(Press-News.org) The Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), part of City of Hope, today announced that is has received Certified Service Provider status from PacBio, a leading developer of high-quality, highly accurate sequencing solutions. The certification follows the addition of the Revio and Onso platforms to TGen’s Collaborative Sequencing Service Center, which provides investigators with access to best-in-class short and long read sequencing instrumentation to support all analysis needs including whole genome, telomere-telomere assembly, exomes, RNA sequencing, and full-length transcript sequencing.
To achieve certification, providers must undergo a rigorous process including training on PacBio sample processing and data analysis workflows.
“We’re excited to be recognized as a Certified Service Provider for PacBio,” said Collaborative Sequencing Service Center director Jonathan Keats, Ph.D., who is also an assistant professor in the Clinical Genomics and Therapeutics Division at TGen. “This partnership highlights the efforts we undertook to diversify our sequencing offerings into accurate long-read and highly accurate short-reads to meet researchers needs in their discovery and development efforts.”
The main goal of TGen’s Collaborative Sequencing Center (CSC) is to offer researchers access to advanced genomic analysis platforms and data processing systems to tackle today’s scientific challenges by staying at the forefront of sequencing technology.
“We are delighted to announce TGen as the first Certified Service Provider for Onso,” said Jeff Eidel, chief commercial officer at PacBio. “The robust certification process requires providers to meet very strict training and quality standards. TGen and PacBio are both dedicated to supporting the scientific community in their genomic research projects, and we look forward to continuing to grow our partnership as TGen scales on our Onso and Revio platforms.”
The Onso short read sequencer uses sequencing by binding (SBB) technology to achieve industry leading base call accuracy with >90% of bases exceeding Q40 and median base qualities exceeding Q50, one error in 100,000 bases. The flow cells have two independently addressed lanes that together can produce 800-1000 million paired end reads using 100x100 or 150x150 sequencing formats. There is also a single read 200 cycle option available. A recent TGen-led study utilizing the PacBio SBB technology detected target SNPs down to 0.01% at 100,000x depth and 0.1% at 20,000x, without any error correction methods.
Revio offers high-volume, accurate long-read sequencing through circular consensus sequencing (CCS), producing high-quality HiFi reads. The device has four separate sequencing positions, each using an individual SMRT-cell with 25 million zero-mode waveguide (ZMW) sequencing wells. In 24 hours, one SMRT-cell can easily generate greater than 30x coverage of a human genome with the workflows in place at TGen. Besides long, accurate reads from unaltered DNA, the system detects 5mC methylation at CpG sites in eukaryotes and 4mC and 6mA methylation in prokaryotes. The KINNEX array kits are designed both to enable the efficient analysis of full-length RNA isoforms from bulk or single-cell RNA samples and to perform complete 16S ribosomal RNA analysis of microbial populations.
TGen’s comprehensive service offerings are available to academic institutions, non-profit organizations, and commercial enterprises, providing tailored solutions for a wide range of research and development needs. For questions or quotes, please contact thecsc@tgen.org or visit the website at tgen.org/csc
END
TGen named Certified Service Provider for PacBio
Addition of the Revio and Onso enhances TGen’s Collaborative Sequencing Center offerings
2024-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The environmental impacts of genetically modified crops
2024-09-24
Genetically modified (GM) crops are widely used around the world, but their effects on the environment need to be explored more.
New research, published in Science on August 30, 2024, takes a look at common genetic modifications in four crops: soybean, corn, cotton, and canola. Although GM crops can produce more yield and profits, it can lead to changes in agricultural practices that could inadvertently impact the environment. For example, farmers may increase pesticide use as crops become more resistant to herbicides ...
Graphene spike mat and fridge magnet technology to fight against antibiotic resistance
2024-09-24
With strong bactericidal properties, graphene has the potential to become a game changer in the fight against antibiotic-resistant bacteria. So far there have been no efficient ways to control these properties – and thus no way to make use of graphene’s potential in healthcare. Now researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, in Sweden, have solved the problem by using the same technology found in an ordinary fridge magnet. The result of which, is an ultra-thin acupuncture-like surface that can act as a coating on catheters and implants – killing 99.9 percent of all bacteria on a surface.
Healthcare-associated infections are a widespread problem around ...
