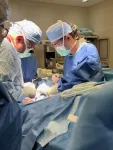
(Press-News.org) UChicago Medicine has become the first medical center in Illinois to implant the Revi neuromodulation device, an exciting new treatment option that could offer relief for patients with urinary urgency incontinence (UUI).
“I am really happy that we can offer this innovative approach to all our patients and very proud to be at the real forefront of medicine as the first in the state to have done this surgery,” said urologist Ervin Kocjancic, MD, the surgeon who performed the procedure.
UUI, a chronic, debilitating, and often embarrassing condition, affects millions of people and can significantly impact daily life. Existing treatments to improve bladder control, such as medications and other surgical interventions, often come with limitations or side effects. The new, single-step procedure involves placing a small, battery-free implant near the ankle, avoiding the need for follow-up surgeries often required with other implants. When activated with a lightweight external wearable device, the implant stimulates the posterior tibial nerve to calm the bladder and provide relief from UUI.
“This is a brand new technology — real innovation in the field of female and functional urology,” Kocjancic said. “With this minimally invasive approach, done using local anesthesia, patients are able to regain a normal life without being at the mercy of their malfunctioning bladders."
"I was really pleasantly surprised by our patient when he asked me candidly if the surgery was really over," Kocjancic added. "He didn't feel any discomfort from the procedure."
END
UChicago Medicine performs first-in-Illinois procedure to treat bladder leaks
2024-09-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Previously unknown Neolithic society in Morocco discovered: shining light on North Africa’s role in Mediterranean prehistory
2024-09-23
Multi-disciplinary archaeological survey at the site of Oued Beht, Morocco, reveals a previously unknown 3400–2900 BC farming society.
This is the earliest and largest agricultural complex yet found in Africa beyond the Nile.
It shares similar features with contemporaneous sites in Iberia.
This suggests the Maghreb was instrumental to the shaping of the western Mediterranean during the fourth and third millennia BC.
Archaeological fieldwork in Morocco has discovered the earliest, previously unknown farming society from a poorly understood period of north-west African prehistory.
This study, published today in Antiquity, reveals for the first ...
Study finds PrEP use among gay and bisexual men in Ontario linked to higher STI rates
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is a preventive medicine that reduces the risk of contracting HIV. There is concern that PrEP use may be associated with an increase in bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis among men who are gay or bisexual. This study explored the relationship between PrEP use and the rates of bacterial STIs over time.
Study Approach: Researchers used data from the iCruise Study, an online longitudinal study of men who are gay or bisexual or have sex with men, in Ontario from July 2017 to April 2018. The study examined how PrEP use related to the number of self-reported ...
Technology-assisted health coaching intervention does not improve weight loss in veterans and high-risk patients
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: Obesity is a significant health issue, particularly among veterans and racial/ethnic minority groups. Primary care is a key setting for addressing obesity. However, many barriers, including time constraints and limited patient engagement, make effective treatment challenging. This study evaluated whether a technology-assisted health coaching intervention called Goals for Eating and Moving (GEM) could help high-risk patients lose weight more effectively than enhanced usual care (EUC).
Study Approach: Researchers conducted a two-arm, cluster-randomized controlled trial involving 19 primary care teams ...
Underserved patients reduce blood pressure and heart disease risk using remote monitoring program
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: Underserved communities are at higher risk for uncontrolled high blood pressure (hypertension), which can lead to heart disease and higher death rates. This study evaluated the impact of a remote monitoring program called DIG IT on blood pressure control in underserved patients at a Federally Qualified Health Center (FQHC) in Orange County, California.
Study Approach: Researchers compared two groups: 70 patients using the DIG IT program, which includes digital blood pressure monitoring, medication management, and a team-based care approach, and a historical control group of 70 patients who received standard care without digital tools. The ...
The HOMER study evolves to adapt opioid treatment research amid COVID-19 challenges
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: The HOMER study was launched to determine the most effective setting for starting buprenorphine treatment for opioid use disorder. The study faced challenges including shifts in health care delivery, changes in patient preferences, and the emergence of telehealth. The goal was to adapt the study to these circumstances while maintaining its focus on patient-centered care and effective treatment outcomes.
Key Insights: The HOMER study had to quickly adapt to challenges brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic. With community input, the study design evolved to include a third arm, ...
High-sensitivity troponin shows promise in diagnosing acute coronary syndrome in primary care settings
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: Chest pain is a common but challenging symptom for general practitioners to evaluate, as it can be caused by both serious conditions and more benign issues. This study assessed the effectiveness of various risk stratification tools, including clinical decision rules and troponin tests, in helping general practitioners rule out acute coronary syndrome in patients with chest pain.
Study Approach: Researchers conducted a systematic review of studies involving adult patients presenting ...
September/October Annals of Family Medicine Tip Sheet
2024-09-23
Original Research
Family Physicians in Rural Hospitals Associated With Lower Cesarean Rates and Safer Maternal Care Culture
Background and Goal: The U.S. is experiencing a maternal health crisis, particularly in rural areas. This issue is compounded by rising rates of severe maternal morbidity and mortality. Family physicians often fill critical gaps in care in rural areas where obstetricians are scarce. This study examined how the presence of family physicians in rural hospitals impacts cesarean delivery rates and the overall quality of care during childbirth.
Study Approach: The study analyzed data from rural ...
Risk model identifies advanced cancer trial patients at highest risk for acute care use
2024-09-23
Investigators from the SWOG Cancer Research Network have developed and validated a risk prediction model for identifying which patients with advanced cancer who are enrolled to clinical trials are at highest risk for unplanned emergency room (ER) visits and hospital stays.
Determining which patients are at significantly higher risk could inform interventions to reduce the need for such visits, improving care quality and reducing costs.
The work will be delivered as an oral presentation by Dawn L. Hershman, MD, MS, at the 2024 ASCO Quality Care Symposium, which will ...
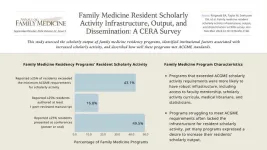
Robust family medicine residency programs help residents meet scholarly output requirements
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: Family medicine residency programs are essential for training future primary care physicians. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) program requires family medicine residents to perform two scholarly projects. One must be a quality improvement project, and the second project type is at the program's discretion. This study assessed the scholarly activity output of family medicine residency programs in the U.S., identified institutional factors associated with increased scholarly ...
Using transparent capsules in dry powder inhalers could significantly improve medication delivery
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: This study examined whether patients with non-reversible chronic airway disease using a transparent capsule in single-dose dry powder inhalers affects the amount of medication delivered. The goal was to determine if patients who use transparent capsules that allow them to see if the medication has been fully inhaled have better inhalation results compared to those using opaque capsules.
Study Approach: Researchers conducted an observational cross-sectional study between October 2020 and October ...