(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan – An international research team led by Osaka University has identified a new mechanism crucial for the initiation of autophagy, a self-degradation process cells use to eliminate unneeded or damaged components. In recent years, autophagy has also been recognized for its roles in aging and lifespan regulation.
During autophagy, intracellular molecules and structures are sequestered within a membrane-bound structure known as an autophagosome, which is subsequently degraded in lysosomes. It is well-established that the formation of autophagosomes involves the coordinated action of multiple autophagy-related proteins.
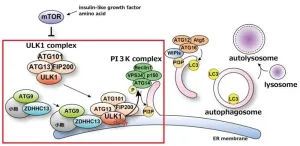
Previously, the research group revealed that autophagosome formation takes place on the endoplasmic reticulum membrane in close proximity to mitochondria within cells. They also discovered that the PI3K complex, an autophagy-related protein, is essential for this formation process. The activity of the PI3K complex is controlled by the ULK1 complex.
The ULK1 complex is known to translocate from the cytoplasm to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane, where autophagosomes are formed at the onset of autophagy. However, the underlying mechanism and significance of this process were not fully understood until now. In a recent article published in Nature Communications, the research team revealed that the palmitoylation of ULK1 triggers a series of reactions that initiate autophagy.
The team identified ZDHHC13, a palmitoylation enzyme, as a key player in this process through their search for intracellular factors involved in the initiation of autophagy.
Mutations of ZDHHC13 have been linked to various diseases, including Huntington’s disease, while autophagy is also implicated in the development and progression of conditions such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
Senior author Maho Hamasaki explained, “Our team discovered that ZDHHC13 palmitoylates ULK1, thereby localizing the ULK1 complex to autophagosome formation sites. This palmitoylation is also involved in the phosphorylation of the ATG14L protein within the PI3K complex, which in turn regulates the activity of the PI3K complex.”
Understanding the molecular mechanisms that initiate autophagy is expected to enhance our knowledge of autophagy-related diseases.
Lead author Keisuke Tabata added, “Autophagy not only provides a nutrient source through intracellular degradation but also plays a crucial role in maintaining normal cellular function and preventing various pathologies. We will continue to investigate how autophagy begins, furthering our understanding of the mechanisms behind related diseases.”
###
The article, “Palmitoylation of ULK1 by ZDHHC13 plays a crucial role in autophagy,” was published in Nature Communications at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-51402-w
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world. Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
END
Mechanism behind autophagy trigger unveiled
A research team led by Osaka University has uncovered a novel mechanism essential for initiating autophagy
2024-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study: Good nutrition boosts honey bee resilience against pesticides, viruses
2024-09-24
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — In a new study, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign tackled a thorny problem: How do nutritional stress, viral infections and exposure to pesticides together influence honey bee survival? By looking at all three stressors together, the scientists found that good nutrition enhances honey bee resilience against the other threats.
Their findings are detailed in the journal Science of the Total Environment.
“Multiple stressors are often bad for survival,” said graduate student Edward Hsieh, who led the research ...
New battery cathode material could revolutionize EV market and energy storage
2024-09-24
A multi-institutional research team led by Georgia Tech’s Hailong Chen has developed a new, low-cost cathode that could radically improve lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) — potentially transforming the electric vehicle (EV) market and large-scale energy storage systems.
“For a long time, people have been looking for a lower-cost, more sustainable alternative to existing cathode materials. I think we’ve got one,” said Chen, an associate professor with appointments in the ...
Inexpensive drug can prevent cerebral palsy in premature babies
2024-09-24
Giving women at risk of premature birth a simple magnesium sulphate infusion (or ‘drip’) can prevent their babies from developing cerebral palsy, a recent Cochrane review has confirmed. The drug itself costs approximately £5 (~$6.50) per dose in England, and requires hospital admission with experienced staff to administer the drug safely to the mother. A new editorial calls for this intervention to be implemented more widely and equitably, as it is still not consistently available worldwide.
