristics. In order to meet the market demand throughout the year, cucumber is now mainly planted in facility greenhouses. However, the loss of soil nutrients and the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms are inevitable in successive years of cultivation. Cucumber corynespora leaf spot, also known as cucumber target spot disease, is a major foliar disease that causes cucumber yield reduction, and its pathogen is the Corynespora cassiicola. The pathogen harms cucumber leaves, causing irregular spots and affecting the photosynthesis of cucumber. Under high temperature and high humidity, the conidia of C. cassiicola can directly penetrate the epidermis of the host leaf blade through germination and production of bud tubes, or invade the host through stomata and natural wounds, causing the host to develop. At present, the control of plant fungal diseases mainly relies on agrochemicals and cultivation measures, but due to the frequent use of pesticides, resistance of pathogens has subsequently emerged and the effectiveness of fungicides has decreased. At the same time, consumers are increasingly concerned about the environmental impacts and food residues of fungicides.
Therefore, there is an urgent need for methods that can replace chemical pesticides in the control of plant diseases. Biological control offers a viable solution for plant disease management and is an environmentally friendly method that promotes disease management while maintaining ecosystem balance. Through biological control, plant diseases can be effectively controlled without disturbing the natural balance of flora and fauna. In addition, this method improves soil fertility and is an important tool for sustainable agriculture.
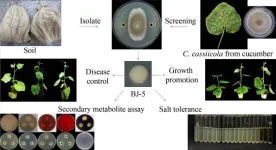
In order to achieve the goal of pollution-free and environmentally friendly, this study screened a biocontrol bacterial strain BJ-5 using Corynespora cassiicola as the target pathogen, and BJ-5 was determined to be Paenarthrobacter nitroguajacolicus by morphological and molecular methods. The effect of BJ-5 on C. cassiicola was studied, including the spore germination, cell membrane permeability, and infected cucumbers. BJ-5 inhibited the germination of C. cassiicola spores in vitro and led to atrophy and deformation of the C. cassiicola budding tubes. BJ-5 caused the relative extracellular conductivity of C. cassiicola mycelia to increase compared with the control. Additionally, BJ-5 reduced the severity of cucumber corynespora leaf spot of cucumber infected with C. cassiicola. The inhibition efficacy of BJ-5 suspension as a foliar spray against cucumber corynespora leaf spot reached 63% inhibition, which is higher than a 5000-fold dilution of Luna-Son SC fungicide. In addition, BJ-5 was tested on the emergence of cucumber seedlings, recording the biomass and photosynthesis of cucumber during the growth period. BJ-5 at 1.5 × 105 CFU·mL–1 promoted the germination of cucumber seeds and increased biomass and photosynthesis at the adult plant stage. Also, the secondary metabolites of BJ-5 were determined. BJ-5 could produce chitinases, siderophore, cellulase, amylase, and protease in the respective medium. Finally, adaptation assay of BJ-5 showed good salt tolerance and good adaptability in alkaline conditions, and that BJ-5 retains inhibition of fungi activity at higher temperatures.
When controlling harmful microorganisms in production, attention should be paid to the impact of pesticides on the environment. Finding natural methods to control harmful microorganisms has great potential and is environmentally friendly. This is the first report of the biocontrol by P. nitroguajacolicus with antagonism to C. cassiicola and promote cucumber growth and indicates that P. nitroguajacolicus may serve as potential biocontrol agents against cucumber corynespora leaf spot fungus.
This study has been published in Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering in 2024, Volume 11, Issue 3. DOI: 10.15302/J-FASE-2024537
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-19
Globally, more than 13,000 plant species, equivalent to the entire native flora of Europe, have been naturalized outside their native ranges. A recent study, jointly conducted by scientists from China and the USA, has provided new insights about biodiversity, exotic invasion, and their relationship to climate change.
Published in Nature Plants, the research uncovers the climatic niche mechanisms that shape both the vulnerability of native ecosystems and the invasiveness of exotic species in a warming world.
A long-standing debate exists over the impact of exotic species on native ecosystems and ...
2024-09-19
The Arctic frequently experiences temperatures that support the formation of mixed-phase clouds that contain supercooled liquid droplets and ice crystals. The composition of such clouds plays a crucial role in the region's energy balance and climate system. Clouds with more liquid last longer and reflect more sunlight than those with more ice crystals.
