(Press-News.org) Figshare, a leading provider of institutional repository infrastructure that supports open research, is pleased to announce that Queen’s University Belfast has chosen Figshare as its new repository platform to store, showcase and manage its research data and theses outputs.
Queen’s – a prestigious Russell Group UK university and ranked in the top 250 universities in the world – chose Figshare as its new repository platform owing to a selection of core features and functionality that will support the team in creating proficient research management workflows for its outputs.
Notably, Queen’s had an interest in providing an accessible submission page for theses that didn’t require users to have an existing account or relationship with the platform they were submitting to – a use case Figshare supports with its option of a non-logged-in submission page.
Queen’s was also looking for a platform that would be able to handle the upload and storage of large files, particularly in regards to the growing need for research data sharing. The existing publications-focused repository in place at Queen’s lacked the flexibility needed to support the breadth and size of some research data being produced, and Figshare was identified as a suitable alternative platform to support this, with its 5TB upload limit on single files.
The team at Queen’s also saw the potential of Figshare’s flexible API and hope to be able to utilize its functionality to assist in their reporting and integration needs. As the new repository project at Queen’s evolves, the intention is to set up an integration between its CRIS system (Pure) and the Figshare repository, to create a joined-up environment and a comprehensive research management workflow. This will drive the visibility and potential impact of open research data and theses outputs.
Jane O’Neill, University Librarian, Academic Services at Queen’s, said: “The ability to issue persistent identifiers (e.g. DOIs) to our thesis content will be facilitated by the new Figshare repository. This is an exciting development, which will ensure that content is more FAIR-enabled (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable). Assigning DOIs to digital content is probably the most important element to achieving FAIR, ensuring permanence, persistent identification and helping other researchers cite the work of our authors.
Improvements in terms of the scale and scope of the new repository will also benefit the look and feel of its content, including access controls for datasets, ensuring for the first time that we have a specifically dedicated thesis and data repository, designed and developed overtly for this unique type of content.”
Mark Hahnel, Figshare Founder and Digital Science’s VP of Open Research, said: “It’s wonderful to see the prestigious Queen’s University Belfast choose Figshare to support the open and FAIR sharing of research data for its research community. I’m also thrilled that the Figshare-powered repository will be used to showcase Queen’s theses, with the platform’s capabilities lending itself to such a broad range of disciplines; I’m very much looking forward to seeing the breadth of research that will be shared in the new repository.”
About Queen’s University Belfast
A member of the Russell Group UK’s 24 leading research-intensive universities, Queen’s University Belfast is an international centre of research and education, with a student-centred ethos. Queen’s is ranked 4th in the world for international outlook (Times Higher Education World University Rankings 2024), 2nd in the UK for entrepreneurial impact (Octopus Ventures, 2022) and in the top 150 in the world for research quality (Times Higher Education World University Rankings 2024). Queen’s is also ranked 85th in the world in the Times Impact Rankings 2023.
About Figshare
Figshare, a Digital Science Solution, is a provider of institutional repository infrastructure. Our solutions help institutions share, showcase and manage their research outputs in a discoverable, citable, reportable and transparent way. We support institutions in meeting the growing demands for research to become open, freer, FAIRer and more connected. We provide the flexibility and control for you to create research management workflows that work for you. We take care of implementation, updates, security and maintenance – ensuring you and your researchers can always depend on your repository, leaving you to focus on what really matters; research and its impact on the world.
About Digital Science
Digital Science is an AI-focused technology company providing innovative solutions to complex challenges faced by researchers, universities, funders, industry and publishers. We work in partnership to advance global research for the benefit of society. Through our brands – Altmetric, Dimensions, Figshare, IFI CLAIMS Patent Services, metaphacts, OntoChem, Overleaf, ReadCube, Scismic, Symplectic, and Writefull – we believe when we solve problems together, we drive progress for all. Visit digital-science.com and follow @digitalsci on X or on LinkedIn.
Media contacts
Simon Linacre, Head of Content, Brand & Press, Digital Science: Mobile +44 7484 381477, s.linacre@digital-science.com
David Ellis, Press, PR & Social Manager, Digital Science: Mobile +61 447 783 023, d.ellis@digital-science.com
END
Queen’s University Belfast to launch Figshare-powered repository to share, showcase and manage its research data and theses
2024-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nursing shortages can be deadly
2024-09-24
A new paper in the British Journal of Surgery, published by Oxford University Press, shows that nursing shortages result in longer hospital stays and worse patient outcomes, including higher mortality.
Doctors perform over 300 million surgeries each year worldwide. Observers have expressed concern about the quality of care for adult patients undergoing surgery and the rising cost of avoidable complications, extended hospitalizations, and readmissions. Some 55% of surgical site infections are preventable.
Until now ...
