(Press-News.org) Background and Goal: Family medicine residency programs are essential for training future primary care physicians. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) program requires family medicine residents to perform two scholarly projects. One must be a quality improvement project, and the second project type is at the program's discretion. This study assessed the scholarly activity output of family medicine residency programs in the U.S., identified institutional factors associated with increased scholarly activity, and determined how well these programs meet ACGME standards.
Study Approach: The study surveyed family medicine residency program directors from across the U.S. to gather data on their programs’ scholarly activity. The survey covered various aspects, including the types of scholarly work produced by residents, the availability of resources such as faculty mentorship and access to Institutional Review Boards, and how often residents exceeded the minimum scholarly activity requirements.
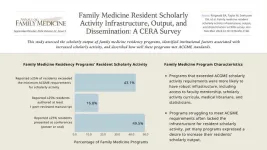
Main Results: 298 program directors completed the survey.
• More than half of the program directors reported fewer than 25% of their residents performed more scholarly activity than ACGME minimum requirements.
• The most common forms of scholarly output were letters to the editor, case reports, and population health projects.
• Only 16.9% of programs reported that more than 25% of their residents published peer-reviewed manuscripts. However, 49.6% reported that over 25% of residents presented their work at conferences, with poster presentations being more common than oral presentations.
• Programs that exceeded ACGME scholarly activity requirements were more likely to have robust infrastructure, including access to faculty mentorship, scholarly activity curricula, IRB, medical librarians, and statisticians.
• Programs struggling to meet ACGME requirements often lacked the necessary infrastructure to support resident scholarly activity. However, many programs expressed a desire to increase their residents’ scholarly output.
Why It Matters: Residency programs that provide strong support—such as mentorship, research support, and technical assistance—for increasing scholarly output help residents meet ACGME requirements and prepare them for future challenges in their medical careers.
Family Medicine Resident Scholarly Activity Infrastructure, Output, and Dissemination: A CERA Survey
Bryce A. Ringwald, MD, et al
OhioHealth Riverside Methodist Hospital Family Medicine Residency Program, Columbus, Ohio
PRE-EMBARGO LINK (Link expires at 5 p.m. September 23rd, 2024)
PERMANENT LINK
END
Robust family medicine residency programs help residents meet scholarly output requirements
2024-09-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Using transparent capsules in dry powder inhalers could significantly improve medication delivery
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: This study examined whether patients with non-reversible chronic airway disease using a transparent capsule in single-dose dry powder inhalers affects the amount of medication delivered. The goal was to determine if patients who use transparent capsules that allow them to see if the medication has been fully inhaled have better inhalation results compared to those using opaque capsules.
Study Approach: Researchers conducted an observational cross-sectional study between October 2020 and October ...
Family physicians in rural hospitals associated with lower cesarean rates and safer maternal care culture
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: The U.S. is experiencing a maternal health crisis, particularly in rural areas. This issue is compounded by rising rates of severe maternal morbidity and mortality. Family physicians often fill critical gaps in care in rural areas where obstetricians are scarce. This study examined how the presence of family physicians in rural hospitals impacts cesarean delivery rates and the overall quality of care during childbirth.
Study Approach: The study analyzed data from rural hospitals in Iowa and collected survey responses from clinicians about their attitudes and practices related to ...
Long COVID patients seek better collaboration with health care professionals
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: “Long COVID” is the continuation or development of new symptoms three months after initial SARS-CoV-2 infection. For many patients with long COVID, primary care is the first point of interaction with the health care system. This study aimed to examine the expectations and experiences of primary care patients seeking treatment for long COVID.
Study Approach: Researchers conducted 20 semistructured interviews between 2022 and 2023 with primary care patients from a ...
EHR messaging before first visit fosters a stronger patient-physician connection
2024-09-23
Inspired by the VA’s My Life, My Story project, this initiative used the Electronic Health Record (EHR) to strengthen the patient-physician relationship. The initiative invited patients to share personal narratives before their first visit with a new primary care physician. Conducted at a regional clinic affiliated with the University of Wisconsin-Madison, the project involved sending secure messages to patients, asking them to describe what they wanted their health care team to know about them as a person. The majority of patients responded ...
SETI AIR announces Cosmic Consciousness residency recipients
2024-09-23
September 23, 2024, Mountain View, CA – The SETI Institute's AIR program announced the recipients of its Cosmic Consciousness residency for mid-career and emerging artists:
Open (Mid-Career) category: The recipients are the artist team of Bart Kuipers, Julie Michele Morin, and daniela brill estrada, with their project Exoplanet Poetry. The artists plan to create a book of poems using an AI trained on chemical data from imagined extraterrestrial sources. The book will be presented as a multi-sensory chemical experience, making ...
Australian crater could offer fresh insight into Earth’s geological history
2024-09-23
A probable crater stretching more than 370 miles, or 600 kilometers, across the heart of Australia could reshape our understanding of Earth’s geological history.
Researcher Daniel Connelly and Virginia Commonwealth University’s Arif Sikder, Ph.D., believe they have found evidence to support the existence of MAPCIS – the Massive Australian Precambrian-Cambrian Impact Structure -– which is a nonconcentric complex crater that could provide new insights into the geological and biological evolution of our planet.
“Working on the MAPCIS project has been an incredible journey,” said Sikder, an associate professor in the Center for ...
New study raises questions about validity of standard model of solar flares
2024-09-23
Solar flares are extremely intense events that occur in the Sun’s atmosphere, lasting anywhere from a few minutes to several hours. According to the standard flare model, the energy that triggers these explosions is transported by accelerated electrons that hurtle from the magnetic reconnection region in the corona to the chromosphere. As the electrons collide with the chromospheric plasma, they deposit their energy in the plasma, which is heated and ionized as a result. They also cause intense radiation in several ...
Paving the way for new treatments
2024-09-23
A University of Missouri researcher has created a computer program that can unravel the mysteries of how proteins work together — giving scientists valuable insights to better prevent, diagnose and treat cancer and other diseases.
Jianlin “Jack” Cheng from Mizzou’s College of Engineering and his student, Nabin Giri, have developed a tool called Cryo2Struct that uses artificial intelligence (AI) to build the three-dimensional atomic structure of large protein complexes, work recently published in Nature Communications. ...
Dream discovery: Melatonin's key role in REM sleep revealed
2024-09-23
A significant breakthrough in the understanding of sleep mechanism opens new promise for treating sleep disorders and associated neuropsychiatric conditions: Scientists have pinpointed the melatonin receptor MT1 as a crucial regulator of REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep.
REM sleep is crucial for dreaming, memory consolidation, and emotional regulation. In the brain, the melatonin MT1 receptor affects a type of neuron that synthesizes the neurotransmitter and hormone noradrenaline, found in an ...
Research quantifying “nociception” could help improve management of surgical pain
2024-09-23
The degree to which a surgical patient’s subconscious processing of pain, or “nociception,” is properly managed by their anesthesiologist will directly affect the degree of post-operative drug side effects they’ll experience and the need for further pain management they’ll require. But pain is a subjective feeling to measure, even when patients are awake, much less when they are unconscious. In a new study, MIT and Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) researchers describe a set of statistical models that objectively quantified nociception during surgery. Ultimately, they hope to help anesthesiologists optimize drug dose and minimize post-operative ...