With Arctic warming, meteorologists have been interested in determining the effect of rising temperatures on cloud composition and its broader effect on the region. Climate models generally predict that as the Arctic warms, clouds in the region will ...
2024-09-19
A researcher from the University of Southampton (UK) has found evidence that the treeless, rugged, grassland landscape of the Falkland Islands was home to a lush, diverse rainforest up to 30 million years ago.
A study by Dr Zoë Thomas, leading an international team of scientists, reveals that the South Atlantic archipelago was once covered in cool, wet woodland – similar to the present day rainforests found in Tierra del Fuego, off the tip of South America.
The scientists conducted the research after clues to the whereabouts of buried remains of the ancient forest reached them via word-of-mouth in the tight knit community of Port Stanley, the Falklands’ ...
2024-09-19
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON PRESS RELEASE
Peer reviewed/Systematic review and meta-analysis/People
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL Thursday 19th September at 00:01 UTC (01:01 BST)
Dizziness in older adults is linked to higher risk of future falls
Researchers say it’s not just a normal part of ageing
The first meta-analysis of its kind has shown a conclusive link between older adults experiencing spells of dizziness and a dramatically elevated risk of falling.
Dizziness is a term used to describe sensations such as vertigo, imbalance, light-headedness, and disorientation. It is common in older adults, affecting one in three of those aged 65 years and older. For the first time, dizziness ...
2024-09-18
Some triptans are a more effective treatment for acute migraines than newer, more expensive drugs, finds an analysis of the latest evidence published by The BMJ today.
Triptans work by narrowing blood vessels in the brain and preventing the release of chemicals that cause pain and inflammation.
The findings show that four triptans - eletriptan, rizatriptan, sumatriptan, and zolmitriptan - were better at relieving migraine pain than the recently marketed and more expensive drugs lasmiditan, rimegepant, and ubrogepant, which were comparable to paracetamol ...
2024-09-18
Researchers found that a medicine called ferric carboxymaltose given in drip through the vein works faster and better than an iron tablet taken by mouth for the treatment of anaemia – and it is as safe as the tablet. The findings were published in Lancet Global Health.
Anaemia (low blood level) is a common cause of ill-health or death in mothers and their babies, especially in sub-Saharan Africa and South-East Asia where more than four out of ten pregnant women have the condition. A sizeable proportion of pregnant women in Nigeria proceed to giving birth while still anaemic ...
2024-09-18
Between 1990 and 2021, the number of people who had a new stroke (up by 70%), died from a stroke (up by 44%), and stroke-related health loss (up by 32%), has risen substantially worldwide.
Stroke is highly preventable, with 84% of the stroke burden in 2021 attributable to 23 modifiable risk factors, including air pollution, excess body weight, high blood pressure, smoking, and physical inactivity—presenting a public health challenge and an opportunity for action.
Notably, the contribution of high temperatures to poor health and early death due to stroke has ...
2024-09-18
A new study in the peer-reviewed Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology estimated the incidence of neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS), a potentially fatal adverse effect of antipsychotic treatment, among individuals ages 5-24 years. Click here to read the article now.
Wayne Ray, PhD, from the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, and coauthors, used national Medicaid data from 2004-2013 to identify patients beginning antipsychotic treatment and calculated the incidence of NMS during antipsychotic use. The investigators identified five ...
2024-09-18
Cyclists choosing a new helmet can see how much protection different helmets offer, thanks to new safety testing and ratings from Imperial College London.
Researchers at Imperial College London have developed a simple new cycle helmet safety rating system with simple-to-understand scores from 0-5, designed to help buyers select which helmet to buy and assist manufacturers in future helmet design. The system is based on extensive new safety testing experiments on medium-sized helmets at Imperial.
Testing on the UK’s 30 most popular helmets, funded by The Road Safety Trust, revealed significant ...
2024-09-18
Pupils with special educational needs and disabilities (SEND) are continuing to fall behind their peers with the gap widening despite the introduction of SEND legislation.
This is according to a new study by Durham University which analysed data on 2.5 million Year 6 pupils across four school years from 2014-2019.
The research suggests there is a need to re-evaluate the policies for SEND provision and how pupils with SEND are supported in schools.
It calls for more investment to support SEND pupils and for increased professional development for teachers and teaching assistants.
Using ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How do look for microbes in nature that are beneficial to plant?




