(Press-News.org) UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 10AM (UK TIME) ON TUESDAY 1 OCTOBER 2024.
Peer reviewed | Observational study | People
Research led by scientists at Queen Mary University of London is heralding in a new era for genetic sequencing and testing.
In the largest study of its kind to date, published today in Nature Medicine, an international group of researchers led by Queen Mary used new bioinformatics techniques to scan the genetic profiles of 80,000 people to understand the frequency of specific expansions of short repetitive DNA sequences in the general population.
These expansions are the most common cause of inherited neurological conditions, known as repeat expansion disorders (REDs). The study’s results showed that REDs are up to three times more frequent than current estimates, which are based on clinical observation or disease diagnosis. It was also found that their frequency is common between different populations.
Dr Arianna Tucci, Clinical Reader in Genomic Medicine at Queen Mary University of London who led the research, said: “This very important advance may indicate that REDs like Huntington’s disease are nearly three times more common than we think, meaning we’re underdiagnosing these conditions. Alternatively, the presence of certain DNA repeats may not lead to illness in some people. This could herald a major shift in how we think about genetic testing, profiling and counselling.
“These findings were only possible because we are able to study whole genomes from the 100,000 Genomes Project in many individuals at scale. This represents a paradigm shift from traditional studies of small families with a history of a genetic condition to the analysis of large populations of individuals. Our next steps will be to study large cohorts of people that carry these genetic changes, to help us better understand what leads them to develop in certain individuals.”
Dr Sarah Tabrizi, Professor of Clinical Neurology at the UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology and co-author on the paper, said: “These results are extremely important. These data will force us as a community of researchers, academics and doctors to evaluate whether these DNA repeats address an unmet diagnostic need in rare neurological diseases, meaning the investigation of repeat expansion disorders deserves much more close attention now.”
ENDS
NOTES TO EDITORS
Examples of RED conditions include Fragile X syndrome, the commonest inherited form of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia, Huntington’s disease, inherited ataxias (Friedreich ataxia), and RFC1-Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, Vestibular Areflexia syndrome (CANVAS).
Contact
Honey Lucas
Faculty Communications Officer – Medicine and Dentistry
Queen Mary University of London
Email: h.lucas@qmul.ac.uk or press@qmul.ac.uk
Paper details:
Kristina Ibañez, et al. “Increased frequency of repeat expansion mutations across different populations.” Published in Nature Medicine.
DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03190-5
Available after publication at: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03190-5
Under strict embargo until 10am (UK time) on Tuesday 1 October 2024.
A copy of the paper is available upon request.
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Funded by: This research is funded by Medical Research Council, Department of Health and Social Care, National Health Service England, National Institute for Health Research, and Barts Charity.
About Queen Mary
www.qmul.ac.uk
At Queen Mary University of London, we believe that a diversity of ideas helps us achieve the previously unthinkable.
Throughout our history, we’ve fostered social justice and improved lives through academic excellence. And we continue to live and breathe this spirit today, not because it’s simply ‘the right thing to do’ but for what it helps us achieve and the intellectual brilliance it delivers.
Our reformer heritage informs our conviction that great ideas can and should come from anywhere. It’s an approach that has brought results across the globe, from the communities of east London to the favelas of Rio de Janeiro.
We continue to embrace diversity of thought and opinion in everything we do, in the belief that when views collide, disciplines interact, and perspectives intersect, truly original thought takes form.
About UCL – London’s Global University
UCL is a diverse global community of world-class academics, students, industry links, external partners, and alumni. Our powerful collective of individuals and institutions work together to explore new possibilities.
Since 1826, we have championed independent thought by attracting and nurturing the world's best minds. Our community of more than 50,000 students from 150 countries and over 16,000 staff pursues academic excellence, breaks boundaries and makes a positive impact on real world problems.
The Times and Sunday Times University of the Year 2024, we are consistently ranked among the top 10 universities in the world and are one of only a handful of institutions rated as having the strongest academic reputation and the broadest research impact.
We have a progressive and integrated approach to our teaching and research – championing innovation, creativity and cross-disciplinary working. We teach our students how to think, not what to think, and see them as partners, collaborators and contributors.
For almost 200 years, we are proud to have opened higher education to students from a wide range of backgrounds and to change the way we create and share knowledge.
We were the first in England to welcome women to university education and that courageous attitude and disruptive spirit is still alive today. We are UCL.
END
Research heralds new era for genetics
2024-10-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Deep brain stimulation instantly improves arm and hand function post-brain injury
2024-10-01
Deep brain stimulation may provide immediate improvement in arm and hand strength and function weakened by traumatic brain injury or stroke, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine researchers report today in Nature Communications.
Encouraging results from extensive tests in monkeys and humans open a path for a new clinical application of an already widely used brain stimulation technology and offer insights into neural mechanisms underlying movement deficits caused by brain injury.
“Arm and hand paralysis significantly impacts the quality ...
