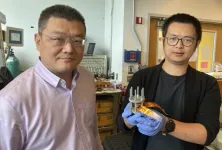
(Press-News.org) A multi-institutional research team led by Georgia Tech’s Hailong Chen has developed a new, low-cost cathode that could radically improve lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) — potentially transforming the electric vehicle (EV) market and large-scale energy storage systems.
“For a long time, people have been looking for a lower-cost, more sustainable alternative to existing cathode materials. I think we’ve got one,” said Chen, an associate professor with appointments in the George W. Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering and the School of Materials Science and Engineering.
The revolutionary material, iron chloride (FeCl3), costs a mere 1-2% of typical cathode materials and canstore the same amount of electricity. Cathode materials affect capacity, energy, and efficiency, playing a major role in a battery’s performance, lifespan, and affordability.
“Our cathode can be a game-changer,” said Chen, whose team describes its work in Nature Sustainability. “It would greatly improve the EV market — and the whole lithium-ion battery market.”
First commercialized by Sony in the early 1990s, LIBs sparked an explosion in personal electronics, like smartphones and tablets. The technology eventually advanced to fuel electric vehicles, providing a reliable, rechargeable, high-density energy source. But unlike personal electronics, large-scale energy users like EVs are especially sensitive to the cost of LIBs.
Batteries are currently responsible for about 50% of an EV’s total cost, which makes these clean-energy cars more expensive than their internal combustion, greenhouse-gas-spewing cousins. The Chen team’s invention could change that.
Building a Better Battery
Compared to old-fashioned alkaline and lead-acid batteries, LIBs store more energy in a smaller package and power a device longer between charges. But LIBs contain expensive metals, including semiprecious elements like cobalt and nickel, and they have a high manufacturing cost.
So far, only four types of cathodes have been successfully commercialized for LIBs. Chen’s would be the fifth, and it would represent a big step forward in battery technology: the development of an all-solid-state LIB.
Conventional LIBs use liquid electrolytes to transport lithium ions for storing and releasing energy. They have hard limits on how much energy can be stored, and they can leak and catch fire. But all-solid-state LIBs use solid electrolytes, dramatically boosting a battery’s efficiency and reliability and making it safer and capable of holding more energy. These batteries, still in the development and testing phase, would be a considerable improvement.
As researchers and manufacturers across the planet race to make all-solid-state technology practical, Chen and his collaborators have developed an affordable and sustainable solution. With the FeCl3 cathode, a solid electrolyte, and a lithium metal anode, the cost of their whole battery system is 30-40% of current LIBs.
“This could not only make EVs much cheaper than internal combustion cars, but it provides a new and promising form of large-scale energy storage, enhancing the resilience of the electrical grid,” Chen said. “In addition, our cathode would greatly improve the sustainability and supply chain stability of the EV market.”
Solid Start to New Discovery
Chen’s interest in FeCl3 as a cathode material originated with his lab’s research into solid electrolyte materials. Starting in 2019, his lab tried to make solid-state batteries using chloride-based solid electrolyteswith traditional commercial oxide-based cathodes. It didn’t go well — the cathode and electrolyte materials didn’t get along.
The researchers thought a chloride-based cathode could provide a better pairing with the chloride electrolyte to offer better battery performance.
“We found a candidate (FeCl3) worth trying, as its crystal structure is potentially suitable for storing and transporting Li ions, and fortunately, it functioned as we expected,” said Chen.
Currently, the most popularly used cathodes in EVs are oxides and require a gigantic amount of costly nickel and cobalt, heavy elements that can be toxic and pose an environmental challenge. In contrast, the Chen team’s cathode contains only iron (Fe) and chlorine (Cl)—abundant, affordable, widely used elements found in steel and table salt.
In their initial tests, FeCl3 was found to perform as well as or better than the other, much more expensive cathodes. For example, it has a higher operational voltage than the popularly used cathode LiFePO4 (lithium iron phosphate, or LFP), which is the electrical force a battery provides when connected to a device, similar to water pressure from a garden hose.
This technology may be less than five years from commercial viability in EVs. For now, the team will continue investigating FeCl3 and related materials, according to Chen. The work was led by Chen and postdoc Zhantao Liu (the lead author of the study). Collaborators included researchers from Georgia Tech’s Woodruff School (Ting Zhu) and the School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences (Yuanzhi Tang), as well as the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (Jue Liu) and the University of Houston (Shuo Chen).
“We want to make the materials as perfect as possible in the lab and understand the underlying functioning mechanisms,” Chen said. “But we are open to opportunities to scale up the technology and push it toward commercial applications.”
CITATION: Zhantao Liu, Jue Liu, Simin Zhao, Sangni Xun, Paul Byaruhanga, Shuo Chen, Yuanzhi Tang, Ting Zhu, Hailong Chen. “Low-cost iron trichloride cathode for all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries.” Nature Sustainability.
FUNDING: National Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 1706723 and 2108688)
END
New battery cathode material could revolutionize EV market and energy storage
2024-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Inexpensive drug can prevent cerebral palsy in premature babies
2024-09-24
Giving women at risk of premature birth a simple magnesium sulphate infusion (or ‘drip’) can prevent their babies from developing cerebral palsy, a recent Cochrane review has confirmed. The drug itself costs approximately £5 (~$6.50) per dose in England, and requires hospital admission with experienced staff to administer the drug safely to the mother. A new editorial calls for this intervention to be implemented more widely and equitably, as it is still not consistently available worldwide.
