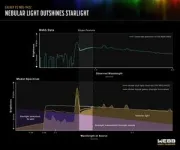
(Press-News.org) Looking deep into the early universe with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have found something unprecedented: a galaxy with an odd light signature, which they attribute to its gas outshining its stars. Found approximately one billion years after the big bang, galaxy GS-NDG-9422 (9422) may be a missing-link phase of galactic evolution between the universe’s first stars and familiar, well-established galaxies.
“My first thought in looking at the galaxy’s spectrum was, ‘that’s weird,’ which is exactly what the Webb telescope was designed to reveal: totally new phenomena in the early universe that will help us understand how the cosmic story began,” said lead researcher Alex Cameron of the University of Oxford.
Cameron reached out to colleague Harley Katz, a theorist, to discuss the strange data. Working together, their team found that computer models of cosmic gas clouds heated by very hot, massive stars, to an extent that the gas shone brighter than the stars, was nearly a perfect match to Webb’s observations.
“It looks like these stars must be much hotter and more massive than what we see in the local universe, which makes sense because the early universe was a very different environment,” said Katz, of Oxford and the University of Chicago.
In the local universe, typical hot, massive stars have a temperature ranging between 70,000 to 90,000 degrees Fahrenheit (40,000 to 50,000 degrees Celsius). According to the team, galaxy 9422 has stars hotter than 140,000 degrees Fahrenheit (80,000 degrees Celsius).
The research team suspects that the galaxy is in the midst of a brief phase of intense star formation inside a cloud of dense gas that is producing a large number of massive, hot stars. The gas cloud is being hit with so many photons of light from the stars that it is shining extremely brightly.
In addition to its novelty, nebular gas outshining stars is intriguing because it is something predicted in the environments of the universe’s first generation of stars, which astronomers classify as Population III stars.
“We know that this galaxy does not have Population III stars, because the Webb data shows too much chemical complexity. However, its stars are different than what we are familiar with – the exotic stars in this galaxy could be a guide for understanding how galaxies transitioned from primordial stars to the types of galaxies we already know,” said Katz.
At this point, galaxy 9422 is one example of this phase of galaxy development, so there are still many questions to be answered. Are these conditions common in galaxies at this time period, or a rare occurrence? What more can they tell us about even earlier phases of galaxy evolution? Cameron, Katz, and their research colleagues are actively identifying more galaxies to add to this population to better understand what was happening in the universe within the first billion years after the big bang.
“It’s a very exciting time, to be able to use the Webb telescope to explore this time in the universe that was once inaccessible,” Cameron said. “We are just at the beginning of new discoveries and understanding.”
The research paper is published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory. Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).
END
In odd galaxy, NASA's Webb finds potential missing link to first stars
2024-10-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Adding beans and pulses can lead to improved shortfall nutrient intakes and a higher diet quality in American adults
2024-10-03
Moscow, Idaho, October 3, 2024: New research showing the association between greater bean and pulse consumption and improved shortfall nutrient intakes and a higher diet quality in American adults will be presented during the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics (the Academy) Food & Nutrition Conference & Expo (FNCE) 2024 in Minneapolis, MN. The poster session is scheduled for Tuesday, October 8, 2024, from 10:45 – 11:45 AM CT at the Minneapolis Convention Center.
Researchers assessed the effect of increased bean and pulse consumption, in the typical US dietary pattern, on shortfall ...
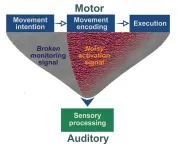
What happens in the brain when a person with schizophrenia “hears voices”?
2024-10-03
Auditory hallucinations are likely the result of abnormalities in two brain processes: a “broken” corollary discharge that fails to suppress self-generated sounds, and a “noisy” efference copy that makes the brain hear these sounds more intensely than it should. That is the conclusion of a new study published October 3rd in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Xing Tian, of New York University Shanghai, China, and colleagues.
Patients with certain mental disorders, including schizophrenia, often hear voices in the absence of sound. Patients may fail to distinguish between their ...
Ant agriculture began 66 million years ago in the aftermath of the asteroid that doomed the dinosaurs
2024-10-03
When humans began farming crops thousands of years ago, agriculture had already been around for millions of years. In fact, several animal lineages have been growing their own food since long before humans evolved as a species.