The first Cochrane review showing that magnesium sulphate protects premature babies against cerebral palsy was published in 2009, and the recent update includes newer trials which further ...
Studying sex-specific pain levels in wheelchair users
2024-09-23
Josh Leonardis received funding from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health to study why female manual wheelchair users experience shoulder pain and pathology at greater rates than males.
Leonardis is a researcher at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, an assistant professor of health and kinesiology at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the director of the Musculoskeletal Morphology and Biomechanics Laboratory.
“It’s well-documented in literature that ...
UChicago Medicine performs first-in-Illinois procedure to treat bladder leaks
2024-09-23
UChicago Medicine has become the first medical center in Illinois to implant the Revi neuromodulation device, an exciting new treatment option that could offer relief for patients with urinary urgency incontinence (UUI).
“I am really happy that we can offer this innovative approach to all our patients and very proud to be at the real forefront of medicine as the first in the state to have done this surgery,” said urologist Ervin Kocjancic, MD, the surgeon who performed the procedure.
UUI, a chronic, debilitating, ...
Previously unknown Neolithic society in Morocco discovered: shining light on North Africa’s role in Mediterranean prehistory
2024-09-23
Multi-disciplinary archaeological survey at the site of Oued Beht, Morocco, reveals a previously unknown 3400–2900 BC farming society.
This is the earliest and largest agricultural complex yet found in Africa beyond the Nile.
It shares similar features with contemporaneous sites in Iberia.
This suggests the Maghreb was instrumental to the shaping of the western Mediterranean during the fourth and third millennia BC.
Archaeological fieldwork in Morocco has discovered the earliest, previously unknown farming society from a poorly understood period of north-west African prehistory.
This study, published today in Antiquity, reveals for the first ...
Study finds PrEP use among gay and bisexual men in Ontario linked to higher STI rates
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is a preventive medicine that reduces the risk of contracting HIV. There is concern that PrEP use may be associated with an increase in bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis among men who are gay or bisexual. This study explored the relationship between PrEP use and the rates of bacterial STIs over time.
Study Approach: Researchers used data from the iCruise Study, an online longitudinal study of men who are gay or bisexual or have sex with men, in Ontario from July 2017 to April 2018. The study examined how PrEP use related to the number of self-reported ...
Technology-assisted health coaching intervention does not improve weight loss in veterans and high-risk patients
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: Obesity is a significant health issue, particularly among veterans and racial/ethnic minority groups. Primary care is a key setting for addressing obesity. However, many barriers, including time constraints and limited patient engagement, make effective treatment challenging. This study evaluated whether a technology-assisted health coaching intervention called Goals for Eating and Moving (GEM) could help high-risk patients lose weight more effectively than enhanced usual care (EUC).
Study Approach: Researchers conducted a two-arm, cluster-randomized controlled trial involving 19 primary care teams ...
Underserved patients reduce blood pressure and heart disease risk using remote monitoring program
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: Underserved communities are at higher risk for uncontrolled high blood pressure (hypertension), which can lead to heart disease and higher death rates. This study evaluated the impact of a remote monitoring program called DIG IT on blood pressure control in underserved patients at a Federally Qualified Health Center (FQHC) in Orange County, California.
Study Approach: Researchers compared two groups: 70 patients using the DIG IT program, which includes digital blood pressure monitoring, medication management, and a team-based care approach, and a historical control group of 70 patients who received standard care without digital tools. The ...
The HOMER study evolves to adapt opioid treatment research amid COVID-19 challenges
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: The HOMER study was launched to determine the most effective setting for starting buprenorphine treatment for opioid use disorder. The study faced challenges including shifts in health care delivery, changes in patient preferences, and the emergence of telehealth. The goal was to adapt the study to these circumstances while maintaining its focus on patient-centered care and effective treatment outcomes.
Key Insights: The HOMER study had to quickly adapt to challenges brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic. With community input, the study design evolved to include a third arm, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
[Press-News.org] Mechanism behind autophagy trigger unveiledA research team led by Osaka University has uncovered a novel mechanism essential for initiating autophagy