(Press-News.org) In a groundbreaking study published in Brain Medicine (Genomic Press), UCI researchers have uncovered a striking correlation between internet searches for ADHD medications and actual prescription rates during the COVID-19 pandemic. This finding opens up new possibilities for using online search data to predict and prevent prescription drug shortages.
The study, led by Dr. Steven Grieco from the University of California, Irvine, analyzed Google Trends data spanning 20 years, with a particular focus on the period following the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in January 2020. The researchers found a significant surge in searches for ADHD medications during this time, mirroring the known increase in ADHD drug prescriptions reported in other studies.
"Our findings suggest that Google Trends data could serve as a real-time proxy for prescription drug usage, especially during rapidly changing public health situations," says Dr. Grieco. "This approach could be invaluable when actual prescription data is not immediately available."
The research team employed sophisticated analytical techniques, including cross-correlation analysis and k-medoids clustering, to identify trends and subtrends in the search data. They also performed seasonal trend analysis for 187 disorders and 113 medication keywords, providing a comprehensive view of public interest in various health conditions and treatments.
One of the most intriguing aspects of the study was the strong correlation (r = 0.876) between Google Trends searches for ADHD medications and actual prescription rates from the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) database. This correlation held true up until the onset of the pandemic, after which MEPS data was no longer available.
The study raises several important questions for future exploration:
1. How might this approach be scaled up and refined to cover a wider range of health topics?
2. Could real-time predictions of prescription drug usage help prevent shortages like the Adderall shortage announced by the FDA in October 2022?
3. What are the long-term implications of increased public interest in and usage of ADHD medications post-pandemic?
4. How can public health departments, drug manufacturers, and data industry partners collaborate effectively to make real-time predictions about public prescription usage?
While the study provides valuable insights, the researchers acknowledge several limitations. The data may not be representative of the general population, potentially excluding individuals with limited online literacy or internet access. Additionally, the correlation between internet searches and actual prescription use may not hold for all health issues or in different contexts.
Despite these limitations, the study's findings have significant implications for public health and pharmaceutical industries. By leveraging Google Trends data, health officials and drug manufacturers could potentially detect early signs of changing drug demands and respond more quickly to prevent shortages.
As we move forward from the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency, which ended in May 2023, this research provides a novel approach to monitoring and predicting public health trends. It underscores the potential of big data analytics in healthcare and opens up new avenues for proactive health management strategies.
The study, titled “Internet searches for ADHD medications surged during the COVID-19 pandemic," will be published in Brain Medicine on September 24, 2024. It will be freely available online at https://bm.genomicpress.com/aop/
About Brain Medicine: Brain Medicine (ISSN: 2997-2639) is a peer-reviewed journal published by Genomic Press, New York. Brain Medicine is a new home for the cross-disciplinary pathway from innovation in fundamental neuroscience to translational initiatives in brain medicine. The journal’s scope includes the underlying science, causes, outcomes, treatments, and societal impact of brain disorders, across all clinical disciplines and their interface.
Contact: Dr. Steven Grieco, University of California, Irvine, CA: sgrieco@hs.uci.edu
END
Google trends reveals surge in ADHD medication searches during COVID-19 pandemic
New study suggests online search data could help predict prescription drug demand and prevent shortages
2024-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Multiple sclerosis symptoms at onset linked to long-term disability
2024-09-24
In a significant advance for multiple sclerosis (MS) research, a new study has uncovered a potential link between certain initial symptoms and long-term disability outcomes. The research, published in the latest issue of Brain Medicine (Genomic Press, New York), could have far-reaching implications for early intervention strategies and treatment decisions in MS care.
Led by Dr. João Pedro F. Gonçalves from the Federal University of Bahia, Brazil, the study analyzed data from 195 MS patients, focusing ...
New catalyst developed for sustainable propylene production from biomass
2024-09-24
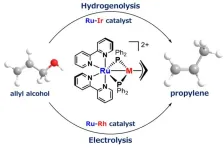
Achieving carbon neutrality requires the effective use of renewable biomass. In the production of biodiesel, for instance, glycerol is generated as a major byproduct. Researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University have developed a new catalyst that efficiently converts a derivative of glycerol into bio-based propylene, contributing to sustainable chemical production.
Propylene is typically produced from petroleum and is widely used in the manufacture of plastics, such as automobile bumpers and food containers. The research team, led by Associate Professor Shin Takemoto and Professor Hiroyuki Matsuzaka from the Graduate School of Science, developed a catalyst that ...