The first Cochrane review showing that magnesium sulphate protects premature babies against cerebral palsy was published in 2009, and the recent update includes newer trials which further ...
Studying sex-specific pain levels in wheelchair users
2024-09-23
Josh Leonardis received funding from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health to study why female manual wheelchair users experience shoulder pain and pathology at greater rates than males.
Leonardis is a researcher at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, an assistant professor of health and kinesiology at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the director of the Musculoskeletal Morphology and Biomechanics Laboratory.
“It’s well-documented in literature that ...
UChicago Medicine performs first-in-Illinois procedure to treat bladder leaks
2024-09-23
UChicago Medicine has become the first medical center in Illinois to implant the Revi neuromodulation device, an exciting new treatment option that could offer relief for patients with urinary urgency incontinence (UUI).
“I am really happy that we can offer this innovative approach to all our patients and very proud to be at the real forefront of medicine as the first in the state to have done this surgery,” said urologist Ervin Kocjancic, MD, the surgeon who performed the procedure.
UUI, a chronic, debilitating, ...
Previously unknown Neolithic society in Morocco discovered: shining light on North Africa’s role in Mediterranean prehistory
2024-09-23
Multi-disciplinary archaeological survey at the site of Oued Beht, Morocco, reveals a previously unknown 3400–2900 BC farming society.
This is the earliest and largest agricultural complex yet found in Africa beyond the Nile.
It shares similar features with contemporaneous sites in Iberia.
This suggests the Maghreb was instrumental to the shaping of the western Mediterranean during the fourth and third millennia BC.
Archaeological fieldwork in Morocco has discovered the earliest, previously unknown farming society from a poorly understood period of north-west African prehistory.
This study, published today in Antiquity, reveals for the first ...
Study finds PrEP use among gay and bisexual men in Ontario linked to higher STI rates
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is a preventive medicine that reduces the risk of contracting HIV. There is concern that PrEP use may be associated with an increase in bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis among men who are gay or bisexual. This study explored the relationship between PrEP use and the rates of bacterial STIs over time.
Study Approach: Researchers used data from the iCruise Study, an online longitudinal study of men who are gay or bisexual or have sex with men, in Ontario from July 2017 to April 2018. The study examined how PrEP use related to the number of self-reported ...
Technology-assisted health coaching intervention does not improve weight loss in veterans and high-risk patients
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: Obesity is a significant health issue, particularly among veterans and racial/ethnic minority groups. Primary care is a key setting for addressing obesity. However, many barriers, including time constraints and limited patient engagement, make effective treatment challenging. This study evaluated whether a technology-assisted health coaching intervention called Goals for Eating and Moving (GEM) could help high-risk patients lose weight more effectively than enhanced usual care (EUC).
Study Approach: Researchers conducted a two-arm, cluster-randomized controlled trial involving 19 primary care teams ...
Underserved patients reduce blood pressure and heart disease risk using remote monitoring program
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: Underserved communities are at higher risk for uncontrolled high blood pressure (hypertension), which can lead to heart disease and higher death rates. This study evaluated the impact of a remote monitoring program called DIG IT on blood pressure control in underserved patients at a Federally Qualified Health Center (FQHC) in Orange County, California.
Study Approach: Researchers compared two groups: 70 patients using the DIG IT program, which includes digital blood pressure monitoring, medication management, and a team-based care approach, and a historical control group of 70 patients who received standard care without digital tools. The ...
The HOMER study evolves to adapt opioid treatment research amid COVID-19 challenges
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: The HOMER study was launched to determine the most effective setting for starting buprenorphine treatment for opioid use disorder. The study faced challenges including shifts in health care delivery, changes in patient preferences, and the emergence of telehealth. The goal was to adapt the study to these circumstances while maintaining its focus on patient-centered care and effective treatment outcomes.
Key Insights: The HOMER study had to quickly adapt to challenges brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic. With community input, the study design evolved to include a third arm, ...
High-sensitivity troponin shows promise in diagnosing acute coronary syndrome in primary care settings
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: Chest pain is a common but challenging symptom for general practitioners to evaluate, as it can be caused by both serious conditions and more benign issues. This study assessed the effectiveness of various risk stratification tools, including clinical decision rules and troponin tests, in helping general practitioners rule out acute coronary syndrome in patients with chest pain.
Study Approach: Researchers conducted a systematic review of studies involving adult patients presenting ...
September/October Annals of Family Medicine Tip Sheet
2024-09-23
Original Research
Family Physicians in Rural Hospitals Associated With Lower Cesarean Rates and Safer Maternal Care Culture
Background and Goal: The U.S. is experiencing a maternal health crisis, particularly in rural areas. This issue is compounded by rising rates of severe maternal morbidity and mortality. Family physicians often fill critical gaps in care in rural areas where obstetricians are scarce. This study examined how the presence of family physicians in rural hospitals impacts cesarean delivery rates and the overall quality of care during childbirth.
Study Approach: The study analyzed data from rural ...