(Press-News.org) Ron Mittler is on a quest to create a smarter soybean. For years, mid-Missouri has withstood unpredictable weather patterns, including drought, heat waves and flooding — conditions that are known to hamper agricultural yields and make it difficult for farmers to produce. While we can’t control the weather, Mittler and his team are working to harness soybean crops’ natural ability to adapt to unfavorable weather conditions while also increasing their yields.
Working with $2.4 million from the National Science Foundation, Mittler hopes to add to his more than two decades of research by investigating the mechanisms behind how plants cool themselves while under heat and drought stress. He’ll achieve this by genetically engineering soybean plants in ways that improve their resistance to these stresses.
This research brings Mittler one step closer to helping Missouri farmers adapt to harmful weather patterns while continuing to meet demand.
“What excites me is learning how plants solve problems and adapt to changes in their environment,” said Mittler, a professor of plant sciences in the University of Missouri’s College of Agriculture, Food and Natural Sciences. “Based on what we’ve learned from plants’ adaptation strategies, my team is able to take these new fundings and continue to innovate and improve upon what we already know.”
How do soybeans still produce yields when they’re hot and thirsty?
Having tracked weather patterns in Missouri for two decades, Mittler knows heat waves that frequently traverse the state are responsible for significant yield destructions. He sees exploring genetic variability — the differences in genes among populations — as a helpful way to figure out what soybean genes create plants most likely to withstand a combination of stress conditions.
Thanks to generations in tough environments, soybeans have evolved to manipulate cells — called guard cells — that control the opening and closing of stomatal pores on the surface of their leaves, sepals and flowers to become even more resilient to harsh weather conditions.
When there is a drought, the plant closes its stomata to retain water. However, when there is heat stress on top of the drought, the plant can’t breathe. Interestingly, some species of soybean plants have learned to cool themselves by only opening the stomata on their reproductive surfaces (the flowers and sepals) while closing the stomata on their leaves to retain water.
This balance allows the plant to cool itself and retain the water it needs to hydrate, ultimately keeping it alive long enough to produce its seasonal yield.
The answers are in teamwork
As a Bond Life Science Center principal investigator, Mittler said being a part of the Interdisciplinary Plant Group (IPG) is key to the success of his research. The IPG is an internationally recognized collective of professionals who research solutions to challenging questions in plant biology and beyond.
“Being a part of the IPG and working at Bond Life Science Center has been transformative for my research,” Mittler said. “IPG is home to incredible collaborators, world-class facilities and resources. These things enhance collaborations and inspire international conferences that spur growth and partnerships that move our research forward and support our students as they progress in their careers. I’m very happy to be here.”
Co-investigators on this grant include MizzouForward and Bond LSC researcher Marc Libault and Felix Fritschi, both professors of plant science in the Division of Plant Science and Technology.
Story written by Courtney Perrett
END
Making soybeans smarter
Mizzou plant geneticist Ron Mittler is finding ways to breed soybean crops that can handle heat, drought and water-logging stresses, improving yields under pressure.
2024-09-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
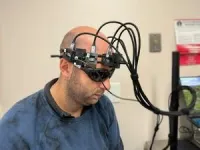
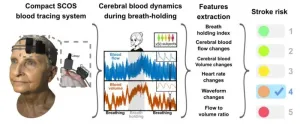
New wearable laser device monitors brain blood flow to gauge stroke risk
2024-09-30
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a laser-based device that can be placed on the head to non-invasively monitor changes in brain blood flow and volume. The new device could one day help save lives by offering a direct and simple way to assess stroke risk based on physiological markers rather than indirect markers like lifestyle factors.
Strokes occur when blood flow to the brain is blocked or reduced, causing debilitating brain cell damage. With about 15 million people worldwide affected by strokes each year, it is the second leading cause of death and ...
BU professor receives $29M NIH grant to study dementia risk factors, prevention, and treatment
2024-09-30
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Monday, September 30, 2024
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
BU Professor Receives $29M NIH Grant to Study Dementia Risk Factors, Prevention, and Treatment
The Triangulation of Innovative Methods to End Alzheimer’s Disease project will use large, diverse datasets to examine whether interventions targeting alcohol use, depression, vision or hearing impairments, or social isolation can protect people from Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. This project is a collaboration among Dr. Maria Glymour at Boston University School of Public Health, Dr. Jacqueline ...