60-second heartbeat recordings offer window into autonomic health after severe brain trauma
2024-09-24
For the over 1 million Americans who survive severe traumatic brain injuries each year, the road to recovery is often long and challenging. Disruption of the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary functions like heart rate, is a common yet poorly understood consequence of TBI. While heart rate variability (HRV) is a widely used measure of autonomic function, the standard 5-minute recording can be cumbersome for patients with cognitive and physical impairments.
Now, a team led by researchers at Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina has found ...
Psychedelic drug psilocybin changes brain connectivity to treat body dysmorphic disorder
2024-09-24
New York, NY - Body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) is a debilitating mental illness characterized by an obsessive preoccupation with perceived flaws in one's physical appearance. Patients with BDD often have distorted self-image, intrusive thoughts, and compulsive behaviors that significantly impair daily functioning and quality of life. Current therapies have limited efficacy, leaving many sufferers without relief.
A new study led by researchers at Columbia University and published in Psychedelics (Genomic Press, New York, USA) provides hope by revealing how the psychedelic drug ...
Google trends reveals surge in ADHD medication searches during COVID-19 pandemic
2024-09-24
In a groundbreaking study published in Brain Medicine (Genomic Press), UCI researchers have uncovered a striking correlation between internet searches for ADHD medications and actual prescription rates during the COVID-19 pandemic. This finding opens up new possibilities for using online search data to predict and prevent prescription drug shortages.
The study, led by Dr. Steven Grieco from the University of California, Irvine, analyzed Google Trends data spanning 20 years, with a particular focus on the period following the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in January 2020. The researchers found a significant surge in searches for ADHD medications during ...
Multiple sclerosis symptoms at onset linked to long-term disability
2024-09-24
In a significant advance for multiple sclerosis (MS) research, a new study has uncovered a potential link between certain initial symptoms and long-term disability outcomes. The research, published in the latest issue of Brain Medicine (Genomic Press, New York), could have far-reaching implications for early intervention strategies and treatment decisions in MS care.
Led by Dr. João Pedro F. Gonçalves from the Federal University of Bahia, Brazil, the study analyzed data from 195 MS patients, focusing ...
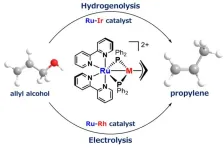
New catalyst developed for sustainable propylene production from biomass
2024-09-24
Achieving carbon neutrality requires the effective use of renewable biomass. In the production of biodiesel, for instance, glycerol is generated as a major byproduct. Researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University have developed a new catalyst that efficiently converts a derivative of glycerol into bio-based propylene, contributing to sustainable chemical production.
Propylene is typically produced from petroleum and is widely used in the manufacture of plastics, such as automobile bumpers and food containers. The research team, led by Associate Professor Shin Takemoto and Professor Hiroyuki Matsuzaka from the Graduate School of Science, developed a catalyst that ...
Nearly 200 potential mammary carcinogens found in food contact materials: new study highlights regulatory shortcomings
2024-09-24
About this study: Research identifies nearly 200 potential breast carcinogens in food contact materials, including plastics and paper, highlighting widespread exposure despite existing regulation. The findings underscore an urgent need for stronger preventative measures to reduce these chemicals in everyday products.
Researchers from the Food Packaging Forum identify and discuss nearly 200 potential breast carcinogens that have been detected in food contact materials (FCMs) on the market. ...
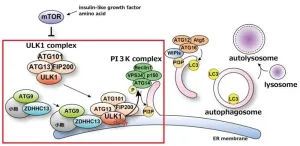
Mechanism behind autophagy trigger unveiled
2024-09-24
Osaka, Japan – An international research team led by Osaka University has identified a new mechanism crucial for the initiation of autophagy, a self-degradation process cells use to eliminate unneeded or damaged components. In recent years, autophagy has also been recognized for its roles in aging and lifespan regulation.
During autophagy, intracellular molecules and structures are sequestered within a membrane-bound structure known as an autophagosome, which is subsequently degraded in lysosomes. It is well-established that the formation of autophagosomes ...
Study: Good nutrition boosts honey bee resilience against pesticides, viruses
2024-09-24
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — In a new study, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign tackled a thorny problem: How do nutritional stress, viral infections and exposure to pesticides together influence honey bee survival? By looking at all three stressors together, the scientists found that good nutrition enhances honey bee resilience against the other threats.
Their findings are detailed in the journal Science of the Total Environment.
“Multiple stressors are often bad for survival,” said graduate student Edward Hsieh, who led the research ...
New battery cathode material could revolutionize EV market and energy storage
2024-09-24
A multi-institutional research team led by Georgia Tech’s Hailong Chen has developed a new, low-cost cathode that could radically improve lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) — potentially transforming the electric vehicle (EV) market and large-scale energy storage systems.
“For a long time, people have been looking for a lower-cost, more sustainable alternative to existing cathode materials. I think we’ve got one,” said Chen, an associate professor with appointments in the ...