(Press-News.org) Part of many people’s pandemic experience included working from home. Even after lockdowns, videoconferencing remains a big part of life as people continue to work remotely, connect with families and friends online, and attend virtual events hosted on videoconferencing platforms.
Spending hours on video calls, however, can be exhausting and manifest as physical, emotional, or cognitive tiredness – a phenomenon known as videoconferencing fatigue (VF). Now, researchers in Singapore have asked if a relationship between virtual backgrounds and VF exists and what the underlying mechanisms are.
“We show that the use of different types and contents of virtual backgrounds can contribute to VF,” said Heng Zhang, co-author of the study published in Frontiers in Psychology and a researcher at the Nanyang Technological University Wee Kim Wee School of Communication and Information. “Users who utilize video virtual backgrounds experience higher levels of VF compared to those who use image or blurred virtual backgrounds.”
Tiring backgrounds
The researchers carried out a survey with more than 600 participants in which they asked people whether they use virtual backgrounds, and what type of background (static image, blurred image, video, or no virtual background) they choose. The researchers also measured VF using a five-point scale that indicated levels of general, visual, social, motivational, and emotional fatigue. Participants were aged between 22 and 76 years and worked from home around three days a week.
The results showed that participants who use video backgrounds experienced the highest levels of VF. Users who use blurred backgrounds also experienced higher VF than those who use static images. “Our brains automatically react to new information in the environment. This consumes cognitive resources, which then increases cognitive load and consequently leads to VF,” Zhang explained.
The key, the researchers said, is how much new information is contained in the background. “Image backgrounds initially present new information, but users might gradually shift their attention elsewhere. Blurred backgrounds don’t introduce new information, but occasionally users may catch glimpses of the real environment, which presents new information. Video backgrounds, however, continuously introduce new information, constantly interrupting users’ attention and putting a demand on cognitive resources.”
Virtual nature
In addition to the type of background, the environment that is depicted in the background can also influence VF. “Users who use nature-themed backgrounds report lower levels of VF compared to others,” Zhang said. Other backgrounds, such as office settings or public spaces can increase users’ pressure to self-present as if they actually were in one of those settings, leading to increased fatigue. “In a work setting, a nature-themed image background might be the ideal choice,” Zhang pointed out.
When being on calls in relaxed settings, participants who used lighthearted and funny backgrounds reported the lowest VF levels. It is important that users choose backgrounds appropriately, as different contexts call for different types of backgrounds, the authors said. Making thoughtful choices could not only enhance meeting effectiveness, but also improve the users’ psychological experience, reducing the fatigue associated with videoconferencing.
Optimizing video calls
Their study provides a scientific foundation for further optimizing the videoconferencing experience and helping users make more informed choices, the researchers said. These insights may be especially valuable to users who use video calls in their work and could help them maintain well-being while maximizing the benefits of this way of working.
Nevertheless, the authors said that further study is needed to focus on how different age groups and video call purposes influence the relationship between virtual backgrounds and VF. In addition – and despite of the fact that many people spend significant amounts of time watching themselves when on a video call – the role of other users’ backgrounds on VF needs to be investigated. “A more comprehensive understanding of the role of virtual backgrounds in videoconferencing could provide more targeted recommendations for future research and practice,” concluded Zhang.
END
Your Zoom background could influence how tired you feel after a video call
Researchers found which type of background could leave you feeling less exhausted after a day of videoconferencing
2024-09-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
With the use of visual cues, hospital rooms get nearly 70% cleaner
2024-09-19
With the Use of Visual Cues, Hospital Rooms Get Nearly 70% Cleaner
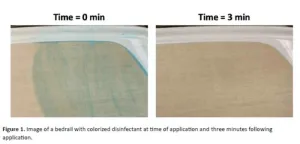
New study shows that a simple color additive in disinfectant wipes dramatically improved room cleanliness and even reduced time needed for cleaning
Arlington, Va. — September 19, 2024 — A new study published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) reports a comparison of hospital room cleanliness using standard disinfectant wipes versus wipes with a color additive that allows users to see which surfaces have been sanitized. With the color additive, rooms ...
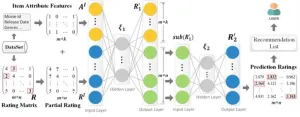
Serial-autoencoder for personalized recommendation
2024-09-19
In the last decade, auxiliary information has been widely used to address data sparsity. Due to the advantages of feature extraction and the no-label requirement, autoencoder-based methods addressing auxiliary information have become quite popular. However, most existing autoencoder-based methods discard the reconstruction of auxiliary information, which poses a huge challenge for better representation learning and model scalability.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Zhu YI published their new research on 15 August 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
The team proposed a novel representation ...
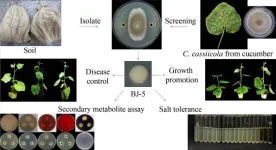
How do look for microbes in nature that are beneficial to plant?
