(Press-News.org) Lead researcher Dr Sarah Nason, from Bangor University’s School of History, Law and Social Sciences explained: “Debt, benefits, special educational needs, healthcare issues, these are everyday problems that many of us face, and it’s only natural to turn to people you know and trust for help and advice. However, we found that having to talk to more people or support services was an indicator that the problem was more complex and difficult to resolve.”
The team studied four distinct areas across England and Wales: Bryngwran, a village on Anglesey in North Wales; Deeplish, a district of Rochdale in Greater Manchester; the town of Dartmouth in Devon; and three wards in the London borough of Hackney.
In total, the researchers conducted individual interviews with 191 people, mapping out who they spoke to on a regular basis, such as friends, family, work colleagues or community volunteers, and who they might turn to with any problems relating to social welfare. They also asked how many of these contacts knew each other, to determine how well-connected the person’s social network was.
The researchers also spoke to community organisations and local authorities, identifying available sources of formal and informal advice and community support in each area.
They found that individuals living in the rural communities in Devon and North Wales had larger networks with more interconnections, compared to smaller, less well-connected networks of people in the urban locations in Hackney. In Deeplish in Rochdale, social networks were comparatively small, but quite well-connected. This was linked to ethnicity, with the primarily South Asian participants in Deeplish also having networks with the highest proportion of family members. For those with White ethnicity, people who identified as English generally had smaller social networks than those identifying as British or Welsh. The most interconnected networks were amongst people who identified as Welsh.
The researchers also found greater similarities between social networks within each case study community than between those of people with individual characteristics, such as age, gender, employment status or disability across the case study areas.
Dr Nason said: “Our research isn’t intended to be statistically representative of the case study areas, as we only spoke to a relatively small group of people in each community. However, from those interviews and from our analysis, location and ethnicity appear to be important factors in understanding how people relate to their community and access support. This highlights how important it is to provide local, community-based and culturally sensitive support and advice rather than ‘one size fits all’ services at a national level.”
Although many services are moving to ‘digital by default’ rather than offering face-to-face support, digital services did not meet many people’s needs. In all case study areas, interviewees said that accessing help and advice locally and in-person was important to them, with local access being seen as essential to many people.
Despite the differences between the four areas studied, the researchers found that the size and connectedness of social networks had a limited impact on the likelihood of people’s social welfare problems being resolved.
The biggest factor in resolving problems was the nature of the problem itself. Across all four areas, people with welfare benefits or financial problems were more likely to have received help from formal advice services and to have their problems resolved, than those with problems around housing, social care, special educational needs provision or mental health services.
“There are well-established processes for dealing with welfare disputes or debt, and although these can be daunting, with the right support and advice these issues generally get resolved,” said Dr Nason. “However, it’s noticeable that the problems which were least likely to be resolved relate to local authority services which have seen substantial budget cuts over recent decades, and where services are stretched to the point of failure. Stronger social networks and more support and advice can’t completely compensate for this lack of investment in public services.”
Other factors impacting people’s ability to get help were lack of education around rights and entitlements, limited awareness of advice services, feelings of stigma or shame in seeking help, and loss of trust in the state. However, the significance of each of these factors was different across the case study areas. For example, stigma/shame was perceived as a particular issue in rural North Wales, lack of formal education was a challenge in Rochdale, and mistrust of the state was highest amongst marginalised communities in Dartmouth and younger people in Hackney.
The study highlights the important role played by community centres or hubs, which provide vital services to their local community, including social welfare advice. However, the researchers caution that these organisations are often under-resourced and cannot be a substitute for more formal legal advice services.
“Across all the communities we studied, the local hubs or centres were really valued by people, providing day-to-day support such as food banks,” explained Dr Nason. “However, some problems that people face need specialist legal advice, and these community centres rely on being able to signpost people on to more formal services. Without proper funding for the formal advice sector, problems continue. Communities may be able to access help, but there won’t be access to justice.”
