(Press-News.org) The Hunga Tonga underwater volcano was one of the largest volcanic eruptions in history, and now, two years later, new research from The Australian National University (ANU) has revealed its main trigger.
Until now, the cause of the cataclysmic event has remained largely a mystery to the scientific community, yet a student-led team of ANU seismologists has been able to shed new light on the natural explosion that initiated the event.
The student researchers analysed the climactic event’s noisy but valuable seismic records to decipher its mysterious physical mechanism.
“Our findings confirm there was an explosion, possibly due to a gas-compressed rock, which released energy that equated to five of the largest underground nuclear explosions conducted by North Korea in 2017,” study co-author and ANU PhD student, Jinyin Hu, said.
“Our model suggests the event resulted from the gas-compressed rock being trapped underneath a shallow sea, like an overcooked pressure cooker.
“This would be surprising to many because it had been commonly thought that the interaction of hot magma with cold seawater caused such massive underwater volcanic eruptions.
“We used a technique previously developed to study underground explosions for this natural explosion.”
Study co-author, Dr Thanh-Son Pham, said the explosion caused a massive vertical push of water upwards into the atmosphere, causing tsunamis that reached as high as 45 metres at nearby islands.
“The water volume that was uplifted during the event was huge. Based on our estimates, there was enough water to fill about one million standard Olympic-sized swimming pools,” Dr Phạm said.
Study co-author, Professor Hrvoje Tkalčić, from ANU, added: “Using seismic waveform modelling, we observed a significant vertical force pointing upward during the event. At first, we were confused by it. But then we realised that the solid earth rebounded upwards after the water column got uplifted,” he said.
“A couple of weeks ago, we saw how seismology was used to explain an extraordinary sequence of events in Greenland that included a landslide due to glacial melting, a tsunami, and a seiche lasting for nine days observed globally.
“With Hunga Tonga, we have a relatively short-duration explosive event observed globally and, again, academically driven curiosity and forensic seismology at its best.”
According to the ANU seismologists, the Tonga eruption is the best instrumentally recorded event compared to events of similar sizes in the recent past.
“This is one of the largest events in our lifetime. Luckily, we had multiple ways to record the event, from data from satellite images to seismic sensors that record the sound waves and structure,” Mr Hu said.
“There was another event that happened in 1991 that was a similar size in Pinatubo in the Philippines, but back then, monitoring systems weren’t as sophisticated as they are now.”
The ANU seismologists believe that monitoring the release of gases and micro-seismicity from volcanic sites can help better prepare for future events.
The research is published in Geophysical Research Letters.
END
Tongan volcanic eruption triggered by explosion as big as ‘five underground nuclear bombs’
2024-10-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
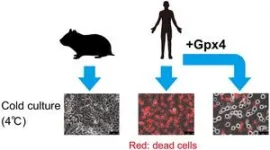
Syrian hamsters reveal genetic secret to hibernation
2024-10-01
A gene that limits cellular damage could be the key to surviving prolonged cold exposure.
Researchers have identified a gene that enables mammalian cells to survive for long periods at extremely low temperature, which animals experience during hibernation.
Body temperatures below 10 degrees Celsius (°C) swiftly prove fatal for humans and many other mammals, because prolonged cold stress causes cells to accumulate damaging free radicals—in particular lipid peroxide radicals—resulting in cell death and organ failure. But a few mammalian species can survive cold stress by hibernating. Hibernation in many small mammals involves ...
Tracking microplastics: FAMU-FSU College of Engineering researcher helps discover how microplastics move for better storm water management
2024-10-01
Microplastic pollution is a significant environmental problem that harms animals and people and affects ecosystems worldwide. These tiny pieces of plastic, smaller than five millimeters, are pushed by wind and water to move around the globe.
Nasrin Alamdari, an assistant professor in the FAMU-FSU College of Engineering’s Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, is on a mission to learn more about microplastics and how they move.
In research published in Environmental Pollution, she helped examine how shape, size and density affect the speed at which ...