According to a new study, colonies of ants began farming fungi when an asteroid struck Earth 66 million years ago. This impact caused a global mass extinction but also created ideal conditions for fungi to thrive. Innovative ants began cultivating the fungi, creating an evolutionary partnership that became even more tightly intertwined 27 million years ago and continues to this day.
In a paper published today, Oct. 3, in the journal Science, scientists at the Smithsonian’s ...
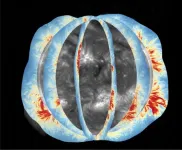
A new era of solar observation
2024-10-03
EMBARGOED: Not for Release Until 2:00 pm U.S. Eastern Time Thursday, 3 October 2024.
A new era of solar observation
International team produces global maps of coronal magnetic field
Contacts:
Audrey Merket, NSF NCAR and UCAR Science Writer and Public Information Officer
amerket@ucar.edu
303-497-8293
David Hosansky, NSF NCAR and UCAR Manager of Media Relations
hosansky@ucar.edu
720-470-2073
For the first time, scientists have taken near-daily measurements of the Sun’s global coronal magnetic field, a region of the Sun that has only been observed irregularly in the past. The resulting observations ...
The true global impact of species-loss caused by humans is far greater than expected – new study reveals
2024-10-03
The extinction of hundreds of bird species caused by humans over the last 130,000 years has has led to substantial reductions in avian functional diversity – a measure of the range of different roles and functions that birds undertake within the environment –
and resulted in the loss of approximately 3 billion years of unique evolutionary history, according to a new study published today in Science.
Whilst humans have been driving a global erosion of species richness for millennia, the consequences of past extinctions for other dimensions of biodiversity are poorly known. ...
Smartphone-assisted “scavenger hunt” identifies people at risk for dementia
2024-10-03
Researchers from DZNE and Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg have identified individuals with increased risk for dementia using mobility data, recorded during a smartphone-based wayfinding task on the university campus. The findings, reported in the journal PLOS Digital Health, show the potential of smartphone data, collected in conditions close to everyday life, for the early detection and monitoring of Alzheimer’s disease. The study included 72 adults; about a third of them with subjective cognitive decline (SCD), a condition that is a known risk factor for dementia.
Alzheimer’s disease usually develops unnoticed over years and eventually ...
Green subsidies may have hidden costs, experts warn
2024-10-03
Government subsidies for business practices and processes should be approached with caution, even when they seem to be environmentally friendly, writes a group of scientists and economists in this week’s Policy Forum in the journal Science.
They argue that subsidies can alter market pressures, leading to unintended consequences that not only perpetuate harmful subsidies over time but also diminish the overall effectiveness of those intended to promote environmental sustainability.
Therefore, when they must be used, subsidies should have clear end-dates, advise the authors.
“We’ve got this odd juxtaposition of ...
Small brains can accomplish big things, according to new theoretical research
2024-10-03
Neuroscientists had a problem.
For decades, researchers had a theory about how an animal’s brain keeps track of where it is relative to its surroundings without outside cues – like how we know where we are, even with our eyes closed.
According to the theory, which was based on brain recordings from rodents, networks of neurons called ring attractor networks maintain an internal compass that keeps track of where you are in the world. An accurate internal compass was thought to require a large network with many neurons, while a small network with few neurons would cause the compass’s needle to drift, creating errors.
Then researchers discovered an internal compass ...
UTA professor honored for science education leadership
2024-10-03
University of Texas at Arlington UTeach Master Teacher Karen Jo Matsler will be awarded the 2025 Melba Newell Phillips Medal in January from the American Association of Physics Teachers (AAPT) in recognition of her extensive contributions to physics education and her tireless efforts to support educators nationwide. Founded in 1930, AAPT is a national organization dedicated to advancing the teaching and understanding of physics.
For more than 20 years, Dr. Matsler has been a tireless advocate of physics education, working with state legislators and educational agencies ...
Decline of mpox antibody responses after modified vaccinia Ankara–Bavarian Nordic vaccination
2024-10-03
About The Study: The modified vaccinia Ankara–Bavarian Nordic (MVA-BN) vaccination generated mpox antibodies that waned by 6 to 12 months. In participants who received 2 doses of MVA-BN vaccine, mpox antibody responses at 12 months were comparable to or lower than peak antibody responses in people receiving 1 dose, which provided limited protection.
Quote from corresponding author Dan H. Barouch, MD, PhD:
“In this observational study, we show that mpox antibody responses decline 6-12 months following Jynneos (MVA-BN) vaccination. Our data suggest that protective immunity may ...