Parkinson’s disease (PD), also known simply as Parkinson’s, is a disorder of the nervous system that affects millions of people worldwide. The nerve cell damage associated with Parkinson’s can cause tremors, slowed movements, problems with balance, and many other symptoms which worsen gradually over time. Although there is no cure, there are medications available that can treat PD symptoms. Some of these medications, however, have previously unexplained side effects – including impaired decision-making that leads to potentially harmful behaviors such as pathological gambling, binge eating and compulsive shopping.
Now, in a study published online on 14 August 2024 in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, researchers at Fujita Health University in Japan, led by Assistant Professor Hisayoshi Kubota from the Division of Behavioral Neuropharmacology, International Center for Brain Science (ICBS), Fujita Health University, have investigated the mechanism by which a drug called pramipexole or PPX impairs the decision-making process in mice with Parkinson’s disease. The research was co-authored by Professor Taku Nagai from the Division of Behavioral Neuropharmacology, International Center for Brain Science (ICBS), and Professor Hirohisa Watanabe from the Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, both at Fujita Health University.
To take a closer look at the findings of this study, we first need to understand how PPX works to alleviate PD symptoms. PD mainly results from a loss of nerve cells or neurons that produce a compound called dopamine. Some neurons are dependent on dopamine for their regular functioning – they have structures called ‘dopamine receptors’ which can be thought of as locks which can then be activated using dopamine as the ‘key’. Drugs like PPX can imitate the function of dopamine and bind to these receptors instead, especially in patients with PD who lack dopamine-producing neurons.
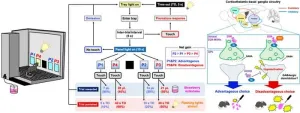
To study the effects of PPX on PD, the researchers injected the brains of mice with a toxin called 6-hydroxydopamine (or 6-OHDA). 6-OHDA damages neurons in a very similar manner to that observed in the brains of patients with PD. The mice were treated with PPX and then subjected to a touchscreen-based ‘gambling task’ to test their decision-making skills. Interestingly, these mice picked the high-risk/high-reward option much more often – they opted for a disadvantageous outcome where they received a large reward (of strawberry milkshake), which also comes with an increased risk of a large punishment by exposure to flashing lights.
But which part of the brain is responsible for this behavior? Investigating the brains of mice treated with PPX revealed that a region deep inside the brain called the external globus pallidus (GPe) was hyperactivated, or showed a much higher level of neuron activity. The researchers then chemically inhibited the neurons in the GPe, which actually reduced disadvantageous risk-taking activity in the mice. This proved that hyperactivation of the GPe was indeed responsible for poor decision-making in the mice treated with PPX.
This study has huge implications for treating patients with Parkinson’s disease. “Our findings could lead to the development of new medications or interventions that specifically target the external globus pallidus,” explains Dr. Kubota. ‘This would help to prevent or reduce decision-making impairments in Parkinson's disease patients.’
Besides helping medical professionals develop better treatments for Parkinson’s disease, these findings can also help improve awareness among affected patients, their families, as well as the general public. Dr. Kubota, explains that “Investigating how Parkinson's disease medications affect decision-making will help the public to better understand the complexity of the disease and its treatment.” He also says “This will benefit patients, their families and carers, and motivate them to consider early care and preventive strategies.”
These findings shed new light on the complex processes in the brain that aid our everyday decision-making skills, and promise to improve quality of life for patients affected by Parkinson’s disease. Maybe we can take away some important lessons from this study as well, and think twice before we indulge in poor decision-making in our daily lives!
***
Reference
Title of original paper: Pramipexole Hyperactivates the External Globus Pallidus and Impairs Decision-Making in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease
Journal: International Journal of Molecular Sciences
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25168849
About Fujita Health University
Fujita Health University is a private university situated in Toyoake, Aichi, Japan. It was founded in 1964 and houses one of the largest teaching university hospitals in Japan in terms of the number of beds. With over 900 faculty members, the university is committed to providing various academic opportunities to students internationally. Fujita Health University has been ranked eighth among all universities and second among all private universities in Japan in the 2020 Times Higher Education (THE) World University Rankings. THE University Impact Rankings 2019 visualized university initiatives for sustainable development goals (SDGs). For the “good health and well-being” SDG, Fujita Health University was ranked second among all universities and number one among private universities in Japan. The university became the first Japanese university to host the "THE Asia Universities Summit" in June 2021. The university’s founding philosophy is “Our creativity for the people (DOKUSOU-ICHIRI),” which reflects the belief that, as with the university’s alumni and alumnae, current students also unlock their future by leveraging their creativity.
Website: https://www.fujita-hu.ac.jp/en/index.html
About Assistant Professor Hisayoshi Kubota from Fujita Health University
Hisayoshi Kubota is an Assistant professor at the Division of Behavioral Neuropharmacology in the International Center for Brain Science (ICBS), Fujita Health University, and he is the primary author of this paper. With 20+ publications in the field, his current research interests include identifying the neural circuits involved in behavioral addictions and elucidating the pathological mechanisms of psychiatric disorders, focusing on risk genes.
Funding information
This work was supported by the following funding sources: AMED grant numbers JP21wm0425017 (T.N.), 21wm0425008 (T.N.), and JP23tm0524001 (T.N.); JSPS KAKENHI grant numbers 23K27360 (T.N.), 23H02669 (T.N.), 24K18223 (H.K.), and 24K02218 (T.N.); faculty research grant of Fujita Health University, CSC-FHU joint scholarship program (T.N.); and The Hori Sciences and Arts Foundation (H.K.).
END