(Press-News.org) Toronto -- Modern crowdfunding has grown from relatively modest beginnings in the late 1990s to a multi-billion-dollar financing market for all kinds of early-stage innovations. The platform Kickstarter alone went from $276 million pledged in 2012 to $7.8 billion in 2024. There are even professional project designers to help craft that winning proposal.
With stakes like those, getting the pitch right is everything.
Enter machine learning to assist. Researchers from the University of Toronto’s Rotman School of Management put four different types of this artificial intelligence application to the test, including Deep Learning. Machine learning proved not only superior to conventional statistical methods for predicting whether a crowdfunding campaign would reach its goal, it also identified which elements helped most, and how.
“Running a crowdfunding campaign is costly and could fail,” says Ramy Elitzur, a professor of accounting at the Rotman School. “Our analysis shows project creators ways to improve their chances of success, or, alternatively, whether they should pursue a different project funding strategy.”
Kickstarter is an all-or-nothing platform meaning that project creators don’t receive any money unless they meet their fundraising goal. Analyzing more than 100,000 Kickstarter projects, Prof. Elitzur, Prof. David Soberman, who is the Canadian National Chair of Strategic Marketing, and other researchers found that the size of the campaign’s monetary goal accounted for more than half of a project’s success. The creator’s social capital, the number of reward options offered, and the campaign’s duration were also top factors.
Machine learning also got into the nitty-gritty of how much and how long. A project’s chances of success remained pretty much the same up to a fundraising goal of $100,000, then began to drop beyond that, with a sharper drop-off over $133,300. Conventional standard regression models however predict that the chance of success consistently drops as the monetary goal increases. That’s because these models lean towards identifying “linear” relationships where influencing factors and outcomes move in only one direction.
Crowdfunding, like many things, is more complex, with multiple variables acting on each other as well as the outcome. “One of the things machine learning does is model all possible interactions among variables,” says Prof. Elitzur. “It gives us the direct effect on the outcome of each variable and the total effect of the interaction with other variables.”
While standard regression showed success increased with greater social capital -- measured through the number of comments a project earned -- machine learning revealed that success actually increased up to about 750 comments, then levelled off. Its results also suggested the sweet spot for campaign duration was 10 to 15 days and that the number of project reward options has a moderate positive effect on success up to about 15 reward options, then slightly negative effects between 15 and 20 options, followed by a positive effect in waves between 20 and 50 reward options, finally plateauing after 50 options.
When machine learning’s text analysis capabilities were deployed – something numerically based standard methods can’t do—they could reach beyond Kickstarter’s 15 main project classifications to identify “gadgets” as the least successful project type.
It turns out that creators looking for that winning proposal should steer clear of flyable Second World War aircraft. In that case, “the deck is stacked against you and you would have a lower likelihood of success than any other domain,” says Prof. Elitzur, who is currently applying the same methods to predicting high-tech start-up success.
In addition, the text analysis capabilities of the models illustrate that, like real estate, the location of the project counts.
The research was also co-written with Noam Katz of Ben Gurion University in Israel and Perri Mutath of The Israel Innovation Authority. It appears in the Journal of Business Venturing Design.
Bringing together high-impact faculty research and thought leadership on one searchable platform, the Rotman Insights Hub offers articles, podcasts, opinions, books and videos representing the latest in management thinking and providing insights into the key issues facing business and society. Visit www.rotman.utoronto.ca/insightshub.
The Rotman School of Management is part of the University of Toronto, a global centre of research and teaching excellence at the heart of Canada’s commercial capital. Rotman is a catalyst for transformative learning, insights and public engagement, bringing together diverse views and initiatives around a defining purpose: to create value for business and society. For more information, visit www.rotman.utoronto.ca
-30-
For more information:
Ken McGuffin
Manager, Media Relations
Rotman School of Management
University of Toronto
E-mail: mcguffin@rotman.utoronto.ca
END
Finding the sweet spot: Machine learning reveals factors for successful crowdfunding
2024-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
University of Houston unveils guideline to enhance treatment access for opioid use disorder in community pharmacies
2024-09-24
Pharmacists now have more guidance in combatting the opioid crisis and providing treatment to patients thanks to new national guidelines developed at the University of Houston College of Pharmacy. The Pharmacy Access to Resources and Medication for Opioid Use Disorder Guideline, released today, addresses critical barriers in the treatment of Opioid Use Disorder across the nation’s community pharmacies.
With approximately 2.7 million individuals in the U.S. affected by OUD, the need for effective management strategies has never been more urgent. The PhARM-OUD Guideline marks a significant advancement as ...
Atmospheric methane increase during pandemic due primarily to wetland flooding
2024-09-24
A new analysis of satellite data finds that the record surge in atmospheric methane emissions from 2020 to 2022 was driven by increased inundation and water storage in wetlands, combined with a slight decrease in atmospheric hydroxide (OH). The results have implications for efforts to decrease atmospheric methane and mitigate its impact on climate change.
“From 2010 to 2019, we saw regular increases – with slight accelerations – in atmospheric methane concentrations, but the increases that occurred from ...
