(Press-News.org) Deep brain stimulation may provide immediate improvement in arm and hand strength and function weakened by traumatic brain injury or stroke, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine researchers report today in Nature Communications.
Encouraging results from extensive tests in monkeys and humans open a path for a new clinical application of an already widely used brain stimulation technology and offer insights into neural mechanisms underlying movement deficits caused by brain injury.
“Arm and hand paralysis significantly impacts the quality of life of millions of people worldwide,” said senior and corresponding author Elvira Pirondini, Ph.D., assistant professor of physical medicine and rehabilitation at Pitt. “Currently, we don’t have effective solutions for patients who suffered a stroke or traumatic brain injury but there is a growing interest in the use of neurotechnologies that stimulate the brain to improve upper-limb motor functions.”
Brain lesions caused by serious brain trauma or stroke can disrupt neural connections between the motor cortex, a key brain region essential for controlling voluntary movement, and the muscles. Weakening of these connections prevents effective activation of muscles and results in movement deficits, including partial or complete arm and hand paralysis.
To boost the activation of existing, but weakened, connections, researchers proposed to use deep brain stimulation (DBS), a surgical procedure that involves placing tiny electrodes in specific areas of the brain to deliver electrical impulses that regulate abnormal brain activity. Over the past several decades, DBS has revolutionized the treatment of neurological conditions such as Parkinson's disease by providing a way to control symptoms that were once difficult to manage with medication alone.
“DBS has been life-changing for many patients. Now, thanks to ongoing advancements in the safety and precision of these devices, DBS is being explored as a promising option for helping stroke survivors recover their motor functions,” said senior author and surgical leader of the project, Jorge González-Martínez, M.D., Ph.D., professor and vice-chair of neurosurgery and director of the epilepsy and movement disorders program at Pitt. “It offers new hope to millions of people worldwide.”
Taking cues from another successful Pitt project that used electrical stimulation of the spinal cord to restore arm function in individuals affected by stroke, scientists hypothesized that stimulating the motor thalamus – a structure nested deep in the brain that acts as a key relay hub of movement control – using DBS could help restore movements that are essential for tasks of daily living, such as object grasping. However, because the theory has not been tested before, they first had to test it in monkeys, which are the only animals that have the same organization of the connections between the motor cortex and the muscles as humans.
To understand the mechanism of how DBS of the motor thalamus helps improve voluntary arm movement and to finesse the specific location of the implant and the optimal stimulation frequency, researchers implanted the FDA-approved stimulation device into monkeys that had brain lesions affecting how effectively they could use their hands.
As soon as the stimulation was turned on, it significantly improved activation of muscles and grip force. Importantly, no involuntary movement was observed.
To verify that the procedure could benefit humans, the same stimulation parameters were used in a patient who was set to undergo DBS implantation into the motor thalamus to help with arm tremors caused by brain injury from a serious motor vehicle accident that resulted in severe paralysis in both arms.
As soon as the stimulation was turned on again, the range and strength of arm motion was immediately improved: The participant was able to lift a moderately heavy weight and reach, grasp and lift a drinking cup more efficiently and smoothly than without the stimulation.
To help bring this technology to more patients in the clinic, researchers are now working to test the long-term effects of DBS and determine whether chronic stimulation could further improve arm and hand function in individuals affected by traumatic brain injury or stroke.
Other authors of this research are Jonathan Ho, B.S., Erinn Grigsby, Ph.D., Arianna Damiani, M.S., Lucy Liang, M.S., Josep-Maria Balaguer, M.S., Sridula Kallakuri, Lilly Tang, B.S., Jessica Barrios-Martinez, M.D., Vahagn Karapetyan, M.D., Ph.D., Daryl Fields, M.D., Ph.D., Peter Gerszten, M.D., T. Kevin Hitchens, Ph.D., M.B.A., Theodora Constantine, P.A.-C., Gregory Adams, B.S., Donald Crammond, Ph.D., and Marco Capogrosso, Ph.D., all of Pitt.
This research is supported by internal funding from the departments of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation and of Neurological Surgery at Pitt. Additional funding was provided by the Walter L. Copeland Foundation, the Hamot Health Foundation and the National Institutes of Health (R01NS122927-01A1).
END
Deep brain stimulation instantly improves arm and hand function post-brain injury
2024-10-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
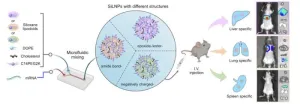
Siloxane nanoparticles unlock precise organ targeting for mRNA therapy
2024-10-01
Penn Engineers have discovered a novel means of directing lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), the revolutionary molecules that delivered the COVID-19 vaccines, to target specific tissues, presaging a new era in personalized medicine and gene therapy.
While past research — including at Penn Engineering — has screened “libraries” of LNPs to find specific variants that target organs like the lungs, this approach is akin to trial and error. “We’ve never understood how the structure of one key component of the LNP, ...
