(Press-News.org) Public health degree programs provide key competencies demanded by employers, but graduate employability could be improved by using more real-time data from employer job postings, according to a new study at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. This could help public health schools and programs ensure that graduates obtain specific technical skills listed in job postings, meet current employer needs, and prepare graduates for the demands of today’s labor market. The findings are published in the American Journal of Public Health.
The competencies required for the MPH curriculum are established by the Council on Education in Public Health (CEPH). Competencies are generally in alignment with current employer needs.
This the first study to use real-time data from a large-scale data set of job postings to analyze the top skills, certifications and software in demand by current employers seeking to hire Master of Public Health graduates, while comparing them with the competencies required by the accreditation body, CEPH.
“Our research revealed labor market competition for public health degree graduates, as well as certain technical skills desired by today’s employers, while showing that the CEPH competencies do, in large part, match current employer demands,” noted Heather Krasna, PhD, EdM, associate dean of Career and Professional Development at Columbia Mailman School.
Using a dataset of 70,343 job postings for MPH graduates from Lightcast, which collects, and analyzes millions of job postings per year, the researchers contrasted skills from the postings with CEPH competencies. They used real-time job postings data, to validate whether required competencies match employer needs, and to illustrate ongoing labor market competition for public health graduates.
Lightcast uses machine learning and natural language processing tools to deduplicate job postings, to code the job postings by occupation type, job title, company name, industry, and skills, and to provide a list of salary ranges. Lightcast assesses job postings for “sequences of words that indicate skills,” and matches them to a “comprehensive taxonomy of over 32,000 skills collected from hundreds of millions of job postings, resumes, and online profiles,” to categorize skills.
Employers currently seeking to hire MPH graduates are predominantly in for-profit industry, followed by academia/research, and healthcare. Only 12% of unique job postings were in government agencies, illustrating ongoing labor market competition for public health graduates from other sectors, especially from higher-paying industries like consulting, insurance and pharmaceuticals. “The job market for MPH graduates seems to continue moving towards for-profit companies such as insurance firms and healthcare, which is in alignment with other research on employment outcomes of public health graduates,” said Krasna. “Public health graduates’ skills are in demand in many sectors where they can make a positive impact on the public’s health.”
Noteworthy is that job postings from employers seeking to hire MPH graduates did not appear to prioritize diversity and inclusion, health equity, policy, advocacy, and other related skills which are required competencies by CEPH. According to Krasna there are several possible explanations for this. “It is possible that the large proportion of job postings in for-profit corporations (26%), healthcare/hospitals (14%), and academia/research (26%) and the relative scarcity of job postings in government or nonprofits (12%) as well as the skewing of job titles towards analytical, technical and epidemiological roles meant that technical and statistical skills were more in-demand than skills in community partnerships and diversity.”
Even if health equity skills are not listed as the top requirements in job postings, graduates with training in health equity will bring these skills to the employers seeking a public health perspective in their workplace. “Since health equity is at the center of the Essential Public Health Services, ensuring public health graduates receive these skills is crucial, regardless of where graduates find jobs,” said Krasna.
The most common titles from Lightcast Job postings collected July 2022-Feb. 2023 were Epidemiologists at 1,344 and biostatisticians at 1,323, followed by Environmental Health and Safety Specialists at 1,185.
Competencies in communications and management and applied leadership skills were considered critically important for communicating public health content.
“We believe our study is a thorough analysis on first-destination employment outcomes of public health graduates and offers valuable insights into the alignment between academic training and industry needs and complements articles on labor market competition for public health graduates,” said Krasna.
Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health
Founded in 1922, the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health pursues an agenda of research, education, and service to address the critical and complex public health issues affecting New Yorkers, the nation and the world. The Columbia Mailman School is the fourth largest recipient of NIH grants among schools of public health. Its nearly 300 multi-disciplinary faculty members work in more than 100 countries around the world, addressing such issues as preventing infectious and chronic diseases, environmental health, maternal and child health, health policy, climate change and health, and public health preparedness. It is a leader in public health education with more than 1,300 graduate students from 55 nations pursuing a variety of master’s and doctoral degree programs. The Columbia Mailman School is also home to numerous world-renowned research centers, including ICAP and the Center for Infection and Immunity. For more information, please visit www.mailman.columbia.edu.
END
Do MPH programs prepare graduates for employment in today's market? Mostly yes, but who is hiring may be surprising
2024-10-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New article provides orientation to using implementation science in policing
2024-10-03
Since the 2020 murder by Minneapolis police of George Floyd brought nationwide calls for change amid concerns that prevailing practices were not grounded in evidence and created harm, policing has been in turmoil. Implementation science (IS) involves integrating effective and evidence-based innovations into routine practice in fields like health care. Yet despite its potential, IS—and specifically, evidence-based policing (EBP)—remain vastly understudied and unused in police settings. In a new article, researchers provide an orientation to these issues ...