Violence, harassment from students is overwhelmingly ‘part of the job’ for Saskatchewan education sector workers
2024-09-24
Saskatchewan education sector workers are experiencing disturbing levels of workplace violence and harassment, says a new report spotlighting a situation that has reached “a breaking point,” according to its authors.
Testimonies catalogued by University of Ottawa researchers found Saskatchewan schools are far from offering a safe and violence-free environment as workplace violence becomes increasingly normalized.
“I’ve been punched in the face, had push pins held to my eyeballs, and scissors held to my throat,” the report quotes one ...
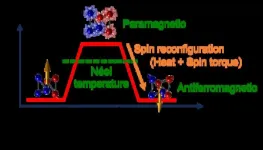
Thermal effects in spintronics systematically assessed for first time
2024-09-24
Spintronics – devices that use microscopic magnetism in conjunction with electric current – could lead to computing technology as fast as conventional electronics but much more energy efficient. As such devices are developed and studied, an important unresolved question is how device operation is affected by heating.
A new experimental technique, reported by researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign in the journal APL Materials, directly measures heating in spintronic devices, allowing direct comparison to other effects. The researchers say that this technique can be used to select spintronic materials whose magnetic behavior is minimally impacted by heating, ...
Study shows rates of e-bike injuries rise fourfold and powered scooter injuries nearly double
2024-09-24
September 24, 2024-- The rate of e-bike and powered scooter injuries surged between 2019 and 2022-- by 293 percent and 88 percent, respectively, according to a new study at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. The research adds to the existing information and gap in knowledge on the sociodemographic and risk factor variables that might be contributing to micromobility vehicle–related injuries. The findings are published in the American Journal of Public Health.
Micromobility generally refers to any small, low-speed, human- or electric-powered transportation device. Between 2019 and 2022, e-bike sales increased by 269 ...
Prediabetes during adolescence and young adulthood linked with likelihood of adverse pregnancy outcomes
2024-09-24
September 24, 2024-- New research conducted at Columbia Mailman School of Public Health and Mount Sinai School of Medicine shows a link between prediabetes among young people and adverse pregnancy outcomes later in life. The findings could alter how doctors routinely screen or counsel youth on blood glucose levels, and subsequently, minimize potential maternal and neonatal risks. The results are published in JAMA Network Open.
“This study is an important step in tying lifecourse cardiometabolic health to optimal pregnancy outcomes,” said Teresa Janevic, PhD, associate professor of Epidemiology at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and senior author. ...
Researchers discover new role of immune cells in eye health
2024-09-24
The eye is an immune-privileged tissue because of the need to keep blood vessels away from the central pathway of light and to restrict entry of inflammatory cells that could cause damage. This has prompted questions about how the eye manages inflammation when it occurs.
A new study led by Thomas Jefferson University researchers has revealed insights into how the eye handles inflammation, particularly in autoimmune uveitis, an inflammatory disease that bypasses the eye’s immune privilege and can damage healthy eye tissue.
Previous studies by Jefferson researcher Sue Menko, PhD, revealed that immune cells ...
Daniel R. Larson to receive 2025 Carolyn Cohen Innovation Award
2024-09-24
ROCKVILLE, MD – The Biophysical Society is pleased to announce that Daniel R. Larson, PhD, of the Center for Cancer Research at the National Cancer Institute within the National Institutes of Health, will receive the 2025 Carolyn Cohen Innovation Award. Larson will be honored at the Society’s 69th Annual Meeting, being held in Los Angeles, California from February 15-19, 2025.
Larson is being recognized for his pioneering contributions to the field of gene regulation using single-cell and single-molecule biophysical ...
James A. Glazier to receive 2025 Klaus Schulten and Zaida Luthey-Schulten Computational Biophysics Lecture Award
2024-09-24
ROCKVILLE, MD – The Biophysical Society is pleased to announce that James A. Glazier, PhD, of Indiana University, Bloomington, has been named the recipient of the 2025 Klaus Schulten and Zaida Luthey-Schulten Computational Biophysics Lecture Award. Glazier will be honored at the Society’s 69th Annual Meeting, being held in Los Angeles, California from February 15-19, 2025.
Glazier will be recognized for his development of algorithms, software, and models describing the emergent multicellular organization of development, homeostasis, and disease.
“I am delighted that the Biophysical Society is recognizing James’s pioneering work the ...
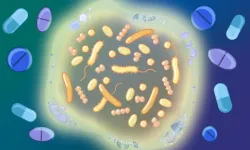
Better together: Gut microbiome communities’ resilience to drugs
2024-09-24
Many human medications can directly inhibit the growth and alter the function of the bacteria that constitute our gut microbiome. EMBL Heidelberg researchers have now discovered that this effect is reduced when bacteria form communities.
In a first-of-its-kind study, researchers from EMBL Heidelberg's Typas, Bork, Zimmermann, and Savitski groups, and many EMBL alumni, including Kiran Patil (MRC Toxicology Unit Cambridge, UK), Sarela Garcia-Santamarina (ITQB, Portugal), André Mateus (Umeå University, ...