(Press-News.org) The American Cancer Society (ACS) today released Breast Cancer Statistics, 2024, the organization’s biennial update on breast cancer occurrence and trends in the United States. The new report finds breast cancer mortality rates overall have dropped by 44% since 1989, averting approximately 517,900 breast cancer deaths. However, not all women have benefited from this progress, notably American Indian and Alaska Native (AIAN) women, whose rates have remained unchanged over the past three decades. Also concerning is the continued upward trend in breast cancer incidence, rising by 1% annually during 2012-2021, with the steepest increase in women younger than 50 years (1.4% per year) and Asian American/Pacific Islander (AAPI) women of any age (2.5%-2.7% per year). These important findings are published in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, alongside its consumer-friendly companion, Breast Cancer Facts & Figures 2024, available on cancer.org.
“The encouraging news is breast cancer mortality rates continue to decrease thanks to advances in early detection and treatment,” said Angela Giaquinto, associate scientist, cancer surveillance research at the American Cancer Society and lead author of the study. “But future progress may be thwarted by increasing incidence, especially among younger women, and consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic, such as delayed diagnosis due to interruptions in screening.”
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among U.S. women after skin cancer and the leading cause of cancer death in Hispanic women. In 2024, an estimated 310,720 new cases of invasive breast cancer will be diagnosed in women, and approximately 42,250 women are expected to die from the disease. While rare, this year, 2,790 men will also be diagnosed with breast cancer, and 530 men will die from the disease.
For the report, researchers analyzed population-based cancer incidence and mortality data collected by the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Program of Cancer Registries (NPCR), and the National Center for Health Statistics. Combined SEER and NPCR data provided by the North American Association of Central Cancer Registries (NAACCR) were the source for short-term incidence trends (1998-2021) and contemporary incidence rates (2017–2021) by race and ethnicity, age, molecular subtype, state, and stage (SEER Summary).
“Women today are a lot less likely to die from breast cancer, but alarming disparities still remain, especially for Asian American, Pacific Islander, Native American and Black women,” said Dr. William Dahut, chief scientific officer at the American Cancer Society. “These gaps need to be rectified through systematic efforts to ensure access to high-quality screening and treatment for every woman.”
Other key findings from the report include:
AIAN women have 10% lower breast cancer incidence than White women, but 6% higher mortality, and only 51% of AIAN women 40 years or older had a mammogram in the past two years compared to 68% of White women.
Breast cancer in women under 50 years has increased in AAPI women by 50% since 2000, surpassing the rate in young Hispanic, AIAN, and Black women to become the highest rate alongside White women (both 86 per 100,000).
Black women continue to have a 38% higher breast cancer mortality rate than White women, despite a 5% lower incidence. Black women also have lower survival than White women for every breast cancer subtype and stage of diagnosis except localized disease, with which they are 10% less likely to be diagnosed (58% versus 68%).
To address ongoing cancer disparities in Black women, the ACS launched the VOICES of Black Women study in May 2024. The study aims to enroll over 100,000 Black women in the U.S. between the ages of 25 and 55 from diverse backgrounds and income levels who have not been diagnosed with cancer to better understand cancer risk and outcomes. For more information and to participate, visit voices.cancer.org.
“Building upon the progress we have made in reducing breast cancer mortality rates requires ensuring more individuals have access to breast cancer screenings,” said Lisa A. Lacasse, president of the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network (ACS CAN), the advocacy affiliate of the American Cancer Society. “Through cooperative agreements with all 50 states, tribal organizations and territories, the National Breast and Cervical Cancer Early Detection Program (NBCCEDP) has been a lifeline for limited-income, uninsured and underinsured women, providing them with critical screenings and treatment. Congress has a chance to pass the Screening for Communities to Receive Early and Equitable Needed Services (SCREENS) for Cancer Act, which would reauthorize the NBCCEDP and expand its reach to more people who may not otherwise be screened. We urge Congress to take this step towards saving lives from cancer while reducing costs for our health care system.”
Rebecca Siegel is senior author of the report. Other ACS authors participating in the study include Dr. Ahmedin Jemal, Dr. Hyuna Sung, Jessica Star and Dr. Robert Smith.
More information on breast cancer can be found here.
# # #
About the American Cancer Society
The American Cancer Society is the leading cancer-fighting organization with a vision to end cancer as we know it for everyone. For more than 110 years, we have been the only organization improving the lives of people with cancer and their families through advocacy, research, and patient support, to ensure that everyone has an opportunity to prevent, detect, treat, and survive cancer. To learn more, visit cancer.org or call our 24/7 helpline at 1-800-227-2345. Connect with us on Facebook, X, and Instagram.
END
Children of immigrants to the United States typically incorporate themselves into US economic and cultural life, and this pattern of assimilation has not markedly changed in over a century. Today, one in seven US residents was born abroad, rates similar to those seen in the late nineteenth century. As immigrants’ countries of origin have shifted from Europe to Asia and the Americas, a narrative has developed that contemporary immigrants do not assimilate as thoroughly as older immigrants. But is this true? In a Perspective, Ran Abramitzky and Leah Boustan summarize their long-running research program matching individuals across historical US Censuses. The authors compare ...
