(Press-News.org) About this study: Research identifies nearly 200 potential breast carcinogens in food contact materials, including plastics and paper, highlighting widespread exposure despite existing regulation. The findings underscore an urgent need for stronger preventative measures to reduce these chemicals in everyday products.
Researchers from the Food Packaging Forum identify and discuss nearly 200 potential breast carcinogens that have been detected in food contact materials (FCMs) on the market. Many nations have food contact material legislation intended to protect citizens from hazardous chemicals, often specifically by regulating genotoxic carcinogens. As cancer is one of the few health endpoints specifically targeted in FCM regulations and testing, carcinogenic chemicals in food packaging and other food contact materials and articles should not be commonplace.
“This study is important because it shows that there is a huge opportunity for prevention of human exposure to breast cancer-causing chemicals,” said Jane Muncke, Managing Director of the Food Packaging Forum and co-author of the study. “The potential for cancer prevention by reducing hazardous chemicals in your daily life is underexplored and deserves much more attention.”
By comparing a recently published list of potential breast carcinogens developed by scientists at the Silent Spring Institute with the Food Packaging Forum’s own Database on migrating and extractable food contact chemicals (FCCmigex), the authors find that 189 potential breast carcinogens have been detected in FCMs, including 143 in plastics and 89 in paper or board.
“Identifying the presence of these hazardous chemicals in food contact materials was possible thanks to our FCCmigex Database,” said Lindsey Parkinson, Data Scientist and Scientific Editor at the Food Packaging Forum and lead author of the study. “This resource brings valuable information from thousands of published scientific studies on chemicals in food contact materials together into a single and easily explorable place.”
When limiting the comparison to the most recently available studies in FCCmigex (2020-2022) that used migration experiments that mimic realistic conditions, there is evidence of exposure to 76 suspected mammary carcinogens from FCMs purchased all over the world, 61 of which (80%) are from plastics. This indicates continued exposure of the global population to these chemicals under realistic use conditions.
Despite existing regulations intended to limit carcinogenic substances in FCMs, the study highlights gaps in current regulatory frameworks. The food contact articles were purchased within the last few years from markets in highly regulated regions, including the EU and the US. "Our findings imply that chronic exposure of the entire population to suspected mammary carcinogens from FCMs is the norm and highlights an important, but currently underappreciated, opportunity for prevention," the authors explain.
END
Nearly 200 potential mammary carcinogens found in food contact materials: new study highlights regulatory shortcomings
2024-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mechanism behind autophagy trigger unveiled
2024-09-24
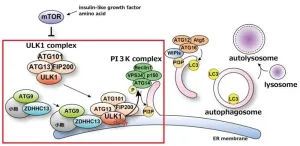
Osaka, Japan – An international research team led by Osaka University has identified a new mechanism crucial for the initiation of autophagy, a self-degradation process cells use to eliminate unneeded or damaged components. In recent years, autophagy has also been recognized for its roles in aging and lifespan regulation.
During autophagy, intracellular molecules and structures are sequestered within a membrane-bound structure known as an autophagosome, which is subsequently degraded in lysosomes. It is well-established that the formation of autophagosomes ...
Study: Good nutrition boosts honey bee resilience against pesticides, viruses
2024-09-24
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — In a new study, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign tackled a thorny problem: How do nutritional stress, viral infections and exposure to pesticides together influence honey bee survival? By looking at all three stressors together, the scientists found that good nutrition enhances honey bee resilience against the other threats.
Their findings are detailed in the journal Science of the Total Environment.
“Multiple stressors are often bad for survival,” said graduate student Edward Hsieh, who led the research ...
New battery cathode material could revolutionize EV market and energy storage
2024-09-24
A multi-institutional research team led by Georgia Tech’s Hailong Chen has developed a new, low-cost cathode that could radically improve lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) — potentially transforming the electric vehicle (EV) market and large-scale energy storage systems.
“For a long time, people have been looking for a lower-cost, more sustainable alternative to existing cathode materials. I think we’ve got one,” said Chen, an associate professor with appointments in the ...