The Lancet Psychiatry: Conversion practice linked to greater risk of mental health symptoms, surveys of LGBTQ+ people in the USA suggest
2024-09-30
Analysis of questionnaires completed by 4,426 LGBTQ+ people in the USA suggests undergoing conversion practice targeting gender identity or sexual orientation is linked with symptoms of depression, PTSD and suicidal thoughts or attempts.
Cisgender and transgender participants also had more severe symptoms of depression and PTSD if they had undergone conversion practice.
Cisgender participants subjected to both types of conversion practice had a greater risk of suicidal thoughts and attempts than transgender participants – but mental health symptoms were more severe for transgender people overall, ...
Most accurate ultrasound test could detect 96% of women with ovarian cancer
2024-09-30
An ultrasound test that detected 96% of ovarian cancers in postmenopausal women should replace current standard of care test in the UK according to a new study.
In a paper published in Lancet Oncology today (Monday 30 September), research funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) and led by Professor Sudha Sundar from the University of Birmingham compared all currently available tests to diagnose ovarian cancer in postmenopausal women head-to-head in a high-quality diagnostic test accuracy study.
Of the six diagnostic tests investigated, ...
Sylvester study: MRI provides early warning system for glioblastoma growth
2024-09-30
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL SEPT. 30, 2024, AT 5:40 P.M. EDT) – A new study shows the potential power of imaging paired with radiation to shape treatment for glioblastoma patients in real time.
The study, led by researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, part of the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, is the first to quantify tumor changes in glioblastoma patients receiving MRI-guided radiation therapy. This novel technique, also known as MRI-linear accelerator or MRI-linac, pairs ...
Making soybeans smarter
2024-09-30
Ron Mittler is on a quest to create a smarter soybean. For years, mid-Missouri has withstood unpredictable weather patterns, including drought, heat waves and flooding — conditions that are known to hamper agricultural yields and make it difficult for farmers to produce. While we can’t control the weather, Mittler and his team are working to harness soybean crops’ natural ability to adapt to unfavorable weather conditions while also increasing their yields.
Working with $2.4 million from ...
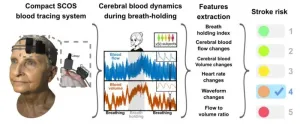
New wearable laser device monitors brain blood flow to gauge stroke risk
2024-09-30
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a laser-based device that can be placed on the head to non-invasively monitor changes in brain blood flow and volume. The new device could one day help save lives by offering a direct and simple way to assess stroke risk based on physiological markers rather than indirect markers like lifestyle factors.
Strokes occur when blood flow to the brain is blocked or reduced, causing debilitating brain cell damage. With about 15 million people worldwide affected by strokes each year, it is the second leading cause of death and ...
BU professor receives $29M NIH grant to study dementia risk factors, prevention, and treatment
2024-09-30
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Monday, September 30, 2024
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
BU Professor Receives $29M NIH Grant to Study Dementia Risk Factors, Prevention, and Treatment
The Triangulation of Innovative Methods to End Alzheimer’s Disease project will use large, diverse datasets to examine whether interventions targeting alcohol use, depression, vision or hearing impairments, or social isolation can protect people from Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. This project is a collaboration among Dr. Maria Glymour at Boston University School of Public Health, Dr. Jacqueline ...
Ninth Circuit reverses lower court, reinforces FDA's authority to regulate unproven stem cell products
2024-09-30
In an important step to protect the public from unproven stem cell products, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit ruled in favor of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in U.S. v. California Stem Cell Treatment Center, Inc., reversing the district court. The reversal fortifies FDA’s tiered, risk-based framework for the regulation of cell therapies and is consistent with a similar ruling in the Eleventh Circuit in 2021.
The appellees urged the Ninth Circuit to uphold the lower court’s ...
Wnt happens in kidney development?
2024-09-30
A group of essential signaling molecules known as the Wnt pathway emerged early in the evolution of multicellular life. Scientists have been studying Wnt actions for four decades to comprehend its complex roles in development and disease. In development of the mammalian kidney, USC Stem Cell scientists from Andy McMahon’s lab undertook a pair of complementary studies, published today in the journal Development, that provide new insight into the critical role of Wnt signaling in initiating the development of the mammalian kidney.
“Many stem and progenitor cells require Wnt signaling, ...