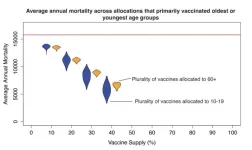
A model suggests that vaccinating children and teens against the flu can help protect the elderly in tropical countries. Influenza kills up to 650,000 people worldwide every year. In part due to the lack of strong seasonality and differences in vaccine supply, optimal vaccination strategies for the tropics may differ from those in temperate zones. Joseph Servadio and colleagues parameterized an age-structured mathematical model of influenza transmission to the asynchronous, non-annual epidemiology of tropical influenza in Vietnam, a country with low vaccine coverage. The model includes three subtypes of the flu virus. Vaccinating year-round was found to be ...
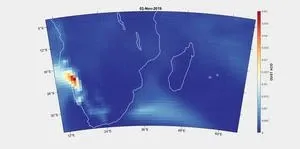
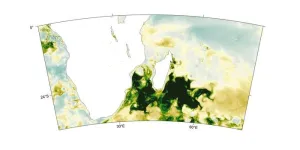
A study links an unusual plankton bloom off the coast of Madagascar to drought in Southern Africa. Climate warming has intensified droughts around the world. When vegetation dies from lack of water, the wind can pick up and carry unprotected soil particles for thousands of kilometers. These dust particles can then act as fertilizer when deposited in seawater. Dionysios Raitsos and colleagues show that dust from drought-stricken Southern Africa caused a bloom of marine phytoplankton off the southeast Madagascar coast from November 2019 through February 2020. The team used standardized anomalies of dust aerosol optical depth from the Copernicus ...
Seven nudges aiming to reduce hateful speech online all failed—but the nudges unexpectedly succeeded in increasing engagement with harmless and wholesome content. Controlling hate speech is an ongoing challenge for online communities. In a pre-registered experiment, Tatiana Celadin and colleagues compared the effects of seven “nudges,” messages designed to promote prosocial behaviors: reminding posters of descriptive norms, injunctive norms, or personal norms; cooling down negative emotions; stimulating deliberation or empathy; and highlighting reputation. Over 4,000 Americans recruited through the online platform ...
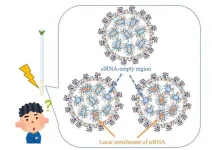
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) molecules hold immense potential for treating diseases by silencing specific genes. Encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), siRNA can be delivered efficiently to target cells. However, the effectiveness of these therapies hinges on the internal structure of the LNPs, which can significantly impact their ability to deliver siRNA. Traditional methods often fall short in providing the detailed molecular insights needed to fine-tune LNP design for optimal therapeutic efficacy.
A study published in the Journal of Controlled Release on August 02, 2024, led by Assistant Professor Keisuke Ueda from ...
Mount Sinai Health System’s Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and the Emergency Department Chair at Mount Sinai Queens have been recognized with top honors for their outstanding achievements at the American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) 2024 Scientific Assembly in Las Vegas during a special ceremony on Monday, September 30.
Brendan G. Carr, MD, MS, FACEP, CEO, Professor and Kenneth L. Davis, MD, Distinguished Chair of the Mount Sinai Health System, received the Colin C. Rorrie, Jr, PhD Award for Excellence in Health Policy.
This award is an extraordinary ...
PULLMAN, Wash. – To appeal to the majority of consumers, winemakers may want to pay as much attention to what’s on the bottle as what’s in it.
A three-part experimental study led by Washington State University researchers found that women were more inclined to purchase wine that had labels with feminine gender cues. The more strongly the participants identified with other women, a phenomenon called “in-group identification,” the greater this effect was. A feminine label also influenced their expectation that they would like the wine better.
With women representing 59% ...
The effects of climate change are not distant future scenarios or confined to remote parts of the world—they are unfolding now, right in our own backyards. In 2023, extreme weather events impacted communities across every inhabited continent, causing major flooding, droughts, and wildfires.
While worldwide changes, such as increases in global mean temperature, often dominate discussions of mitigation actions, a detailed understanding of the regional impacts of a warming world is crucial for protecting communities from escalating risks. A team of researchers writing in Frontiers in Science synthesized results ...
UCLA researchers have developed a deep-learning framework that teaches itself quickly to automatically analyze and diagnose MRIs and other 3D medical images – with accuracy matching that of medical specialists in a fraction of the time. An article describing the work and the system’s capabilities is published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
Unlike the few other models being developed to analyze 3D images, the new framework has wide adaptability across a variety of imaging modalities. The developers have studied it with 3D retinal scans (optical coherence tomography) for disease ...
As many as 249 lives could have been saved in London during the 2018 record-setting hot summer had the city widely adopted cool roofs, estimates a new study by researchers at UCL and the University of Exeter.
The paper, published in Nature Cities, analysed the cooling effect that roofs painted white or other reflective colours would have on London’s ambient temperature between June and August 2018, the city’s hottest summer. From June through August, the average temperature around London was 19.2 degrees C, about ...