Carnegie Mellon to lead development of implantable cell-based bioelectronic devices for patient-specific treatment and disease monitoring
2024-10-02
(Press-News.org) PITTSBURGH – A Carnegie Mellon University-led team has secured an award of up to $42 million from the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H) to accelerate the development of implantable, cell-based bioelectronic devices that deliver patient-specific therapy and monitor disease status, for conditions like hypo- and hyperthyroidism, in real time. This award is part of the ARPA-H REACT program, which supports the advancement of implantable bioelectronic devices to improve patient management of chronic diseases.
Burak Ozdoganlar, professor of mechanical engineering at Carnegie Mellon University, will head the Biointegrated Implantable Systems for Cell-based Sensing and Therapy (BIO-INSYNC) project as the primary investigator. This effort is part of the ongoing Bioelectric Medicine Initiative at Carnegie Mellon University. In addition to Carnegie Mellon researchers, the multidisciplinary project team includes members from the University of Pittsburgh/UPMC, University of Florida, and University of California—Santa Cruz. Two companies, Ginkgo Bioworks and Velentium, are also integral parts of the consortium.
During the six-year project term, the team will develop and test two multi-part, pacemaker-sized system platforms that will be implanted in a patient's chest cavity through an outpatient procedure and offer real-time, adjustable, low-cost therapy and disease monitoring for up to 12 months. Following a “living pharmacy” concept, one of the systems will use human cells to produce and release the necessary dose of a hormone or other therapeutic molecules on demand. Utilizing a “living sentinel” concept, the second system will use cells that measure critical biomarkers to monitor the patient’s disease status continuously in real time. Both will feature remote interfaces to communicate key information and measurements with the patient via smart devices or directly to their healthcare provider.
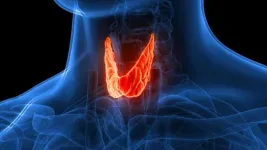
While this technology can be used to treat various diseases and conditions, the collaborative team will specifically focus on its application to thyroid disorders, which impact an estimated 12% of Americans, including children and adults. BIO-INSYNC devices will provide a significant advantage to patients who will be able to continuously monitor key hormones and deliver the right therapeutic dose as needed, eliminating current management protocols like daily medications and regular blood testing. Notably, the project will conduct a first-in-human clinical trial for patients facing thyroid conditions.
“The thyroid gland controls so many integral processes within the body, and thyroid hormone imbalances can lead to weight gain or loss, mental health issues, fertility problems, and even heart diseases,” explained Ozdoganlar. “It’s important also to note that thyroid disorders disproportionally impact vulnerable populations. Our bioelectronic system offers an innovative avenue for patients to self-manage their thyroid hormone levels at a fraction of the cost. The aim is to improve patients’ quality of life by improving thyroid treatments while bridging disparities in healthcare to attain equitable care for all.”
###
About Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University is a private, internationally ranked research university with acclaimed programs spanning the sciences, engineering, technology, business, public policy, humanities, and the arts. Our diverse community of scholars, researchers, creators, and innovators is driven to make real-world impacts that benefit people across the globe. With a bold, interdisciplinary, and entrepreneurial approach, we do the work that matters.
About the College of Engineering
The College of Engineering at Carnegie Mellon University is a top-ranked engineering college that is known for our Advanced Collaboration culture in research and education. The College is well-known for working on problems of both scientific and practical importance. Our “maker” culture is ingrained in all that we do, leading to novel approaches and transformative results. Our acclaimed faculty have a focus on innovation management and engineering to yield transformative results that will drive the intellectual and economic vitality of our community, nation, and world.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-02
CLEVELAND—Researchers at Case Western Reserve University and Vanderbilt University are pioneering a new approach to prostate cancer surgery by combining advanced robotics and “low-field” MRI technology.
The research aims to allow highly accurate, patient-tailored prostate cancer surgeries without the need for traditional incisions. This innovative research marks a major step in developing minimally invasive treatments for prostate cancer, with the potential to improve both safety and efficiency for patients.
The project is being funded by a new five-year, $3.7 million grant from the National Cancer Institute, part of the ...
2024-10-02
PITTSBURGH – A Carnegie Mellon University-led team of researchers has secured an award of up to $34.9 million from the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H). The funds will fast track a bioelectronic implant that could radically improve treatment options and significantly reduce the cost of care for patients with obesity and Type 2 diabetes.