Building better solar cells: assembly of 2D molecular structures with triptycene scaffold
2024-10-01
Research in the field of material science and electronics relies on the innovative arrangement of molecules or atoms to develop materials with unique properties not found in conventional materials. Two-dimensional (2D) assemblies of π-electronic systems, arranged in thin layers, are becoming increasingly important in the fields of materials science and organic electronics. Their unique arrangement allows for specific electronic and physical properties, making them ideal for applications like solar cells, and flexible displays. However, creating such assemblies is challenging because it often requires special designs and techniques for each ...
Maybe we shouldn’t even call low-grade prostate cancer “cancer”
2024-10-01
A new paper in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that patients may benefit if doctors stop calling certain early-stage changes to the prostate “cancer” at all.
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death worldwide in men, but far more patients are diagnosed than die of the disease. In 2022, there were nearly 1.5 million cases of prostate cancer, but only 400,000 deaths. Low-grade prostate cancer, commonly known as GG1 among physicians, virtually never metastasizes or causes symptoms. Some medical researchers have wondered recently if it would be a benefit ...
‘Cheeky’ discovery allows scientists to estimate your risk of dying using cells found in the mouth
2024-10-01
We don’t all age at the same rate. But while some supercentenarians may age exceptionally slowly due to winning the genetics jackpot, a plethora of behavioral and lifestyle factors are known to speed up aging, including stress, poor sleep, poor nutrition, smoking, and alcohol. Since such environmental effects get imprinted on our genome in the form of epigenetic marks, it is possible to quantify molecular aging by characterizing the epigenome at prognostic genomic sites.
Over the past decade, scientists have developed several such ‘epigenetic clocks’, calibrated against chronological age and various lifestyle factors across large ...
ChatGPT shows human-level assessment of brain tumor MRI reports
2024-10-01
As artificial intelligence advances, its uses and capabilities in real-world applications continue to reach new heights that may even surpass human expertise. In the field of radiology, where a correct diagnosis is crucial to ensure proper patient care, large language models, such as ChatGPT, could improve accuracy or at least offer a good second opinion.
To test its potential, graduate student Yasuhito Mitsuyama and Associate Professor Daiju Ueda’s team at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate ...
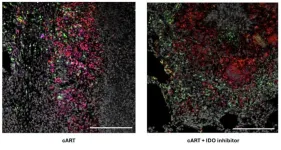
Promising TB therapy safe for patients with HIV
2024-10-01
SAN ANTONIO (October 1, 2024) – A therapy showing promise to help control tuberculosis (TB) does not interfere with combined antiretroviral therapy (cART), according to research by Texas Biomedical Research Institute (Texas Biomed).
“This is an important hurdle that this host-directed therapy had to clear in order to help patients battling both HIV and TB,” said Texas Biomed Professor Smriti Mehra, Ph.D., who led the study recently published in the peer-reviewed journal JCI Insight.
TB is responsible for more than 1.3 million deaths worldwide every year. Dr. Mehra ...
American Academy of Pediatrics examines the impact of school expulsion and recommends ways to create supportive learning environments for all students
2024-10-01
Media Contacts:
Alex Hulvalchick, 630-626-6282
Lisa Robinson, 630-626-6084, lrobinson@aap.org
American Academy of Pediatrics Examines the Impact of School Expulsion and Recommends Ways to Create Supportive Learning Environments for All Students
Updated policy statement on school suspension to be released during the AAP 2024 National Conference & Exhibition in Orlando.
ORLANDO, Fla.--Suspending or expelling a student is one of the most severe punishments a school can impose on a student – and it can have lifelong, devastating consequences. ...
Most pregnant people got vaccinated for COVID-19 in 2022
2024-10-01
A study of more than 28,000 pregnancies from 2022 has found that the majority of pregnant people received the COVID-19 vaccine during its initial release.
The study, co-led by McMaster University and the University of British Columbia, used data from ICES, an independent, not-for-profit research institute, to provide insight into vaccination rates among one of the groups most vulnerable to health complications caused by COVID-19.
The research, published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal (CMAJ) ...
Coral reef destruction a threat to human rights
2024-10-01
A human rights-based approach to coral reef protection could ensure governments are held to account for safeguarding marine ecosystems and empower local and Indigenous communities to demand sustainable solutions and climate justice, a new study suggests.
An estimated one billion people rely on healthy coral reefs globally for food security, coastal protection and income from tourism and other services. If reefs and their ecosystems are lost, the impact on human health and economic wellbeing would be catastrophic.
Lead ...
Tongan volcanic eruption triggered by explosion as big as ‘five underground nuclear bombs’
2024-10-01
The Hunga Tonga underwater volcano was one of the largest volcanic eruptions in history, and now, two years later, new research from The Australian National University (ANU) has revealed its main trigger.
Until now, the cause of the cataclysmic event has remained largely a mystery to the scientific community, yet a student-led team of ANU seismologists has been able to shed new light on the natural explosion that initiated the event.
The student researchers analysed the climactic event’s noisy but valuable seismic ...