Nearly 200 potential mammary carcinogens found in food contact materials: new study highlights regulatory shortcomings
2024-09-24
About this study: Research identifies nearly 200 potential breast carcinogens in food contact materials, including plastics and paper, highlighting widespread exposure despite existing regulation. The findings underscore an urgent need for stronger preventative measures to reduce these chemicals in everyday products.
Researchers from the Food Packaging Forum identify and discuss nearly 200 potential breast carcinogens that have been detected in food contact materials (FCMs) on the market. ...
Mechanism behind autophagy trigger unveiled
2024-09-24
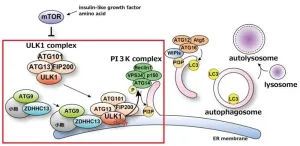
Osaka, Japan – An international research team led by Osaka University has identified a new mechanism crucial for the initiation of autophagy, a self-degradation process cells use to eliminate unneeded or damaged components. In recent years, autophagy has also been recognized for its roles in aging and lifespan regulation.
During autophagy, intracellular molecules and structures are sequestered within a membrane-bound structure known as an autophagosome, which is subsequently degraded in lysosomes. It is well-established that the formation of autophagosomes ...
Study: Good nutrition boosts honey bee resilience against pesticides, viruses
2024-09-24
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — In a new study, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign tackled a thorny problem: How do nutritional stress, viral infections and exposure to pesticides together influence honey bee survival? By looking at all three stressors together, the scientists found that good nutrition enhances honey bee resilience against the other threats.
Their findings are detailed in the journal Science of the Total Environment.
“Multiple stressors are often bad for survival,” said graduate student Edward Hsieh, who led the research ...
New battery cathode material could revolutionize EV market and energy storage
2024-09-24
A multi-institutional research team led by Georgia Tech’s Hailong Chen has developed a new, low-cost cathode that could radically improve lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) — potentially transforming the electric vehicle (EV) market and large-scale energy storage systems.
“For a long time, people have been looking for a lower-cost, more sustainable alternative to existing cathode materials. I think we’ve got one,” said Chen, an associate professor with appointments in the ...
Inexpensive drug can prevent cerebral palsy in premature babies
2024-09-24
Giving women at risk of premature birth a simple magnesium sulphate infusion (or ‘drip’) can prevent their babies from developing cerebral palsy, a recent Cochrane review has confirmed. The drug itself costs approximately £5 (~$6.50) per dose in England, and requires hospital admission with experienced staff to administer the drug safely to the mother. A new editorial calls for this intervention to be implemented more widely and equitably, as it is still not consistently available worldwide.
The first Cochrane review showing that magnesium sulphate protects premature babies against cerebral palsy was published in 2009, and the recent update includes newer trials which further ...
Studying sex-specific pain levels in wheelchair users
2024-09-23
Josh Leonardis received funding from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health to study why female manual wheelchair users experience shoulder pain and pathology at greater rates than males.
Leonardis is a researcher at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, an assistant professor of health and kinesiology at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the director of the Musculoskeletal Morphology and Biomechanics Laboratory.
“It’s well-documented in literature that ...
UChicago Medicine performs first-in-Illinois procedure to treat bladder leaks
2024-09-23
UChicago Medicine has become the first medical center in Illinois to implant the Revi neuromodulation device, an exciting new treatment option that could offer relief for patients with urinary urgency incontinence (UUI).
“I am really happy that we can offer this innovative approach to all our patients and very proud to be at the real forefront of medicine as the first in the state to have done this surgery,” said urologist Ervin Kocjancic, MD, the surgeon who performed the procedure.
UUI, a chronic, debilitating, ...
Previously unknown Neolithic society in Morocco discovered: shining light on North Africa’s role in Mediterranean prehistory
2024-09-23
Multi-disciplinary archaeological survey at the site of Oued Beht, Morocco, reveals a previously unknown 3400–2900 BC farming society.
This is the earliest and largest agricultural complex yet found in Africa beyond the Nile.
It shares similar features with contemporaneous sites in Iberia.
This suggests the Maghreb was instrumental to the shaping of the western Mediterranean during the fourth and third millennia BC.
Archaeological fieldwork in Morocco has discovered the earliest, previously unknown farming society from a poorly understood period of north-west African prehistory.
This study, published today in Antiquity, reveals for the first ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
[Press-News.org] Google trends reveals surge in ADHD medication searches during COVID-19 pandemicNew study suggests online search data could help predict prescription drug demand and prevent shortages