(Press-News.org) Penn Engineers have discovered a novel means of directing lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), the revolutionary molecules that delivered the COVID-19 vaccines, to target specific tissues, presaging a new era in personalized medicine and gene therapy.
While past research — including at Penn Engineering — has screened “libraries” of LNPs to find specific variants that target organs like the lungs, this approach is akin to trial and error. “We’ve never understood how the structure of one key component of the LNP, the ionizable lipid, determines the ultimate destination of LNPs to organs beyond the liver,” says Michael J. Mitchell, Associate Professor in Bioengineering.
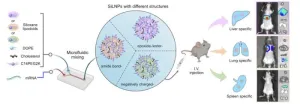
In a new paper published in Nature Nanotechnology, Mitchell’s group describes how subtle adjustments to the chemical structure of the ionizable lipid, a key component of the LNP, allows for tissue-specific delivery, in particular to the liver, lungs and spleen.
The researchers’ key insight was to incorporate siloxane composites, a class of silicon- and oxygen-based compounds already used in medical devices, cosmetics and drug delivery, into the ionizable lipids that give LNPs their name.
Much like silicon housewares, which are known for being durable and easy to sanitize, siloxane composites have been shown in prior research to have high stability and low toxicity. “We sought to explore if these attributes could be exploited to engineer highly stable and minimally toxic LNPs for mRNA delivery,” the researchers report in the paper.
By carefully testing hundreds of variants of the newly christened siloxane-incorporating lipid nanoparticles (SiLNPs), the researchers determined which chemical features had an effect on mRNA delivery. “Identifying their in vivo delivery was a huge challenge,” says Lulu Xue, a postdoctoral fellow in the Mitchell Lab and one of the paper’s co-first authors.
At first, the researchers used the SiLNP variants to deliver mRNA encoding for firefly luciferase, the gene that causes fireflies to glow, to cancerous liver cells in an animal model, as a proxy for using SiLNPs to treat liver cancer. Wherever cells started to glow, the researchers could be confident that SiLNPs had transferred their mRNA payload to cells.
When glowing cells also appeared in the animal models’ lungs, the researchers realized that certain SiLNPs variants were guiding the molecules outside the liver — the holy grail of LNP research, since LNPs tend to congregate in the liver, due to that organ’s convoluted network of blood vessels.
Among the changes the group identified that adjusted the trajectory of the SiLNPs were adjustments as small as substituting one chemical group for another — an amide for an ester, in this case — which led to a 90% success rate in delivering mRNA to lung tissue in the animal model.
“We just changed the structure of the lipids,” says Xue, “but this small change in the lipid chemistry substantially increased extrahepatic delivery.”
The group also determined that a wide variety of chemical factors affected the SiLNPs’ overall efficacy, including the number of silicon groups in the lipids, the length of the lipids’ tails and the structure of the lipids themselves.
In addition, the SiLNPs had a marked affinity for endothelial cells; since blood vessels are made of endothelial cells, SiLNPs may have clinical applications in regenerative medicine that targets damaged blood vessels, in particular in the lungs. Indeed, the researchers found that SiLNPs delivering substances that promote new blood vessel growth dramatically improved blood oxygen levels and lung function in animal models suffering from a viral infection that damaged their lungs’ blood vessels.
The researchers theorized that one reason for SiLNPs' effectiveness could be that silicon atoms are larger than carbon atoms. Because the atoms are less tightly packed, when SiLNPs fuse with target cell membranes, the former likely increases the fluidity of the latter. That extra flexibility in turn helps the mRNA carried by SiLNPs enter the target cell, so the mRNA can be used to produce proteins more readily. As the SiLNPs travel through the bloodstream, proteins that attach to their surface also help guide them to the right tissue.
Ultimately, the SiLNPs showed up to a sixfold improvement in delivering mRNA compared to the current gold-standard LNP varieties, suggesting that the unique properties of the siloxane composites have a pronounced effect on the molecules’ clinical potential. “These SiLNPs show promise for protein replacement therapies, regenerative medicine and CRISPR-Cas-based gene editing,” says Xue.
“We hope that this paper can lead to new clinical applications for lipid nanoparticles by showing how simple alterations to their chemical structure can enable highly specific mRNA delivery to the organ of interest,” adds Mitchell.
This study was conducted at the University of Pennsylvania’s School of Engineering and Applied Science (Penn Engineering), School of Veterinary Medicine (PennVet), Perelman School of Medicine (Penn Medicine); the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China; the University of Delaware; and Temple University and was supported by a U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) Director’s New Innovator Award (DP2 TR002776), a Burroughs Wellcome Fund Career Award at the Scientific Interface (CASI), a U.S. National Science Foundation CAREER Award (CBET-2145491), an American Cancer Society Research Scholar Grant (RSG-22-122-01-ET), and the National Institutes of Health (NICHD R01 HD115877).
Additional co-authors include Ningqiang Gong (co-first author), Xuexiang Han, Sarah J. Shepherd, Rohan Palanki, Junchao Xu, Kelsey L. Swingle, Rakan El-Mayta, Il-Chul Yoon and Jingchen Xu of Penn Engineering; Gan Zhao (co-first author), Zebin Xiao and Andrew E. Vaughan, of PennVet; Vivek Chowdhary, Mohamad-Gabriel Alameh, Claude Warzecha, Lili Wang, James M. Wilson and Drew Weissman of Penn Medicine; Xinhong Xong and Jiaxi Cui of the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China; Darrin J. Pochan of the University of Delaware; and Karin Wang of Temple University.
