(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Sept. 24, 2024 – Coastlines are vital to our world’s ecology and economy. Coastal ecosystems help maintain biodiversity, provide natural barriers against erosion, storms, and flooding, and act as large carbon sinks to reduce greenhouse gases. Sustainable fisheries and seaside tourist venues support local economies.
Natural coastlines, including coral reefs, marshes, and mangroves, are complete and stable, capable of self-regulation and restoration. That is, unless human interventions, such as urbanization, overdevelopment, pollution, and human-made erosion, make these areas vulnerable to devastation.
Artificial coastlines, including human-made dikes and other engineered constructions, can help prevent erosion and protect from storms and flooding. However, ecological functions remain unprotected from many of these structures.
In Biointerphases, an AVS journal published by AIP Publishing, researchers from Southeast University and the University of Chinese Academy of Science investigated the use of specialized types of cement for coastline ecological protection.
“New substrate materials need to be developed to reduce the biological toxicity effects on marine organisms,” said author Xiaolin Lu.
Current artificial reef blocks are built using cement with a highly alkaline pH of +12 which is harmful to biofilm on reef surfaces. Biofilm, made up of such microorganisms as bacteria, algae, and fungi, provides food for grazers and promotes larval settlement.
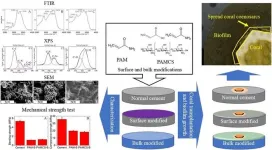
The team started with a limestone and clay cement that hardens underwater. Two types of treatments were added to the cement: polyacrylamide, a synthetic resin used in water treatment, and chitosan, a form of sugar made from the shells of shrimp and other crustaceans. The two treatments were mixed into the cement to form the hardened substrate, and they were sprayed onto previously hardened cement as a surface treatment.
The bulk-treated and surface-treated samples were tested for mechanical strength and biofilm and coral growth. The samples, along with a control of plain cement, were placed in a sea tank and treated with biofilm cultures and transplanted coral.
After two days, biofilm was found active and growing well on the surface-treated samples. After 30 days, biofilm growth was found to be greatest on the surface-treated samples, a little less on the bulk-treated samples, and significantly less on the cement control. The reduced biofilm growth on the control was attributed to the high alkalinity of the cement without anything to block its effects. Transplanted coral samples also survived and grew better on the surface-treated samples.
While the bulk-treated samples supported reduced survival and growth of both biofilm and coral, mechanical properties appeared to be significantly reduced compared to the control and the surface-treated samples.
“These new treatments showed the necessary biocompatibility in a simulated marine eco-environment, which can be used to promote biofilm growth without interfering in extended habitation of model coral samples,” said Lu.
Future research from the team will focus on long-term surface wear testing and biocompatibility in real-life applications.
###
The article “A phenomenological investigation of organic modified cements as biocompatible substrates interfacing model marine organisms” is authored by Jinglun Zhao, Tao Yuan, Hui Huang, and Xiaolin Lu. The article will appear in Biointerphases on Sept. 24, 2024 (DOI: 10.1116/6.0003811). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1116/6.0003811.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Biointerphases, an AVS journal published by AIP Publishing, emphasizes quantitative characterization of biomaterials and biological interfaces. As an interdisciplinary journal, a strong foundation of chemistry, physics, biology, engineering, theory, and/or modelling is incorporated into original articles and reviews. See: https://pubs.aip.org/avs/bip.
ABOUT AVS
AVS is an interdisciplinary, professional society with some 4,500 members worldwide. Founded in 1953, AVS hosts local and international meetings, publishes four journals, serves members through awards, training and career services programs and supports networking among academic, industrial, government, and consulting professionals. Its members come from across the fields of chemistry, physics, biology, mathematics, engineering and business and share a common interest in basic science, technology development and commercialization related to materials, interfaces, and processing. See: https://www.avs.org.
###
END
Improved cement to protect the living treasures of our coastlines
Surface treatments show promise for improving the biocompatibility of artificial coastline structures
2024-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Absolute and functional iron deficiency in the US
2024-09-24
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that absolute and functional iron deficiency affect a large proportion of American adults even in the absence of anemia, heart failure, or chronic kidney disease. Further research on the role of functional iron deficiency in adverse health outcomes and on iron deficiency screening strategies is needed.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Leo F. Buckley, Pharm.D., M.P.H., email lfbuckley@bwh.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed ...