The award will drive the accelerated development and testing of “Rx On-site Generation Using Electronics (ROGUE),” a bioelectrical device that hosts a “living pharmacy,” consisting of engineered cells that produce biological therapy to treat Type 2 diabetes and obesity. The device will offer continuous, ...
2024-10-02
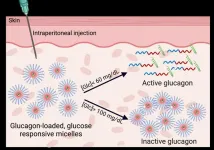
People with diabetes take insulin to lower high blood sugar. However, if glucose levels plunge too low — from taking too much insulin or not eating enough sugar — people can experience hypoglycemia, which can lead to dizziness, cognitive impairment, seizures or comas. To prevent and treat this condition, researchers in ACS Central Science report encapsulating the hormone glucagon. In mouse trials, the nanocapsules activated when blood sugar levels dropped dangerously low and quickly restored glucose levels.
Glucagon is a hormone that signals the liver to ...
2024-10-02
It’s important to eat your veggies, but some essential vitamins and nutrients can only be found in animals, including certain amino acids and peptides. But, in a proof-of-concept study published in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, researchers developed a method to produce creatine, carnosine and taurine — all animal-based nutrients and common workout supplements — right inside a plant. The system allows for different synthetic modules to be easily stacked together to boost production.
Plants can be surprisingly receptive when asked to produce compounds ...
2024-10-02
The American Society of Plant Biologists (ASPB) is excited to announce Pablo Manavella will serve as the next Editor-in-Chief of The Plant Cell. The Plant Cell is a leading international society journal that publishes novel research of special significance in plant biology, especially in the areas of cellular biology, molecular biology, biochemistry, genetics, development, and evolution.
Manavella is currently a Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) researcher at the Institute for Mediterranean and Subtropical Horticulture (IHSM) in Málaga, Spain. He is the Principal Investigator in a lab focusing on the intricate mechanisms regulating ...
2024-10-02
Despite global vaccination efforts, COVID-19 continues to pose significant risks, leading to severe complications and fatalities. These risks are driven by disrupted coagulation, impaired fibrinolysis, which is the process of breaking blood clots, and heightened inflammatory responses. The fibrinolytic system, crucial for maintaining balance within the coagulation cascade, relies on plasmin-mediated fibrin degradation. Plasminogen activators convert plasminogen into plasmin, an enzyme that breaks down ...
2024-10-02
SAN FRANCISCO —PLOS today announced that it has received a $1.5 million grant from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and a $1 million grant from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation to support our mission to drive Open Science forward with meaningful change in scholarly publishing. The funds enable PLOS to embark on an ambitious 18-month research and design project to explore how to tackle two barriers that exclude many researchers from meaningfully participating in Open Science: affordability ...
2024-10-02
Researchers at the RIKEN Cluster for Pioneering Research (CPR) have developed technology that can alter, within the body, the recognized identity of proteins. The innovation, published in Nature Communications on October 2, allowed researchers to target mouse tumors with a protein and then transport that protein out of the body. This means that cancer-killing drugs could be sent directly to tumors and then excreted from the body after dropping off their payload. The technology also has the potential to allow multi-purpose drugs that can travel from organ to organ, performing ...
2024-10-02
Smoke From Megafires Puts Orchard Trees at Risk
Effects Last Months, Reducing Nut Crop Yields
By Amy Quinton | October 2, 2023
Long-term smoke exposure from massive wildfires lowers the energy reserves of orchard trees and can cut their nut production by half, researchers at the University of California, Davis, found. The smoke can affect trees for months after a megafire, depressing their bloom and the next season’s harvest. This finding reveals a new danger from wildfires that could affect plant health in both agricultural and natural environments.
Nature Plants published ...
2024-10-02
Health Data Research UK (HDR UK) and the National Research Foundation Singapore (NRF) are pleased to have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) today, that formalises a collaborative partnership in healthcare and data science. The partnership will leverage cutting-edge data science and research, with a focus on trustworthy data use to power improvements in healthcare, research and innovation, strengthening existing links between the UK and Singapore.
The MoU was signed by Permanent Secretary for National Research and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Carnegie Mellon to lead development of implantable cell-based bioelectronic devices for patient-specific treatment and disease monitoring