END
Siloxane nanoparticles unlock precise organ targeting for mRNA therapy
Changes to chemical structure allow for tissue-specific delivery
2024-10-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Building better solar cells: assembly of 2D molecular structures with triptycene scaffold
2024-10-01
Research in the field of material science and electronics relies on the innovative arrangement of molecules or atoms to develop materials with unique properties not found in conventional materials. Two-dimensional (2D) assemblies of π-electronic systems, arranged in thin layers, are becoming increasingly important in the fields of materials science and organic electronics. Their unique arrangement allows for specific electronic and physical properties, making them ideal for applications like solar cells, and flexible displays. However, creating such assemblies is challenging because it often requires special designs and techniques for each ...
Maybe we shouldn’t even call low-grade prostate cancer “cancer”
2024-10-01
A new paper in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that patients may benefit if doctors stop calling certain early-stage changes to the prostate “cancer” at all.
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death worldwide in men, but far more patients are diagnosed than die of the disease. In 2022, there were nearly 1.5 million cases of prostate cancer, but only 400,000 deaths. Low-grade prostate cancer, commonly known as GG1 among physicians, virtually never metastasizes or causes symptoms. Some medical researchers have wondered recently if it would be a benefit ...
‘Cheeky’ discovery allows scientists to estimate your risk of dying using cells found in the mouth
2024-10-01
We don’t all age at the same rate. But while some supercentenarians may age exceptionally slowly due to winning the genetics jackpot, a plethora of behavioral and lifestyle factors are known to speed up aging, including stress, poor sleep, poor nutrition, smoking, and alcohol. Since such environmental effects get imprinted on our genome in the form of epigenetic marks, it is possible to quantify molecular aging by characterizing the epigenome at prognostic genomic sites.
Over the past decade, scientists have developed several such ‘epigenetic clocks’, calibrated against chronological age and various lifestyle factors across large ...
ChatGPT shows human-level assessment of brain tumor MRI reports
2024-10-01
As artificial intelligence advances, its uses and capabilities in real-world applications continue to reach new heights that may even surpass human expertise. In the field of radiology, where a correct diagnosis is crucial to ensure proper patient care, large language models, such as ChatGPT, could improve accuracy or at least offer a good second opinion.
To test its potential, graduate student Yasuhito Mitsuyama and Associate Professor Daiju Ueda’s team at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate ...
Promising TB therapy safe for patients with HIV
2024-10-01
SAN ANTONIO (October 1, 2024) – A therapy showing promise to help control tuberculosis (TB) does not interfere with combined antiretroviral therapy (cART), according to research by Texas Biomedical Research Institute (Texas Biomed).
“This is an important hurdle that this host-directed therapy had to clear in order to help patients battling both HIV and TB,” said Texas Biomed Professor Smriti Mehra, Ph.D., who led the study recently published in the peer-reviewed journal JCI Insight.
TB is responsible for more than 1.3 million deaths worldwide every year. Dr. Mehra ...
American Academy of Pediatrics examines the impact of school expulsion and recommends ways to create supportive learning environments for all students
2024-10-01
Media Contacts:
Alex Hulvalchick, 630-626-6282
Lisa Robinson, 630-626-6084, lrobinson@aap.org
American Academy of Pediatrics Examines the Impact of School Expulsion and Recommends Ways to Create Supportive Learning Environments for All Students
Updated policy statement on school suspension to be released during the AAP 2024 National Conference & Exhibition in Orlando.
ORLANDO, Fla.--Suspending or expelling a student is one of the most severe punishments a school can impose on a student – and it can have lifelong, devastating consequences. ...
Most pregnant people got vaccinated for COVID-19 in 2022
2024-10-01
A study of more than 28,000 pregnancies from 2022 has found that the majority of pregnant people received the COVID-19 vaccine during its initial release.
The study, co-led by McMaster University and the University of British Columbia, used data from ICES, an independent, not-for-profit research institute, to provide insight into vaccination rates among one of the groups most vulnerable to health complications caused by COVID-19.
The research, published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal (CMAJ) ...
Coral reef destruction a threat to human rights
2024-10-01
A human rights-based approach to coral reef protection could ensure governments are held to account for safeguarding marine ecosystems and empower local and Indigenous communities to demand sustainable solutions and climate justice, a new study suggests.
An estimated one billion people rely on healthy coral reefs globally for food security, coastal protection and income from tourism and other services. If reefs and their ecosystems are lost, the impact on human health and economic wellbeing would be catastrophic.
Lead ...
Tongan volcanic eruption triggered by explosion as big as ‘five underground nuclear bombs’
2024-10-01
The Hunga Tonga underwater volcano was one of the largest volcanic eruptions in history, and now, two years later, new research from The Australian National University (ANU) has revealed its main trigger.
Until now, the cause of the cataclysmic event has remained largely a mystery to the scientific community, yet a student-led team of ANU seismologists has been able to shed new light on the natural explosion that initiated the event.
The student researchers analysed the climactic event’s noisy but valuable seismic ...
Syrian hamsters reveal genetic secret to hibernation
2024-10-01
A gene that limits cellular damage could be the key to surviving prolonged cold exposure.
Researchers have identified a gene that enables mammalian cells to survive for long periods at extremely low temperature, which animals experience during hibernation.
Body temperatures below 10 degrees Celsius (°C) swiftly prove fatal for humans and many other mammals, because prolonged cold stress causes cells to accumulate damaging free radicals—in particular lipid peroxide radicals—resulting in cell death and organ failure. But a few mammalian species can survive cold stress by hibernating. Hibernation in many small mammals involves ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
EANM launches new award to accelerate alpha radioligand therapy research
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
[Press-News.org] Siloxane nanoparticles unlock precise organ targeting for mRNA therapyChanges to chemical structure allow for tissue-specific delivery