END
Social networks help people resolve welfare problems - but only sometimes, new research finds
Sharing a social welfare problem with several friends, family or support services doesn’t always mean the issue is more likely to be resolved, finds new research.
2024-09-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Honey, I shrunk the city: What should declining Japanese cities do?
2024-09-30
Aging societies and population decline have been on the rise globally, but in Japan, the situation has exasperated tenfold. A staggering 36.21 million people, or 28.9% of the populace, are 65 and over. Further, 74.6% of Japan’s 1,747 cities are categorized as shrinking, with urban policies struggling to keep up with the decline. However, the factors that correlate with population changes in cities of varying sizes have not been clarified.
Dr. Haruka Kato, a junior associate professor at Osaka Metropolitan University, ...
New brain cell cleaner: astrocytes raise possibility of Alzheimer’s disease treatment
2024-09-30
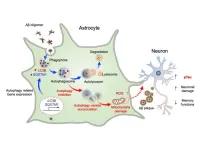
A research team led by Dr. Hoon Ryu from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Sang-Rok Oh) Brain Disease Research Group, in collaboration with Director Justin C. Lee of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS, President Do-Young Noh) and Professor Junghee Lee from Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, has uncovered a new mechanism involving astrocytes for treating Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and proposed a novel therapeutic target. In this study, the researchers revealed that autophagy pathway ...
American Academy of Pediatrics announces its first clinical practice guideline for opioid prescriptions
2024-09-30
Media contacts:
Lisa Robinson, lrobinson@aap.org
Alex Hulvalchick, ahulvalchick@aap.org
American Academy of Pediatrics Announces its First Clinical Practice Guideline for Opioid Prescriptions
Pediatricians should prescribe opioids for pain when necessary, with recommended precautions in place to increase safety, according to a clinical practice guideline released during the AAP 2024 National Conference & Exhibition
ORLANDO, Fla.--The American Academy of Pediatrics has published its first clinical ...
Drivers of electric vehicles are more likely to be at fault in road traffic crashes than drivers of petrol and diesel cars
2024-09-30
Drivers of electric vehicles (EVs) are more likely to be involved in at-fault road traffic accidents than drivers of petrol and diesel cars, research by Lero, the Research Ireland Centre for Software, at University of Limerick and Universitat de Barcelona, reveals.
In the analysis of insurance claims and data from onboard sensors, due to be published in the November issue of the journal Accident Analysis & Prevention, the Lero researchers reveal a number of key findings:
Electric and hybrid drivers exhibit different behaviours ...
Duke-NUS study proposes new heart failure treatment targeting abnormal hormone activity
2024-09-30
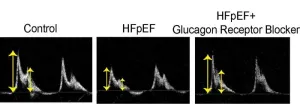
Duke-NUS scientists and their collaborators have discovered a potential new treatment for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), a type of heart disease that is notoriously difficult to treat. The team discovered that the diseased heart cells had high levels of glucagon activity, a pancreatic hormone that raises blood sugar (glucose) levels. Armed with this novel insight, the scientists demonstrated that a drug that blocks the hormone’s activity, can significantly improve heart ...
People who experience side effects from cranial radiation therapy may recover full neurocognitive function within months
2024-09-29
WASHINGTON, September 29, 2024 — A substantial number of patients with brain metastases who experience cognitive side effects following radiation therapy may fully regain cognitive function, according to a pooled analysis of three large, phase III clinical trials. Recovery was more likely for people treated with conformal, or highly targeted, radiation techniques, compared to standard whole-brain treatment. The findings will be presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) ...
Radiopharmaceutical therapy offers promise for people with tough-to-treat meningioma brain tumors
2024-09-29
WASHINGTON, September 29, 2024 — A radiopharmaceutical therapy that has successfully extended progression-free survival for patients with neuroendocrine tumors shows early promise for delivering similar benefits to patients with difficult-to-treat meningioma, a type of brain tumor. Findings of the nonrandomized phase II study will be presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Annual Meeting.