Inexpensive drug can prevent cerebral palsy in premature babies
2024-09-24
Giving women at risk of premature birth a simple magnesium sulphate infusion (or ‘drip’) can prevent their babies from developing cerebral palsy, a recent Cochrane review has confirmed. The drug itself costs approximately £5 (~$6.50) per dose in England, and requires hospital admission with experienced staff to administer the drug safely to the mother. A new editorial calls for this intervention to be implemented more widely and equitably, as it is still not consistently available worldwide.
The first Cochrane review showing that magnesium sulphate protects premature babies against cerebral palsy was published in 2009, and the recent update includes newer trials which further ...
Studying sex-specific pain levels in wheelchair users
2024-09-23
Josh Leonardis received funding from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health to study why female manual wheelchair users experience shoulder pain and pathology at greater rates than males.
Leonardis is a researcher at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, an assistant professor of health and kinesiology at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the director of the Musculoskeletal Morphology and Biomechanics Laboratory.
“It’s well-documented in literature that ...
UChicago Medicine performs first-in-Illinois procedure to treat bladder leaks
2024-09-23
UChicago Medicine has become the first medical center in Illinois to implant the Revi neuromodulation device, an exciting new treatment option that could offer relief for patients with urinary urgency incontinence (UUI).
“I am really happy that we can offer this innovative approach to all our patients and very proud to be at the real forefront of medicine as the first in the state to have done this surgery,” said urologist Ervin Kocjancic, MD, the surgeon who performed the procedure.
UUI, a chronic, debilitating, ...
Previously unknown Neolithic society in Morocco discovered: shining light on North Africa’s role in Mediterranean prehistory
2024-09-23
Multi-disciplinary archaeological survey at the site of Oued Beht, Morocco, reveals a previously unknown 3400–2900 BC farming society.
This is the earliest and largest agricultural complex yet found in Africa beyond the Nile.
It shares similar features with contemporaneous sites in Iberia.
This suggests the Maghreb was instrumental to the shaping of the western Mediterranean during the fourth and third millennia BC.
Archaeological fieldwork in Morocco has discovered the earliest, previously unknown farming society from a poorly understood period of north-west African prehistory.
This study, published today in Antiquity, reveals for the first ...
Study finds PrEP use among gay and bisexual men in Ontario linked to higher STI rates
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is a preventive medicine that reduces the risk of contracting HIV. There is concern that PrEP use may be associated with an increase in bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis among men who are gay or bisexual. This study explored the relationship between PrEP use and the rates of bacterial STIs over time.
Study Approach: Researchers used data from the iCruise Study, an online longitudinal study of men who are gay or bisexual or have sex with men, in Ontario from July 2017 to April 2018. The study examined how PrEP use related to the number of self-reported ...
Technology-assisted health coaching intervention does not improve weight loss in veterans and high-risk patients
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: Obesity is a significant health issue, particularly among veterans and racial/ethnic minority groups. Primary care is a key setting for addressing obesity. However, many barriers, including time constraints and limited patient engagement, make effective treatment challenging. This study evaluated whether a technology-assisted health coaching intervention called Goals for Eating and Moving (GEM) could help high-risk patients lose weight more effectively than enhanced usual care (EUC).
Study Approach: Researchers conducted a two-arm, cluster-randomized controlled trial involving 19 primary care teams ...
Underserved patients reduce blood pressure and heart disease risk using remote monitoring program
2024-09-23
Background and Goal: Underserved communities are at higher risk for uncontrolled high blood pressure (hypertension), which can lead to heart disease and higher death rates. This study evaluated the impact of a remote monitoring program called DIG IT on blood pressure control in underserved patients at a Federally Qualified Health Center (FQHC) in Orange County, California.
Study Approach: Researchers compared two groups: 70 patients using the DIG IT program, which includes digital blood pressure monitoring, medication management, and a team-based care approach, and a historical control group of 70 patients who received standard care without digital tools. The ...