2024-09-19
Cucumber is a common vegetable on people’s table because of its crisp and refreshing characteristics. In order to meet the market demand throughout the year, cucumber is now mainly planted in facility greenhouses. However, the loss of soil nutrients and the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms are inevitable in successive years of cultivation. Cucumber corynespora leaf spot, also known as cucumber target spot disease, is a major foliar disease that causes cucumber yield reduction, and its pathogen is the Corynespora cassiicola. The pathogen harms cucumber leaves, causing irregular spots and affecting the photosynthesis ...
Exotic species invasions enhance biodiversity response to climate change
2024-09-19
Globally, more than 13,000 plant species, equivalent to the entire native flora of Europe, have been naturalized outside their native ranges. A recent study, jointly conducted by scientists from China and the USA, has provided new insights about biodiversity, exotic invasion, and their relationship to climate change.
Published in Nature Plants, the research uncovers the climatic niche mechanisms that shape both the vulnerability of native ecosystems and the invasiveness of exotic species in a warming world.
A long-standing debate exists over the impact of exotic species on native ecosystems and ...
Arctic warming may fuel ice formation in clouds
2024-09-19
The Arctic frequently experiences temperatures that support the formation of mixed-phase clouds that contain supercooled liquid droplets and ice crystals. The composition of such clouds plays a crucial role in the region's energy balance and climate system. Clouds with more liquid last longer and reflect more sunlight than those with more ice crystals.
With Arctic warming, meteorologists have been interested in determining the effect of rising temperatures on cloud composition and its broader effect on the region. Climate models generally predict that as the Arctic warms, clouds in the region will ...
Rugged Falklands landscape was once a lush rainforest
2024-09-19
A researcher from the University of Southampton (UK) has found evidence that the treeless, rugged, grassland landscape of the Falkland Islands was home to a lush, diverse rainforest up to 30 million years ago.
A study by Dr Zoë Thomas, leading an international team of scientists, reveals that the South Atlantic archipelago was once covered in cool, wet woodland – similar to the present day rainforests found in Tierra del Fuego, off the tip of South America.
The scientists conducted the research after clues to the whereabouts of buried remains of the ancient forest reached them via word-of-mouth in the tight knit community of Port Stanley, the Falklands’ ...
Dizziness in older adults is linked to higher risk of future falls
2024-09-19
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON PRESS RELEASE
Peer reviewed/Systematic review and meta-analysis/People
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL Thursday 19th September at 00:01 UTC (01:01 BST)
Dizziness in older adults is linked to higher risk of future falls
Researchers say it’s not just a normal part of ageing
The first meta-analysis of its kind has shown a conclusive link between older adults experiencing spells of dizziness and a dramatically elevated risk of falling.
Dizziness is a term used to describe sensations such as vertigo, imbalance, light-headedness, and disorientation. It is common in older adults, affecting one in three of those aged 65 years and older. For the first time, dizziness ...
Triptans more effective than newer, more expensive migraine drugs
2024-09-18
Some triptans are a more effective treatment for acute migraines than newer, more expensive drugs, finds an analysis of the latest evidence published by The BMJ today.
Triptans work by narrowing blood vessels in the brain and preventing the release of chemicals that cause pain and inflammation.
The findings show that four triptans - eletriptan, rizatriptan, sumatriptan, and zolmitriptan - were better at relieving migraine pain than the recently marketed and more expensive drugs lasmiditan, rimegepant, and ubrogepant, which were comparable to paracetamol ...
Iron given through the vein corrects iron deficiency anaemia in pregnant women faster and better than iron taken by mouth
2024-09-18
Researchers found that a medicine called ferric carboxymaltose given in drip through the vein works faster and better than an iron tablet taken by mouth for the treatment of anaemia – and it is as safe as the tablet. The findings were published in Lancet Global Health.
Anaemia (low blood level) is a common cause of ill-health or death in mothers and their babies, especially in sub-Saharan Africa and South-East Asia where more than four out of ten pregnant women have the condition. A sizeable proportion of pregnant women in Nigeria proceed to giving birth while still anaemic ...
The Lancet Neurology: Air pollution, high temperatures, and metabolic risk factors driving global increases in stroke, with latest figures estimating 12 million cases and over 7 million deaths from st
2024-09-18
Between 1990 and 2021, the number of people who had a new stroke (up by 70%), died from a stroke (up by 44%), and stroke-related health loss (up by 32%), has risen substantially worldwide.
Stroke is highly preventable, with 84% of the stroke burden in 2021 attributable to 23 modifiable risk factors, including air pollution, excess body weight, high blood pressure, smoking, and physical inactivity—presenting a public health challenge and an opportunity for action.
Notably, the contribution of high temperatures to poor health and early death due to stroke has ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] Your Zoom background could influence how tired you feel after a video callResearchers found which type of background could leave you feeling less exhausted after a day of videoconferencing