Three beer-related discoveries to celebrate Oktoberfest
2024-10-03
Frothy or smooth, bitter or sweet, light or dark: There’s a beer for most palates. As people around the world pour over the best brews at Oktoberfest celebrations or ferment about their favorite fall-themed beers, three papers published in ACS journals crack open new insights into these beverages. And if you’re hop-ing to conduct studies to find which beer is good for what ales you, please drink responsibly. Reporters can request free access to these papers by emailing newsroom@acs.org.
Coriander’s origin changes beer flavor. Just like simmering a stew, brewing a beer with herbs and spices can enhance its flavor. A study in ACS Food Science ...
AAAS launches user research project to inform the new AAAS.org
2024-10-03
Washington, D.C. — The American Association for the Advancement of Science, one of the world’s largest general scientific societies and publisher of the Science family of journals, announces an external research project to help the organization reimagine AAAS.org as part of a website overhaul project, which recently kicked off. AAAS is seeking input from its key audiences, including reporters and public information officers, to better align the experience and content of the website. As AAAS embarks on the next ...
In odd galaxy, NASA's Webb finds potential missing link to first stars
2024-10-03
Looking deep into the early universe with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have found something unprecedented: a galaxy with an odd light signature, which they attribute to its gas outshining its stars. Found approximately one billion years after the big bang, galaxy GS-NDG-9422 (9422) may be a missing-link phase of galactic evolution between the universe’s first stars and familiar, well-established galaxies.
“My first thought in looking at the galaxy’s spectrum was, ‘that’s weird,’ which is ...
Adding beans and pulses can lead to improved shortfall nutrient intakes and a higher diet quality in American adults
2024-10-03
Moscow, Idaho, October 3, 2024: New research showing the association between greater bean and pulse consumption and improved shortfall nutrient intakes and a higher diet quality in American adults will be presented during the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics (the Academy) Food & Nutrition Conference & Expo (FNCE) 2024 in Minneapolis, MN. The poster session is scheduled for Tuesday, October 8, 2024, from 10:45 – 11:45 AM CT at the Minneapolis Convention Center.
Researchers assessed the effect of increased bean and pulse consumption, in the typical US dietary pattern, on shortfall ...
What happens in the brain when a person with schizophrenia “hears voices”?
2024-10-03
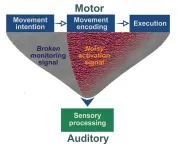
Auditory hallucinations are likely the result of abnormalities in two brain processes: a “broken” corollary discharge that fails to suppress self-generated sounds, and a “noisy” efference copy that makes the brain hear these sounds more intensely than it should. That is the conclusion of a new study published October 3rd in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Xing Tian, of New York University Shanghai, China, and colleagues.
Patients with certain mental disorders, including schizophrenia, often hear voices in the absence of sound. Patients may fail to distinguish between their ...
Ant agriculture began 66 million years ago in the aftermath of the asteroid that doomed the dinosaurs
2024-10-03
When humans began farming crops thousands of years ago, agriculture had already been around for millions of years. In fact, several animal lineages have been growing their own food since long before humans evolved as a species.
According to a new study, colonies of ants began farming fungi when an asteroid struck Earth 66 million years ago. This impact caused a global mass extinction but also created ideal conditions for fungi to thrive. Innovative ants began cultivating the fungi, creating an evolutionary partnership that became even more tightly intertwined 27 million years ago and continues to this day.
In a paper published today, Oct. 3, in the journal Science, scientists at the Smithsonian’s ...
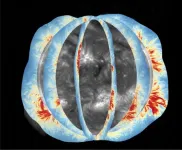
A new era of solar observation
2024-10-03
EMBARGOED: Not for Release Until 2:00 pm U.S. Eastern Time Thursday, 3 October 2024.
A new era of solar observation
International team produces global maps of coronal magnetic field
Contacts:
Audrey Merket, NSF NCAR and UCAR Science Writer and Public Information Officer
amerket@ucar.edu
303-497-8293
David Hosansky, NSF NCAR and UCAR Manager of Media Relations
hosansky@ucar.edu
720-470-2073
For the first time, scientists have taken near-daily measurements of the Sun’s global coronal magnetic field, a region of the Sun that has only been observed irregularly in the past. The resulting observations ...
The true global impact of species-loss caused by humans is far greater than expected – new study reveals
2024-10-03
The extinction of hundreds of bird species caused by humans over the last 130,000 years has has led to substantial reductions in avian functional diversity – a measure of the range of different roles and functions that birds undertake within the environment –
and resulted in the loss of approximately 3 billion years of unique evolutionary history, according to a new study published today in Science.
Whilst humans have been driving a global erosion of species richness for millennia, the consequences of past extinctions for other dimensions of biodiversity are poorly known. ...
Smartphone-assisted “scavenger hunt” identifies people at risk for dementia
2024-10-03
Researchers from DZNE and Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg have identified individuals with increased risk for dementia using mobility data, recorded during a smartphone-based wayfinding task on the university campus. The findings, reported in the journal PLOS Digital Health, show the potential of smartphone data, collected in conditions close to everyday life, for the early detection and monitoring of Alzheimer’s disease. The study included 72 adults; about a third of them with subjective cognitive decline (SCD), a condition that is a known risk factor for dementia.
Alzheimer’s disease usually develops unnoticed over years and eventually ...