Rural-urban disparities in hospital services and outcomes for children with medical complexity
2024-09-24
About The Study: Rural-residing children with medical complexity were significantly more likely to present to hospitals without dedicated pediatric services in this cohort study. These findings suggest that efforts are justified to ensure that all hospital types are prepared to care for children with medical complexity.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, JoAnna K. Leyenaar, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H., email joanna.k.leyenaar@hitchcock.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.35187)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Fewer than half of US jails provide life-saving medications for opioid use disorder
2024-09-24
A new look into addiction treatment availability in the U.S. criminal justice system reveals that fewer than half (43.8%) of 1,028 jails surveyed across the nation offered any form of medication for opioid use disorder, and only 12.8% made these available to anyone with the disorder. With two-thirds of people who are incarcerated in U.S. jails experiencing a substance use disorder – in many cases, an opioid use disorder – the failure to make these medications widely available in criminal justice settings represents a significant missed opportunity to provide life-saving treatments in an environment where people in need of care can be easily reached.
The study, published ...
Voice-activated cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia
2024-09-24
About The Study: This randomized clinical trial of an in-home, voice-activated cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia program among breast cancer survivors found that the intervention improved insomnia symptoms. Future studies may explore how this program can be taken to scale and integrated into ambulatory care.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Hannah Arem, Ph.D., email Hannah.Arem@medstar.net.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: ...
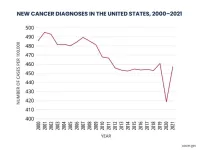
New cancer diagnoses did not rebound as expected following pandemic
2024-09-24
What: Cancer incidence trends in 2021 largely returned to what they were before the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a study by researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH). However, there was little evidence of a rebound in incidence that would account for the decline in diagnoses in 2020, when screening and other medical care was disrupted. One exception was breast cancer, where the researchers did see an uptick in diagnoses of advanced-stage disease in 2021. The study appears Sept. 24, 2024, in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
A previous study showed that new cancer diagnoses fell abruptly ...
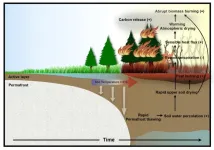
Abrupt intensification of northern wildfires due to future permafrost thawing
2024-09-24
A study, published in the journal Nature Communications by an international team of climate scientists and permafrost experts shows that, according to new climate computer model simulations, global warming will accelerate permafrost thawing and as a result lead to an abrupt intensification of wildfires in the Subarctic and Arctic regions of northern Canada and Siberia.
Recent observational trends suggest that warm and unusually dry conditions have already intensified wildfires in the Arctic region. To understand ...
Review shows bird flu control strategies ‘not working’
2024-09-24
A review of sustained mammal-to-mammal bird flu transmission in diverse species, led by The Pirbright Institute, shows global control strategies are not working.
Writing in Nature, researchers analysed whether outbreaks in European fur farms, South American marine mammals and United States dairy cattle raise questions about whether humans are next. Led by zoonotic influenza specialist Dr Thomas Peacock, the scientists evaluated how recent changes in the ecology and molecular evolution of H5N1 in wild and domestic birds increase opportunities for spillover ...
How a butterfly invasion minimizes genetic diversity
2024-09-24
Until a few years ago, the butterfly known as the southern small white could barely be found north of the Alps. That was before a Europe-wide invasion that brought a huge increase in the insect’s distribution – at the same time as a rapid decrease in genetic diversity within the species.
It took a while for zoologist Daniel Berner to notice that a butterfly species that wasn’t local to his area had become established in his garden. Then, suddenly, he saw it everywhere: Pieris mannii – also known as the southern small ...
Another Franklin expedition crew member has been identified
2024-09-24
The skeletal remains of a senior officer of Sir John Franklin's 1845 Northwest Passage expedition have been identified by researchers from the University of Waterloo and Lakehead University using DNA and genealogical analyses.
In April of 1848 James Fitzjames of HMS Erebus helped lead 105 survivors from their ice-trapped ships in an attempt to escape the Arctic. None would survive. Since the mid-19th century, remains of dozens of them have been found around King William Island, Nunavut.
The identification was made possible by a DNA sample from a living descendant, which matched the ...
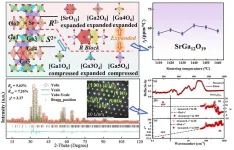
SrGa12O19: The first low-εr Ga-based microwave dielectric ceramic with anomalous positive τf
2024-09-24
As one of the key materials of modern microwave communication technology, microwave dielectric ceramics are widely used in many core components of microwave circuits. In recent years, with the rapid development of microwave communication technology marked by mobile communication, in order to meet the requirements of the development of mobile communication technology, including 5G/6G, new requirements have been put forward for the performance parameters of microwave dielectric ceramics: low dielectric constant to reduce signal delay, low dielectric loss or high quality factor, and near-zero ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Improved cement to protect the living treasures of our coastlinesSurface treatments show promise for improving the biocompatibility of artificial coastline structures