(Press-News.org) For the over 1 million Americans who survive severe traumatic brain injuries each year, the road to recovery is often long and challenging. Disruption of the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary functions like heart rate, is a common yet poorly understood consequence of TBI. While heart rate variability (HRV) is a widely used measure of autonomic function, the standard 5-minute recording can be cumbersome for patients with cognitive and physical impairments.
Now, a team led by researchers at Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina has found that HRV can be accurately captured in severe TBI survivors using recordings as short as 30 to 60 seconds. The study, published in Brain Medicine, is the first to validate ultra-short HRV in this population, a finding with important implications for patient care and research.
“Measuring HRV provides a window into the autonomic nervous system, but the standard 5-minute assessment can be difficult for patients who struggle with prolonged recordings,” said Hiago Melo, a researcher at Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina and the study's first author. “Our findings suggest we can get reliable HRV data in just a fraction of that time, making it feasible to integrate regular autonomic check-ups into clinical care and daily life for TBI survivors.”
The researchers analyzed ECG recordings from 48 patients one year after a severe TBI. By comparing HRV values calculated from the standard 5-minute recording to those from shorter segments of the same recording, they determined that ultra-short measures - particularly from 1-minute segments - strongly correlated with the 5-minute gold standard.
One specific HRV metric known as root mean square of successive differences (RMSSD) proved most robust. RMSSD is thought to reflect parasympathetic (rest-and-digest) activity, an important aspect of healthy autonomic function often suppressed after brain injury.
“RMSSD consistently showed the highest reliability across the ultra-short segments,” noted co-author Guilherme Fialho, a cardiologist and professor at the Graduated Program in Medical Sciences. “This is promising, as RMSSD may be uniquely suited to capture the parasympathetic dysfunction commonly seen in TBI patients.”
According to the authors, ultra-short HRV could serve as an objective marker of post-TBI autonomic health, enabling clinicians to spot problems earlier and intervene more effectively. The study also paves the way for wearable devices that could discreetly monitor HRV during daily activities, providing real-world data on patient recovery.
“We're excited about the potential for ultra-short HRV to enhance post-TBI care,” said senior author Roger Walz, professor at Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina. “By making autonomic assessment quicker and easier, we can expand how we track recovery in the clinic and beyond. It's a simple yet powerful tool that could reshape our understanding of the autonomic impact of these injuries.”
While promising, the researchers caution that larger studies are needed to guide the development of HRV-based recovery markers. With further validation, they believe ultra-short recordings could become a standard part of post-TBI evaluations, leading to more personalized rehabilitation approaches.
As the number of TBI survivors continues to grow, tools like ultra-short HRV offer hope for better identifying those at risk of prolonged autonomic dysfunction and providing targeted interventions to improve quality of life after severe brain injury.
The peer-reviewed study, “Ultra-short heart rate variability reliability for cardiac autonomic tone assessment in severe traumatic brain injury,” will be published on September 24, 2024 in Brain Medicine, a peer-reviewed medical research journal published by Genomic Press (New York, USA).
In addition to Hiago Murilo Melo and Roger Walz, study authors include Norma Beatriz Diaz Rangel, Guilherme Loureiro Fialho and Katia Lin.
END
60-second heartbeat recordings offer window into autonomic health after severe brain trauma
New study validates reliability of ultra-short heart rate variability measures, paving way for faster, easier tracking of recovery in traumatic brain injury survivors
2024-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Psychedelic drug psilocybin changes brain connectivity to treat body dysmorphic disorder
2024-09-24
New York, NY - Body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) is a debilitating mental illness characterized by an obsessive preoccupation with perceived flaws in one's physical appearance. Patients with BDD often have distorted self-image, intrusive thoughts, and compulsive behaviors that significantly impair daily functioning and quality of life. Current therapies have limited efficacy, leaving many sufferers without relief.
A new study led by researchers at Columbia University and published in Psychedelics (Genomic Press, New York, USA) provides hope by revealing how the psychedelic drug ...
Google trends reveals surge in ADHD medication searches during COVID-19 pandemic
2024-09-24
In a groundbreaking study published in Brain Medicine (Genomic Press), UCI researchers have uncovered a striking correlation between internet searches for ADHD medications and actual prescription rates during the COVID-19 pandemic. This finding opens up new possibilities for using online search data to predict and prevent prescription drug shortages.
The study, led by Dr. Steven Grieco from the University of California, Irvine, analyzed Google Trends data spanning 20 years, with a particular focus on the period following the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in January 2020. The researchers found a significant surge in searches for ADHD medications during ...