Ninth Circuit reverses lower court, reinforces FDA's authority to regulate unproven stem cell products
2024-09-30
In an important step to protect the public from unproven stem cell products, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit ruled in favor of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in U.S. v. California Stem Cell Treatment Center, Inc., reversing the district court. The reversal fortifies FDA’s tiered, risk-based framework for the regulation of cell therapies and is consistent with a similar ruling in the Eleventh Circuit in 2021.
The appellees urged the Ninth Circuit to uphold the lower court’s ...
Wnt happens in kidney development?
2024-09-30
A group of essential signaling molecules known as the Wnt pathway emerged early in the evolution of multicellular life. Scientists have been studying Wnt actions for four decades to comprehend its complex roles in development and disease. In development of the mammalian kidney, USC Stem Cell scientists from Andy McMahon’s lab undertook a pair of complementary studies, published today in the journal Development, that provide new insight into the critical role of Wnt signaling in initiating the development of the mammalian kidney.
“Many stem and progenitor cells require Wnt signaling, ...
Where flood policy helps most — and where it could do more
2024-09-30
Flooding, including the devastation caused recently by Hurricane Helene, is responsible for $5 billion in annual damages in the U.S. That’s more than any other type of weather-related extreme event.
To address the problem, the federal government instituted a program in 1990 that helps reduce flood insurance costs in communities enacting measures to better handle flooding. If, say, a town preserves open space as a buffer against coastal flooding, or develops better stormwater management, area policy owners get discounts on their ...
Combining AI and thermal video offers a new window into weightlifting
2024-09-30
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new method that combines video from thermal cameras with AI-based digital processing to enhance weightlifting training. By providing data-driven insights that enable targeted training and recovery strategies, the approach could help to optimize performance and safety in a variety of sport and exercise contexts.
Thermal, or infrared, images can provide valuable information for sports and health by tracking muscle activation and detecting areas of strain or fatigue. This information can be used to prevent injuries, monitor thermal responses and quantify physical exercise, ultimately helping athletes boost their skills. However, most ...
Childhood social interactions combat stereotypes
2024-09-30
Prior research has found that exposure to social diversity in early life, such as through day care, influences how people communicate.
Those early social experiences can also moderate tendencies toward stereotyping down the road, according to a new study published in the NPJ Science of Learning.
"The more time an individual spent in day care as a child, the more likely they are to overcome their own stereotypical beliefs during social interactions later in life," says senior author Arjen Stolk, an assistant professor in the Department ...
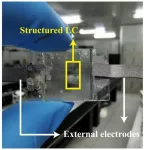
Researchers harness liquid crystal structures to design simple, yet versatile bifocal lenses
2024-09-30
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new type of bifocal lens that offers a simple way to achieve two foci (or spots) with intensities that can be adjusted by applying external voltage. The lenses, which use two layers of liquid crystal structures, could be useful for various applications such as optical interconnections, biological imaging, augmented/virtual reality devices and optical computing.
“Most liquid-crystal-based devices are made from single-layer structures, but this limits light field modulation ...
Suicide attempts decreased after adding suicide care to primary care, study finds
2024-09-30
After suicide care was integrated into routine primary care visits, researchers saw a 25% decrease in the rate of suicide attempts in the following 90 days, a new Kaiser Permanente study finds.
The study, published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, is the first to show that suicide risk screening in primary care, followed by safety planning, improved suicide prevention efforts in a health care setting. The trial took place at Kaiser Permanente clinics in Washington state, using data from January 2015 to July 2018.
“Our findings are important because we know many people seek primary care prior to fatal and nonfatal suicide attempts,” ...
One in three Americans has a dysfunctional metabolism, but intermittent fasting could help
2024-09-30
LA JOLLA (Sept 30, 2024)—More than one-third of adults in the United States have metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that significantly raise a person’s risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. These conditions include high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, excess abdominal fat, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
In a new clinical trial, researchers at the Salk Institute and University of California San Diego School of Medicine found that time-restricted eating—also known as intermittent fasting—could offer significant health benefits to adults with metabolic syndrome. Patients ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
[Press-News.org] Making soybeans smarterMizzou plant geneticist Ron Mittler is finding ways to breed soybean crops that can handle heat, drought and water-logging stresses, improving yields under pressure.