Queen’s University Belfast to launch Figshare-powered repository to share, showcase and manage its research data and theses
2024-09-24
Figshare, a leading provider of institutional repository infrastructure that supports open research, is pleased to announce that Queen’s University Belfast has chosen Figshare as its new repository platform to store, showcase and manage its research data and theses outputs.
Queen’s – a prestigious Russell Group UK university and ranked in the top 250 universities in the world – chose Figshare as its new repository platform owing to a selection of core features and functionality that will support the team in creating proficient ...
Nursing shortages can be deadly
2024-09-24
A new paper in the British Journal of Surgery, published by Oxford University Press, shows that nursing shortages result in longer hospital stays and worse patient outcomes, including higher mortality.
Doctors perform over 300 million surgeries each year worldwide. Observers have expressed concern about the quality of care for adult patients undergoing surgery and the rising cost of avoidable complications, extended hospitalizations, and readmissions. Some 55% of surgical site infections are preventable.
Until now ...
60-second heartbeat recordings offer window into autonomic health after severe brain trauma
2024-09-24
For the over 1 million Americans who survive severe traumatic brain injuries each year, the road to recovery is often long and challenging. Disruption of the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary functions like heart rate, is a common yet poorly understood consequence of TBI. While heart rate variability (HRV) is a widely used measure of autonomic function, the standard 5-minute recording can be cumbersome for patients with cognitive and physical impairments.
Now, a team led by researchers at Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina has found ...
Psychedelic drug psilocybin changes brain connectivity to treat body dysmorphic disorder
2024-09-24
New York, NY - Body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) is a debilitating mental illness characterized by an obsessive preoccupation with perceived flaws in one's physical appearance. Patients with BDD often have distorted self-image, intrusive thoughts, and compulsive behaviors that significantly impair daily functioning and quality of life. Current therapies have limited efficacy, leaving many sufferers without relief.
A new study led by researchers at Columbia University and published in Psychedelics (Genomic Press, New York, USA) provides hope by revealing how the psychedelic drug ...
Google trends reveals surge in ADHD medication searches during COVID-19 pandemic
2024-09-24
In a groundbreaking study published in Brain Medicine (Genomic Press), UCI researchers have uncovered a striking correlation between internet searches for ADHD medications and actual prescription rates during the COVID-19 pandemic. This finding opens up new possibilities for using online search data to predict and prevent prescription drug shortages.
The study, led by Dr. Steven Grieco from the University of California, Irvine, analyzed Google Trends data spanning 20 years, with a particular focus on the period following the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in January 2020. The researchers found a significant surge in searches for ADHD medications during ...
Multiple sclerosis symptoms at onset linked to long-term disability
2024-09-24
In a significant advance for multiple sclerosis (MS) research, a new study has uncovered a potential link between certain initial symptoms and long-term disability outcomes. The research, published in the latest issue of Brain Medicine (Genomic Press, New York), could have far-reaching implications for early intervention strategies and treatment decisions in MS care.
Led by Dr. João Pedro F. Gonçalves from the Federal University of Bahia, Brazil, the study analyzed data from 195 MS patients, focusing ...
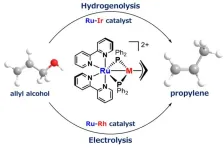
New catalyst developed for sustainable propylene production from biomass
2024-09-24
Achieving carbon neutrality requires the effective use of renewable biomass. In the production of biodiesel, for instance, glycerol is generated as a major byproduct. Researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University have developed a new catalyst that efficiently converts a derivative of glycerol into bio-based propylene, contributing to sustainable chemical production.
Propylene is typically produced from petroleum and is widely used in the manufacture of plastics, such as automobile bumpers and food containers. The research team, led by Associate Professor Shin Takemoto and Professor Hiroyuki Matsuzaka from the Graduate School of Science, developed a catalyst that ...
Nearly 200 potential mammary carcinogens found in food contact materials: new study highlights regulatory shortcomings
2024-09-24
About this study: Research identifies nearly 200 potential breast carcinogens in food contact materials, including plastics and paper, highlighting widespread exposure despite existing regulation. The findings underscore an urgent need for stronger preventative measures to reduce these chemicals in everyday products.
Researchers from the Food Packaging Forum identify and discuss nearly 200 potential breast carcinogens that have been detected in food contact materials (FCMs) on the market. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] TGen named Certified Service Provider for PacBioAddition of the Revio and Onso enhances TGen’s Collaborative Sequencing Center offerings