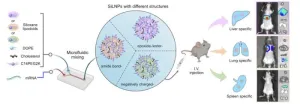
Siloxane nanoparticles unlock precise organ targeting for mRNA therapy
2024-10-01
Penn Engineers have discovered a novel means of directing lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), the revolutionary molecules that delivered the COVID-19 vaccines, to target specific tissues, presaging a new era in personalized medicine and gene therapy.
While past research — including at Penn Engineering — has screened “libraries” of LNPs to find specific variants that target organs like the lungs, this approach is akin to trial and error. “We’ve never understood how the structure of one key component of the LNP, ...
Building better solar cells: assembly of 2D molecular structures with triptycene scaffold
2024-10-01
Research in the field of material science and electronics relies on the innovative arrangement of molecules or atoms to develop materials with unique properties not found in conventional materials. Two-dimensional (2D) assemblies of π-electronic systems, arranged in thin layers, are becoming increasingly important in the fields of materials science and organic electronics. Their unique arrangement allows for specific electronic and physical properties, making them ideal for applications like solar cells, and flexible displays. However, creating such assemblies is challenging because it often requires special designs and techniques for each ...
Maybe we shouldn’t even call low-grade prostate cancer “cancer”
2024-10-01
A new paper in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that patients may benefit if doctors stop calling certain early-stage changes to the prostate “cancer” at all.
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death worldwide in men, but far more patients are diagnosed than die of the disease. In 2022, there were nearly 1.5 million cases of prostate cancer, but only 400,000 deaths. Low-grade prostate cancer, commonly known as GG1 among physicians, virtually never metastasizes or causes symptoms. Some medical researchers have wondered recently if it would be a benefit ...
‘Cheeky’ discovery allows scientists to estimate your risk of dying using cells found in the mouth
2024-10-01
We don’t all age at the same rate. But while some supercentenarians may age exceptionally slowly due to winning the genetics jackpot, a plethora of behavioral and lifestyle factors are known to speed up aging, including stress, poor sleep, poor nutrition, smoking, and alcohol. Since such environmental effects get imprinted on our genome in the form of epigenetic marks, it is possible to quantify molecular aging by characterizing the epigenome at prognostic genomic sites.
Over the past decade, scientists have developed several such ‘epigenetic clocks’, calibrated against chronological age and various lifestyle factors across large ...
ChatGPT shows human-level assessment of brain tumor MRI reports
2024-10-01
As artificial intelligence advances, its uses and capabilities in real-world applications continue to reach new heights that may even surpass human expertise. In the field of radiology, where a correct diagnosis is crucial to ensure proper patient care, large language models, such as ChatGPT, could improve accuracy or at least offer a good second opinion.
To test its potential, graduate student Yasuhito Mitsuyama and Associate Professor Daiju Ueda’s team at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate ...
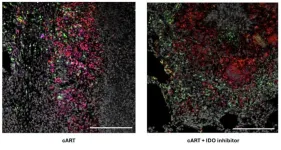
Promising TB therapy safe for patients with HIV
2024-10-01
SAN ANTONIO (October 1, 2024) – A therapy showing promise to help control tuberculosis (TB) does not interfere with combined antiretroviral therapy (cART), according to research by Texas Biomedical Research Institute (Texas Biomed).
“This is an important hurdle that this host-directed therapy had to clear in order to help patients battling both HIV and TB,” said Texas Biomed Professor Smriti Mehra, Ph.D., who led the study recently published in the peer-reviewed journal JCI Insight.
TB is responsible for more than 1.3 million deaths worldwide every year. Dr. Mehra ...
American Academy of Pediatrics examines the impact of school expulsion and recommends ways to create supportive learning environments for all students
2024-10-01
Media Contacts:
Alex Hulvalchick, 630-626-6282
Lisa Robinson, 630-626-6084, lrobinson@aap.org
American Academy of Pediatrics Examines the Impact of School Expulsion and Recommends Ways to Create Supportive Learning Environments for All Students
Updated policy statement on school suspension to be released during the AAP 2024 National Conference & Exhibition in Orlando.
ORLANDO, Fla.--Suspending or expelling a student is one of the most severe punishments a school can impose on a student – and it can have lifelong, devastating consequences. ...
Most pregnant people got vaccinated for COVID-19 in 2022
2024-10-01
A study of more than 28,000 pregnancies from 2022 has found that the majority of pregnant people received the COVID-19 vaccine during its initial release.
The study, co-led by McMaster University and the University of British Columbia, used data from ICES, an independent, not-for-profit research institute, to provide insight into vaccination rates among one of the groups most vulnerable to health complications caused by COVID-19.
The research, published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal (CMAJ) ...
Coral reef destruction a threat to human rights
2024-10-01
A human rights-based approach to coral reef protection could ensure governments are held to account for safeguarding marine ecosystems and empower local and Indigenous communities to demand sustainable solutions and climate justice, a new study suggests.
An estimated one billion people rely on healthy coral reefs globally for food security, coastal protection and income from tourism and other services. If reefs and their ecosystems are lost, the impact on human health and economic wellbeing would be catastrophic.
Lead ...