“We’ve found a therapy with a meaningful signal for effectiveness and safety for people with refractory meningioma, a condition with no ...
American Academy of Pediatrics promotes shared reading starting in infancy as a positive parenting practice with lifelong benefits
2024-09-29
ORLANDO, Fla.--The American Academy of Pediatrics encourages parents and caregivers to read aloud with their newborns and young children as an opportunity to foster loving, nurturing relationships during a critical time of brain development, and recommends that pediatricians support families with guidance and books at well-child visits, according to an updated policy statement.
The policy statement, “Literacy Promotion: An Essential Component of Primary Care Pediatric Practice,” marks the first update in AAP recommendations since 2014. Given the extraordinary amount of research in this area, an accompanying ...
Unexpected human behaviour revealed in prisoner's dilemma study: Choosing cooperation even after defection
2024-09-28
The study also examined the impact of different game structures, such as simultaneous versus alternating decision-making, and the option of voluntary participation. The results showed that these variations significantly influence participants' cooperation rate.
The research reveals that people tend to cooperate even after being defected, which contradicts many traditional game theory models. "This finding is particularly fascinating because it suggests that humans are more forgiving and cooperative than previously thought," said Dr. Hitoshi Yamamoto, the study's lead researcher.
The ...
Distant relatedness in biobanks harnessed to identify undiagnosed genetic disease
2024-09-27
An innovative analysis of shared segments within the genome — an indication of distant “relatedness” — has identified undiagnosed cases of Long QT syndrome, a rare disorder that can lead to abnormal heart rhythms, fainting and sudden cardiac death.
The findings, reported in the journal Nature Communications, illustrate the feasibility of the new approach developed by researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center to detect undiagnosed carriers of rare ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Improved short-term sea level change predictions with better AI training
UAlbany researchers develop new laser technique to test mRNA-based therapeutics
New water-treatment system removes nitrogen, phosphorus from farm tile drainage
Major Canadian study finds strong link between cannabis, anxiety and depression
New discovery of younger Ediacaran biota
Lymphovenous bypass: Potential surgical treatment for Alzheimer's disease?
When safety starts with a text message
CSIC develops an antibody that protects immune system cells in vitro from a dangerous hospital-acquired bacterium
New study challenges assumptions behind Africa’s Green Revolution efforts and calls for farmer-centered development models
Immune cells link lactation to long-lasting health
Evolution: Ancient mosquitoes developed a taste for early hominins
Pickleball players’ reported use of protective eyewear
Changes in organ donation after circulatory death in the US
Fertility preservation in people with cancer
A universal 'instruction manual' helps immune cells protect our organs
Fifteen-year results from SWOG S0016 trial suggest follicular lymphoma is curable
The breasts of a breastfeeding mother may protect a newborn from the cold – researchers offer a new perspective on breast evolution
More organ donations now come from people who die after their heart stops beating
How stepping into nature affects the brain
Study: Cancer’s clues in the bloodstream reveal the role androgen receptor alterations play in metastatic prostate cancer
FAU Harbor Branch awarded $900,000 for Gulf of America sea-level research
Terminal ileum intubation and biopsy in routine colonoscopy practice
Researchers find important clue to healthy heartbeats
Characteristic genomic and clinicopathologic landscape of DNA polymerase epsilon mutant colorectal adenocarcinomas
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
The Lancet: New weight loss pill leads to greater blood sugar control and weight loss for people with diabetes than current oral GLP-1, phase 3 trial finds
Pediatric investigation study highlights two-way association between teen fitness and confidence
Researchers develop cognitive tool kit enabling early Alzheimer's detection in Mandarin Chinese
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
[Press-News.org] Social networks help people resolve welfare problems - but only sometimes, new research findsSharing a social welfare problem with several friends, family or support services doesn’t always mean the issue is more likely to be resolved, finds new research.