(Press-News.org) Cooling in the subsurface waters beneath Greenland’s Nioghalvfjerdsfjorden Glacier (79NG) from 2018 to 2021 was driven by European atmospheric blocking, which forced changes in the large-scale ocean circulation of the Nordic seas, researchers report, slowing glacial melt, despite ongoing global warming trends. The findings highlight the importance of regional atmospheric dynamics in influencing glacier stability. Understanding these dynamics is key to predicting the future of glaciers like 79NG in a warming climate. The Greenland Ice Sheet has experienced accelerated mass loss in recent decades due to a warming atmosphere and ocean, significantly contributing to global sea-level rise. About half of this loss comes from increased ice discharge from marine-terminating glaciers like 79NG as they retreat and thin, a process predominantly driven by ocean warming, resulting in submarine melting. Since the late 1990s, ocean heat flux has increased, warming subsurface Atlantic Intermediate Water (AIW) that flows below the 79NG ice tongue, enhancing melt rates. However, from 2018 to 2021, direct observations at 79NG revealed a significant water cooling blow the glacier, which reduced ice melt and slowed glacier thinning. Rebecca McPherson and colleagues show that changes in large-scale atmospheric circulation drove this cooling event. McPherson et al. linked this cooling to increased atmospheric blocking, which disrupted normal weather patterns and funneled cold arctic air into the region. The ocean responded by losing more heat to the atmosphere, slowing Atlantic water circulation and cooling the water reaching 79NG. According to the authors, the cooling pattern resembles European blocking, a weather regime associated with a stationary high-pressure system over Europe. Although Atlantic water temperatures are likely to continue to rise with global climate warming, the projected slowdown of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) could also bring cooler waters to Northeast Greenland’s glaciers. “An improved understanding of the connection between the 79NG and the large-scale ocean and atmospheric circulation leads to further advances in our understanding of the response of the 79NG to changing ocean conditions,” McPherson et al. write.
END
Atmospheric blocking slows ocean-driven glacier melt in Greenland
Summary author: Walter Beckwith
2024-09-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study: Over nearly half a billion years, Earth’s global temperature has changed drastically, driven by carbon dioxide
2024-09-19
Published in the journal Science, the study presents a curve of global mean surface temperature that reveals Earth's temperature has varied more than previously thought over much of the Phanerozoic Eon a period of geologic time when life diversified, populated land and endured multiple mass extinctions. The curve also confirms Earth's temperature is strongly correlated to the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
The start of the Phanerozoic Eon 540 million years ago is marked by the Cambrian ...
Clinical trial could move the needle in traumatic brain injury
2024-09-19
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Subscribe to UCSF News
Department of Defense-funded study aims to end a decades-long impasse in treatment development.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) results in close to 70,000 deaths in the United States every year, and it is the cause of long-term physical, cognitive and mental disability in 5 million Americans. But despite three decades of work, treatments are sorely lacking.
Now, an innovative drug development trial will be available in emergency departments of 18 level 1 trauma sites nationwide. It is launched by UC San Francisco and the Transforming Research and Clinical Knowledge in Traumatic ...
AI model can reveal the structures of crystalline materials
2024-09-19
For more than 100 years, scientists have been using X-ray crystallography to determine the structure of crystalline materials such as metals, rocks, and ceramics.
This technique works best when the crystal is intact, but in many cases, scientists have only a powdered version of the material, which contains random fragments of the crystal. This makes it more challenging to piece together the overall structure.
MIT chemists have now come up with a new generative AI model that can make it much easier to determine the structures of these powdered crystals. The prediction model could help researchers characterize ...
MD Anderson Research Highlights for September 19, 2024
2024-09-19
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Genetic factors underscore disparities in colorectal cancer survival
Patients with colorectal cancer have varied overall survival, but it remains unclear how the frequency of certain gene mutations among different racial and ethnic groups influences outcomes. To investigate, researchers led by John Paul Shen, M.D., and ...
The role of artificial intelligence in advancing intratumoral immunotherapy
2024-09-19
“We explore how integrating these technologies could revolutionize personalized oncology.”
BUFFALO, NY- September 19, 2024 – A new editorial was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on September 17, 2024, entitled, “The emerging role of AI in enhancing intratumoral immunotherapy care.”
As highlighted in the abstract of this editorial, the emergence of immunotherapy (IO), and more recently, intratumoral IO, offers a novel approach to cancer treatment. This method enhances immune responses, allows for combination therapies, and helps reduce systemic adverse events. These techniques aim to ...
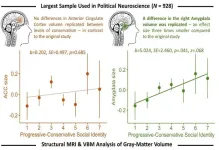
Political ideology is associated with differences in brain structure, but less than previously thought
2024-09-19
Conservative voters have slightly larger amygdalas than progressive voters—by about the size of a sesame seed. In a replication study publishing September 19 in the Cell Press journal iScience, researchers revisited the idea that progressive and conservative voters have identifiable differences in brain morphology, but with a 10x larger and more diverse sample size than the original study. Their results confirmed that the size of a person’s amygdala is associated with their political views but failed to find a consistent association between politics and the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC). Anatomical differences in both ...
Genetic tracing at the Huanan Seafood market further supports COVID animal origins
2024-09-19
A new international collaborative study provides a list of the wildlife species present at the market from which SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, most likely arose in late 2019. The study is based on a new analysis of metatranscriptomic data released by the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The data come from more than 800 samples collected in and around the Huanan Seafood Wholesale market beginning on January 1, 2020, and from viral genomes reported from early COVID-19 patients. The research appears September 19 in the journal Cell.
“This is one of the most ...
Breastfeeding is crucial to shaping infant’s microbes and promoting lung health
2024-09-19
Human breast milk regulates a baby’s mix of microbes, or microbiome, during the infant’s first year of life. This in turn lowers the child’s risk of developing asthma, a new study shows.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health and the University of Manitoba, the study results showed that breastfeeding beyond three months supports the gradual maturation of the microbiome in the infant’s digestive system and nasal cavity, the upper part of the respiratory tract. Conversely, stopping breastfeeding earlier than three months disrupts the paced development of the microbiome and ...
Scientists at the CNIC discover an unexpected involvement of sodium transport in mitochondrial energy generation
2024-09-19
The GENOXPHOS (Functional Genetics of the Oxidative Phosphorylation System) group at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) has discovered a crucial role of sodium in the generation of cellular energy. The study, led by GENOPHOS group leader Dr. José Antonio Enríquez, also involved the participation of scientists from the Complutense University of Madrid, the Biomedical Research Institute at Hospital Doce de Octubre, the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, and the Spanish research networks on frailty and healthy aging (CIBERFES) ...
Origami paper sensors could help early detection of infectious diseases in new simple, low-cost test
2024-09-19
Researchers at Cranfield University have developed an innovative new method for identifying biomarkers in wastewater using origami-paper sensors, enabling the tracking of infectious diseases using the camera in a mobile phone. The new test device is low-cost and fast and could dramatically change how public health measures are directed in any future pandemics.
Wastewater a key way to track infections
Testing wastewater is one of the primary ways to assess the prevalence of infectious diseases in populations. Researchers take samples from various ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
[Press-News.org] Atmospheric blocking slows ocean-driven glacier melt in GreenlandSummary author: Walter Beckwith