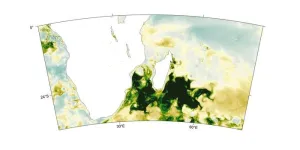
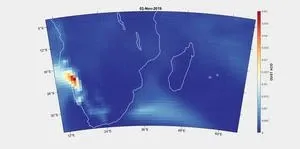
(Press-News.org) A study links an unusual plankton bloom off the coast of Madagascar to drought in Southern Africa. Climate warming has intensified droughts around the world. When vegetation dies from lack of water, the wind can pick up and carry unprotected soil particles for thousands of kilometers. These dust particles can then act as fertilizer when deposited in seawater. Dionysios Raitsos and colleagues show that dust from drought-stricken Southern Africa caused a bloom of marine phytoplankton off the southeast Madagascar coast from November 2019 through February 2020. The team used standardized anomalies of dust aerosol optical depth from the Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) and in situ coarse mode aerosol optical depth retrieved by a nearby Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) station to quantify the density of atmospheric dust aerosols over the Madagascar area through time. Dust aerosol optical depth anomalies averaged over the bloom region were the highest ever observed during the 17 years CAMS has been collecting data. This dust cloud coincided with heavy rains, which deposited the iron-rich particles into the sea, creating ideal nutrient conditions for phytoplankton growth. The authors identify multiple potential sources of these iron-rich dust aerosols in Southern Africa, which experienced high air temperature and drought from 2012–2020. According to the authors, as the climate warms, additional phytoplankton blooms caused by the same mechanism are to be expected—and these blooms could take up carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
END
Climate change, drought, dust, and plankton blooms
2024-10-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nudges fail to reduce online hate
2024-10-01
Seven nudges aiming to reduce hateful speech online all failed—but the nudges unexpectedly succeeded in increasing engagement with harmless and wholesome content. Controlling hate speech is an ongoing challenge for online communities. In a pre-registered experiment, Tatiana Celadin and colleagues compared the effects of seven “nudges,” messages designed to promote prosocial behaviors: reminding posters of descriptive norms, injunctive norms, or personal norms; cooling down negative emotions; stimulating deliberation or empathy; and highlighting reputation. Over 4,000 Americans recruited through the online platform ...
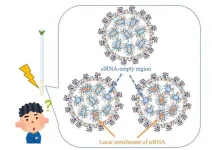
NMR-guided optimization of lipid nanoparticles for enhanced siRNA delivery
2024-10-01
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) molecules hold immense potential for treating diseases by silencing specific genes. Encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), siRNA can be delivered efficiently to target cells. However, the effectiveness of these therapies hinges on the internal structure of the LNPs, which can significantly impact their ability to deliver siRNA. Traditional methods often fall short in providing the detailed molecular insights needed to fine-tune LNP design for optimal therapeutic efficacy.
A study published in the Journal of Controlled Release on August 02, 2024, led by Assistant Professor Keisuke Ueda from ...
Mount Sinai leaders receive prestigious awards during the American College of Emergency Physicians 2024 Scientific Assembly (ACEP24)
2024-10-01
Mount Sinai Health System’s Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and the Emergency Department Chair at Mount Sinai Queens have been recognized with top honors for their outstanding achievements at the American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) 2024 Scientific Assembly in Las Vegas during a special ceremony on Monday, September 30.
Brendan G. Carr, MD, MS, FACEP, CEO, Professor and Kenneth L. Davis, MD, Distinguished Chair of the Mount Sinai Health System, received the Colin C. Rorrie, Jr, PhD Award for Excellence in Health Policy.
This award is an extraordinary ...
Women more likely to choose wine with feminine labels
2024-10-01
PULLMAN, Wash. – To appeal to the majority of consumers, winemakers may want to pay as much attention to what’s on the bottle as what’s in it.
A three-part experimental study led by Washington State University researchers found that women were more inclined to purchase wine that had labels with feminine gender cues. The more strongly the participants identified with other women, a phenomenon called “in-group identification,” the greater this effect was. A feminine label also influenced their expectation that they would like the wine better.
With women representing 59% ...
Understanding regional climate change is essential for guiding effective climate adaptation policy, study finds
2024-10-01
The effects of climate change are not distant future scenarios or confined to remote parts of the world—they are unfolding now, right in our own backyards. In 2023, extreme weather events impacted communities across every inhabited continent, causing major flooding, droughts, and wildfires.
While worldwide changes, such as increases in global mean temperature, often dominate discussions of mitigation actions, a detailed understanding of the regional impacts of a warming world is crucial for protecting communities from escalating risks. A team of researchers writing in Frontiers in Science synthesized results ...
New AI model efficiently reaches clinical-expert-level accuracy in complex medical scans
2024-10-01
UCLA researchers have developed a deep-learning framework that teaches itself quickly to automatically analyze and diagnose MRIs and other 3D medical images – with accuracy matching that of medical specialists in a fraction of the time. An article describing the work and the system’s capabilities is published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
Unlike the few other models being developed to analyze 3D images, the new framework has wide adaptability across a variety of imaging modalities. The developers have studied it with 3D retinal scans (optical coherence tomography) for disease ...
Cool roofs could have saved lives during London’s hottest summer
2024-10-01
As many as 249 lives could have been saved in London during the 2018 record-setting hot summer had the city widely adopted cool roofs, estimates a new study by researchers at UCL and the University of Exeter.
The paper, published in Nature Cities, analysed the cooling effect that roofs painted white or other reflective colours would have on London’s ambient temperature between June and August 2018, the city’s hottest summer. From June through August, the average temperature around London was 19.2 degrees C, about ...
Solidarity drives online virality in a nation under attack, study of Ukrainian social media reveals
2024-10-01
While divisive social media posts get more traction in countries such as the US, a new study shows that celebrating national unity is the way to go viral in Ukraine.
“Ingroup solidarity” statements got far more likes and shares than hostile posts about Russians – a trend that only grew stronger in the wake of the invasion.
The first major study of social media behaviour during wartime has found that posts celebrating national and cultural unity in a country under attack receive significantly more online engagement than derogatory posts about the aggressors.
University of Cambridge psychologists analysed a total of 1.6 million ...
Research heralds new era for genetics
2024-10-01
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 10AM (UK TIME) ON TUESDAY 1 OCTOBER 2024.
Peer reviewed | Observational study | People
Research led by scientists at Queen Mary University of London is heralding in a new era for genetic sequencing and testing.
In the largest study of its kind to date, published today in Nature Medicine, an international group of researchers led by Queen Mary used new bioinformatics techniques to scan the genetic profiles of 80,000 people to understand the frequency of specific expansions of short repetitive DNA sequences in the general population.
These expansions are the most common cause of inherited neurological ...
Deep brain stimulation instantly improves arm and hand function post-brain injury
2024-10-01
Deep brain stimulation may provide immediate improvement in arm and hand strength and function weakened by traumatic brain injury or stroke, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine researchers report today in Nature Communications.
Encouraging results from extensive tests in monkeys and humans open a path for a new clinical application of an already widely used brain stimulation technology and offer insights into neural mechanisms underlying movement deficits caused by brain injury.
“Arm and hand paralysis significantly impacts the quality ...