Multiple sclerosis symptoms at onset linked to long-term disability
2024-09-24
In a significant advance for multiple sclerosis (MS) research, a new study has uncovered a potential link between certain initial symptoms and long-term disability outcomes. The research, published in the latest issue of Brain Medicine (Genomic Press, New York), could have far-reaching implications for early intervention strategies and treatment decisions in MS care.
Led by Dr. João Pedro F. Gonçalves from the Federal University of Bahia, Brazil, the study analyzed data from 195 MS patients, focusing ...
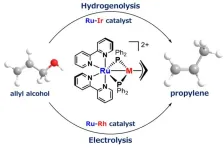
New catalyst developed for sustainable propylene production from biomass
2024-09-24
Achieving carbon neutrality requires the effective use of renewable biomass. In the production of biodiesel, for instance, glycerol is generated as a major byproduct. Researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University have developed a new catalyst that efficiently converts a derivative of glycerol into bio-based propylene, contributing to sustainable chemical production.
Propylene is typically produced from petroleum and is widely used in the manufacture of plastics, such as automobile bumpers and food containers. The research team, led by Associate Professor Shin Takemoto and Professor Hiroyuki Matsuzaka from the Graduate School of Science, developed a catalyst that ...
Nearly 200 potential mammary carcinogens found in food contact materials: new study highlights regulatory shortcomings
2024-09-24
About this study: Research identifies nearly 200 potential breast carcinogens in food contact materials, including plastics and paper, highlighting widespread exposure despite existing regulation. The findings underscore an urgent need for stronger preventative measures to reduce these chemicals in everyday products.
Researchers from the Food Packaging Forum identify and discuss nearly 200 potential breast carcinogens that have been detected in food contact materials (FCMs) on the market. ...
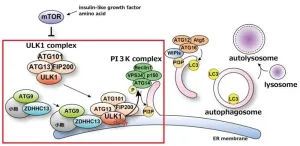
Mechanism behind autophagy trigger unveiled
2024-09-24
Osaka, Japan – An international research team led by Osaka University has identified a new mechanism crucial for the initiation of autophagy, a self-degradation process cells use to eliminate unneeded or damaged components. In recent years, autophagy has also been recognized for its roles in aging and lifespan regulation.
During autophagy, intracellular molecules and structures are sequestered within a membrane-bound structure known as an autophagosome, which is subsequently degraded in lysosomes. It is well-established that the formation of autophagosomes ...
Study: Good nutrition boosts honey bee resilience against pesticides, viruses
2024-09-24
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — In a new study, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign tackled a thorny problem: How do nutritional stress, viral infections and exposure to pesticides together influence honey bee survival? By looking at all three stressors together, the scientists found that good nutrition enhances honey bee resilience against the other threats.
Their findings are detailed in the journal Science of the Total Environment.
“Multiple stressors are often bad for survival,” said graduate student Edward Hsieh, who led the research ...
New battery cathode material could revolutionize EV market and energy storage
2024-09-24
A multi-institutional research team led by Georgia Tech’s Hailong Chen has developed a new, low-cost cathode that could radically improve lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) — potentially transforming the electric vehicle (EV) market and large-scale energy storage systems.
“For a long time, people have been looking for a lower-cost, more sustainable alternative to existing cathode materials. I think we’ve got one,” said Chen, an associate professor with appointments in the ...
Inexpensive drug can prevent cerebral palsy in premature babies
2024-09-24
Giving women at risk of premature birth a simple magnesium sulphate infusion (or ‘drip’) can prevent their babies from developing cerebral palsy, a recent Cochrane review has confirmed. The drug itself costs approximately £5 (~$6.50) per dose in England, and requires hospital admission with experienced staff to administer the drug safely to the mother. A new editorial calls for this intervention to be implemented more widely and equitably, as it is still not consistently available worldwide.
The first Cochrane review showing that magnesium sulphate protects premature babies against cerebral palsy was published in 2009, and the recent update includes newer trials which further ...
Studying sex-specific pain levels in wheelchair users
2024-09-23
Josh Leonardis received funding from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health to study why female manual wheelchair users experience shoulder pain and pathology at greater rates than males.
Leonardis is a researcher at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, an assistant professor of health and kinesiology at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the director of the Musculoskeletal Morphology and Biomechanics Laboratory.
“It’s well-documented in literature that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
[Press-News.org] 60-second heartbeat recordings offer window into autonomic health after severe brain traumaNew study validates reliability of ultra-short heart rate variability measures, paving way for faster, easier tracking of recovery in traumatic brain injury survivors